Abstract
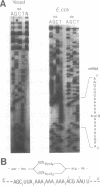
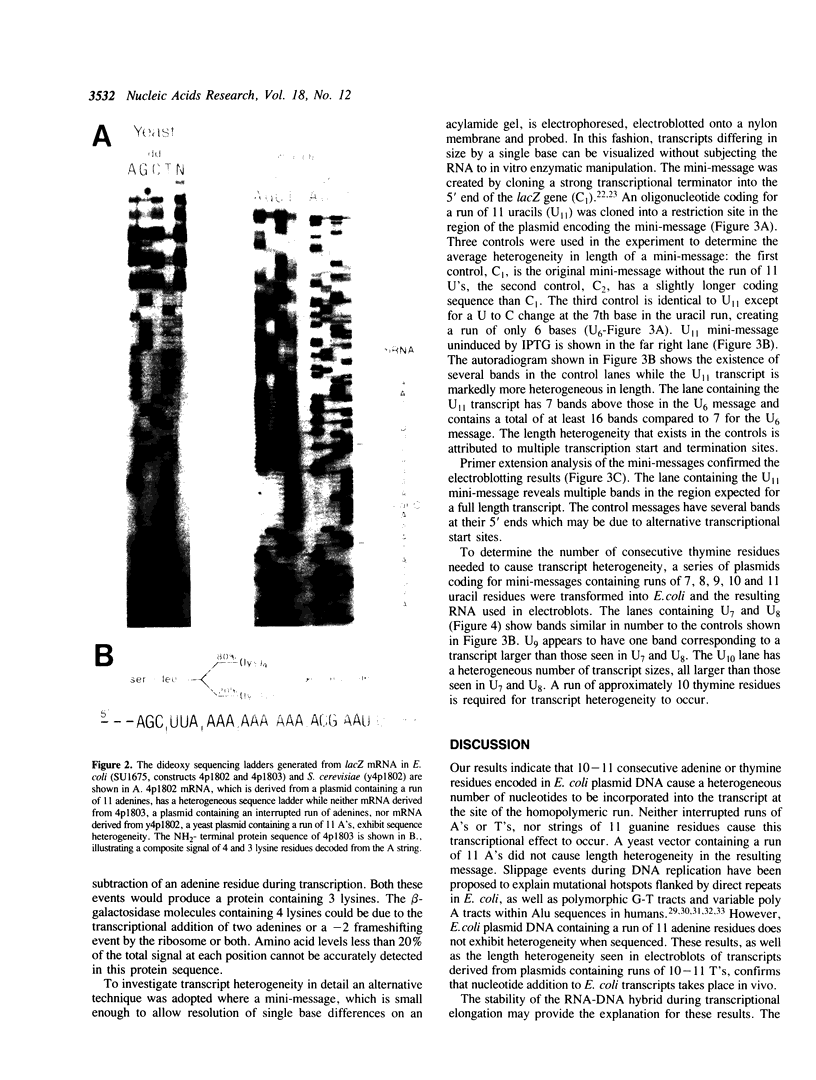
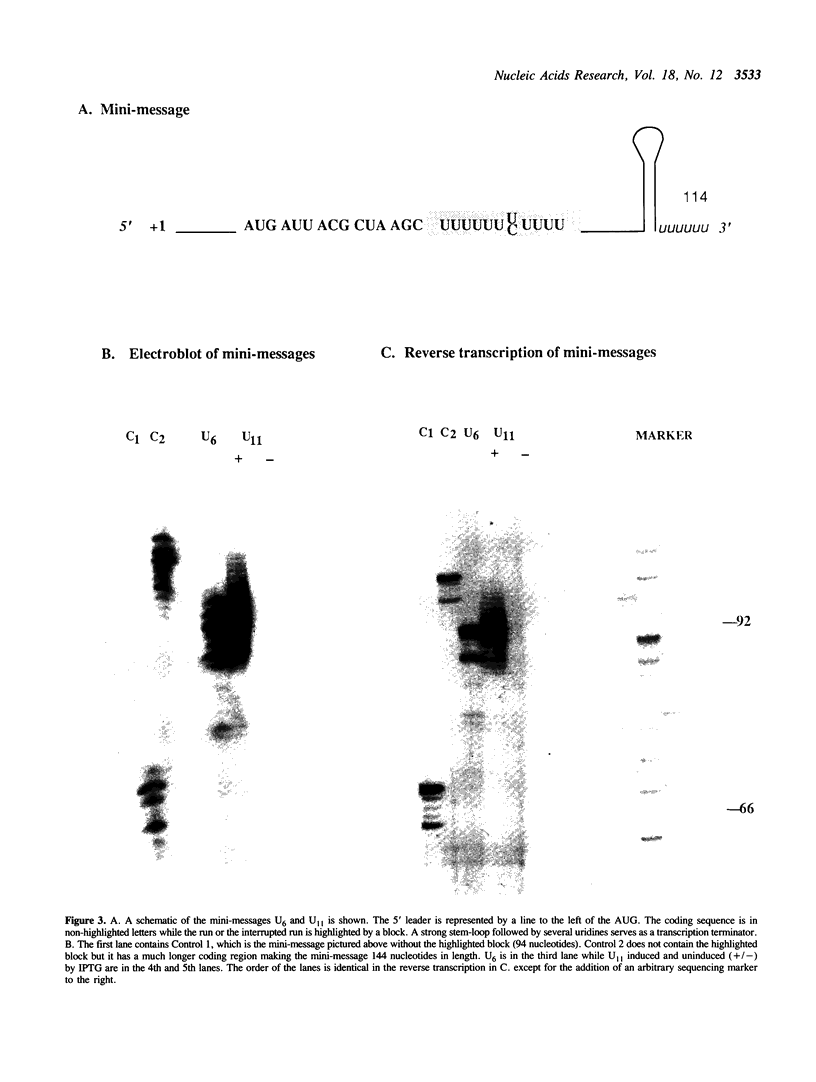
A run of 11 adenine or thymine residues at the 5' end of an out-of-frame lacZ gene causes a high level of beta-galactosidase expression in E. coli. This effect was not observed for a run of guanine residues. Reverse transcription of mRNA isolated from E. coli containing the run of 11 A's reveals heterogeneity of transcript length while reverse transcription of mRNA isolated from S. cerevisiae containing the same gene shows no heterogeneity. Protein sequencing of the beta-galactosidase molecules derived from the out-of-frame construct containing a run of adenines reveals the addition of a lysine at the run. A new method was developed where messages small enough to allow resolution of single nucleotide differences on an acrylamide gel are electrophoresed, electroblotted onto nylon and probed. This confirmed the reverse transcription results and showed that additional residues can be added to transcripts derived from DNA containing 10 or 11 thymine residues. A mechanism for slippage is discussed where the A-U rich RNA-DNA hybrid can denature during elongation and rehybridize in an offset position, causing the addition of extra residues to the transcript.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn B. Y., Moss B. Capped poly(A) leaders of variable lengths at the 5' ends of vaccinia virus late mRNAs. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):226–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.226-232.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank A., Gallant J. A., Burgess R. R., Loeb L. A. An RNA polymerase mutant with reduced accuracy of chain elongation. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):5920–5928. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLIN M., BERG P. MECHANISM OF RNA POLYMERASE ACTION: CHARACTERIZATION OF THE DNA-DEPENDENT SYNTHESIS OF POLYADENYLIC ACID. J Mol Biol. 1964 May;8:708–726. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. Comparative properties of DNA, RNA, and hybrid homopolymer pairs. Fed Proc. 1965 Nov-Dec;24(6):1446–1457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Farnham P. J., Platt T. Synthetic sites for transcription termination and a functional comparison with tryptophan operon termination sites in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4180–4184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley J. C., Kaback D. B. Molecular cloning of chromosome I DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation of the ADE1 gene. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):413–417. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.413-417.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Schmeissner U., Hofer M., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. VII. On the molecular nature of spontaneous hotspots in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamper H. B., Hearst J. E. A topological model for transcription based on unwinding angle analysis of E. coli RNA polymerase binary, initiation and ternary complexes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna M. M., Meares C. F. Topography of transcription: path of the leading end of nascent RNA through the Escherichia coli transcription complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4238–4242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U. M., McClure W. R. Role of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in initiation. II. Release of sigma from ternary complexes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9564–9570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Lawrie J., Boyer H. W., Hedgpeth J. Reiterative copying by E.coli RNA polymerase during transcription initiation of mutant pBR322 tet promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):547–552. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. M., Mehta R., Hutchinson K. L. The L protein of vesicular stomatitis virus modulates the response of the polyadenylic acid polymerase to S-adenosylhomocysteine. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2555–2561. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. M., Smith E. F., Buckley D. W. Aberrant polyadenylation by a vesicular stomatitis virus mutant is due to an altered L protein. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.515-521.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Buc H., Spassky A., Wang J. C. Mapping of single-stranded regions in duplex DNA at the sequence level: single-strand-specific cytosine methylation in RNA polymerase-promoter complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2544–2548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S. A., Krakow J. S. Studies on the product binding sites of the Azotobacter vinelandii ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2878–2884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Makino S., Soe L. H., Shieh C. K., Keck J. G., Fleming J. O. Coronavirus: a jumping RNA transcription. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:359–365. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby R. T., Nelson J. L., Calvo J. M., Gallant J. A. Transcriptional proofreading in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3153–3158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08469.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J. Structure of the gene N:gene NS intercistronic junction in the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):673–681. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger W., Schickor P., Heumann H. A cinematographic view of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase translocation. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2745–2754. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K. Complete intergenic and flanking gene sequences from the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Casadaban M. J., Botstein D. Yeast genes fused to beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli can be expressed normally in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2460–2464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger R. F., Hilton J. The frequency of transcriptional and translational errors at nonsense codons in the lacZ gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(2):207–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00334815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert M., Keene J. D., Herman R. C., Lazzarini R. A. Site on the vesicular stomatitis virus genome specifying polyadenylation and the end of the L gene mRNA. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):550–559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.550-559.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwer B., Stunnenberg H. G. Vaccinia virus late transcripts generated in vitro have a poly(A) head. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1183–1190. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwer B., Visca P., Vos J. C., Stunnenberg H. G. Discontinuous transcription or RNA processing of vaccinia virus late messengers results in a 5' poly(A) leader. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90212-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U. RNA polymerase unwinds an 11-base pair segment of a phage T7 promoter. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):651–652. doi: 10.1038/279651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springgate C. F., Loeb L. A. On the fidelity of transcription by Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):577–591. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streisinger G., Okada Y., Emrich J., Newton J., Tsugita A., Terzaghi E., Inouye M. Frameshift mutations and the genetic code. This paper is dedicated to Professor Theodosius Dobzhansky on the occasion of his 66th birthday. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D. Hypervariability of simple sequences as a general source for polymorphic DNA markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6463–6471. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Dunn D. M., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Slippery runs, shifty stops, backward steps, and forward hops: -2, -1, +1, +2, +5, and +6 ribosomal frameshifting. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:687–693. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Platt T. Transcription termination: nucleotide sequence at 3' end of tryptophan operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5442–5446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]