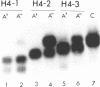
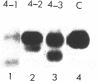
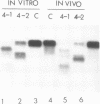
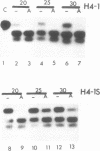
Abstract
Using the endogenous histone H4 mRNA of Xenopus oocytes as a target, we have previously shown that 20mer oligos complementary to different parts of this sequence vary in their effectiveness at causing mRNA cleavage in vivo, and that some of the RNA can never be cleaved. In this paper we show that the resistant RNA is not localised within one part of the oocyte, and that the relative resistance in vivo of endogenous or synthetic H4 mRNA to the different oligos is preserved in an in vitro assay system using deproteinised RNA. If an prior annealing step is included in vitro, all resistance is abolished. Chemical modification of one oligo by end substitution with methylphosphonate or phosphorothioate residues did not improve cleavage efficiency. Oligos with complete phosphorothioate substitution cause slower cleavage in vivo but persist for longer. Consequently phosphorothioate oligos are effective at lower doses than phosphodiester ones, provided that the incubation time is long enough (24 hours). Increasing oligo length from 20nt to 30nt increases phosphorothioate oligo efficiency over long reaction times in vivo, but decreases efficiency during short in vitro assays. Similar increases in length did not affect phosphodiester oligo performance in vivo, but caused a decrease in efficiency in vitro which was overcome by an annealing step.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cazenave C., Chevrier M., Nguyen T. T., Hélène C. Rate of degradation of [alpha]- and [beta]-oligodeoxynucleotides in Xenopus oocytes. Implications for anti-messenger strategies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10507–10521. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Loreau N., Thuong N. T., Toulmé J. J., Hélène C. Enzymatic amplification of translation inhibition of rabbit beta-globin mRNA mediated by anti-messenger oligodeoxynucleotides covalently linked to intercalating agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4717–4736. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Stein C. A., Loreau N., Thuong N. T., Neckers L. M., Subasinghe C., Hélène C., Cohen J. S., Toulmé J. J. Comparative inhibition of rabbit globin mRNA translation by modified antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4255–4273. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Bucher P., Strub K., Birnstiel M. L. Transcription of a cloned Xenopus laevis H4 histone gene in the homologous frog oocyte system depends on an evolutionary conserved sequence motif in the -50 region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8641–8657. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash P., Lotan I., Knapp M., Kandel E. R., Goelet P. Selective elimination of mRNAs in vivo: complementary oligodeoxynucleotides promote RNA degradation by an RNase H-like activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7896–7900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagnor C., Bertrand J. R., Thenet S., Lemaître M., Morvan F., Rayner B., Malvy C., Lebleu B., Imbach J. L., Paoletti C. alpha-DNA. VI: Comparative study of alpha- and beta-anomeric oligodeoxyribonucleotides in hybridization to mRNA and in cell free translation inhibition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10419–10436. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R., Schwab G., Wickstrom E., Loke S. L., Pluznik D. H., Watt R., Neckers L. M. A c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits entry into S phase but not progress from G0 to G1. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):445–449. doi: 10.1038/328445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressmann A., Clarkson S. G., Pirrotta V., Birnstiel M. L. Transcription of cloned tRNA gene fragments and subfragments injected into the oocyte nucleus of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1176–1180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaitre M., Bayard B., Lebleu B. Specific antiviral activity of a poly(L-lysine)-conjugated oligodeoxyribonucleotide sequence complementary to vesicular stomatitis virus N protein mRNA initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus-Sekura C. J., Woerner A. M., Shinozuka K., Zon G., Quinnan G. V., Jr Comparative inhibition of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene expression by antisense oligonucleotide analogues having alkyl phosphotriester, methylphosphonate and phosphorothioate linkages. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5749–5763. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride L. J., McCollum C., Davidson S., Efcavitch J. W., Andrus A., Lombardi S. J. A new, reliable cartridge for the rapid purification of synthetic DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Apr;6(4):362–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Hunt T. The use of single-stranded DNA and RNase H to promote quantitative 'hybrid arrest of translation' of mRNA/DNA hybrids in reticulocyte lysate cell-free translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6433–6451. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C. R., Greene A. R., Heathcliffe G. R., Atkinson T. C., Holland D., Markham A. F., Edge M. D. Ion-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography of oligodeoxyribonucleotides using formamide. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Kuff E. L. Structural gene identification and mapping by DNA-mRNA hybrid-arrested cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4370–4374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Oskarsson M., Copeland T., Brumbaugh J., Vande Woude G. F. Function of c-mos proto-oncogene product in meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):519–525. doi: 10.1038/335519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibahara S., Mukai S., Nishihara T., Inoue H., Ohtsuka E., Morisawa H. Site-directed cleavage of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4403–4415. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth J., Colman A. Antisense oligonucleotide-directed cleavage of mRNA in Xenopus oocytes and eggs. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):427–434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth J., Matthews G., Dale L., Baker C., Colman A. Antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed cleavage of maternal mRNA in Xenopus oocytes and embryos. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. C., Aurelian L., Reddy M. P., Miller P. S., Ts'o P. O. Antiviral effect of an oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate) complementary to the splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early pre-mRNAs 4 and 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2787–2791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. C., Dworkin M. B., Dworkin-Rastl E. Destruction of a translationally controlled mRNA in Xenopus oocytes delays progesterone-induced maturation. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1296–1306. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Subasinghe C., Shinozuka K., Cohen J. S. Physicochemical properties of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3209–3221. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M. L., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma viral RNA translation by a specific oligodeoxyribonucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):285–288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verspieren P., Cornelissen A. W., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Toulmé J. J. An acridine-linked oligodeoxynucleotide targeted to the common 5' end of trypanosome mRNAs kills cultured parasites. Gene. 1987;61(3):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder R. Y., Walder J. A. Role of RNase H in hybrid-arrested translation by antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5011–5015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. L., Bacon T. A., Gonzalez A., Freeman D. L., Lyman G. H., Wickstrom E. Human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cell proliferation and c-myc protein expression are inhibited by an antisense pentadecadeoxynucleotide targeted against c-myc mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1028–1032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Goodchild J., Taguchi Y., Sarin P. S. Inhibition of replication and expression of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III in cultured cells by exogenous synthetic oligonucleotides complementary to viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4143–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]