Abstract
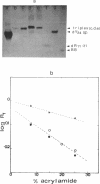
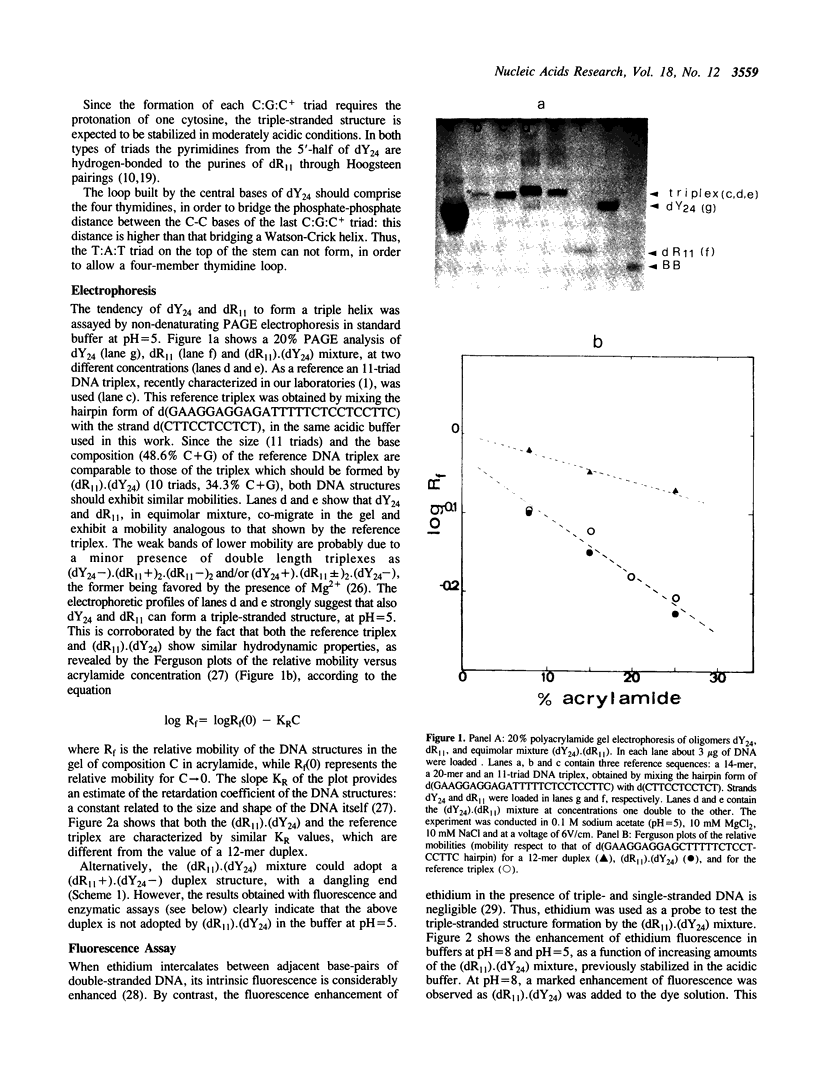
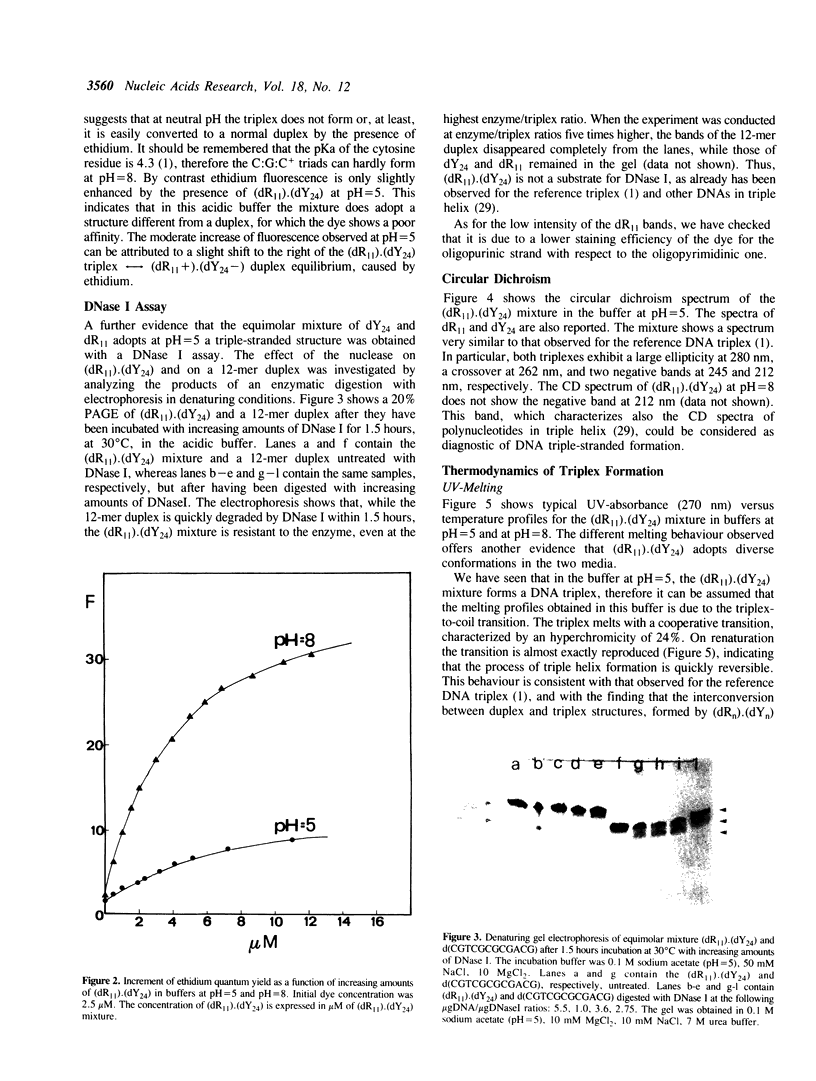
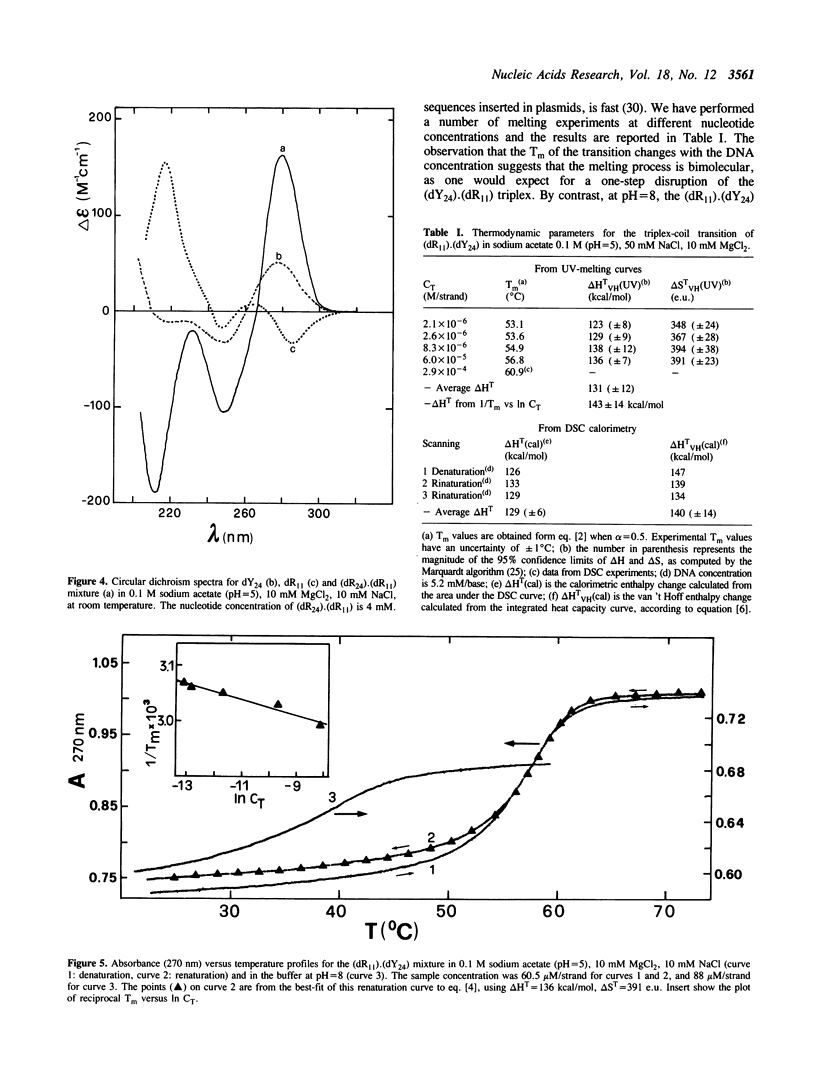
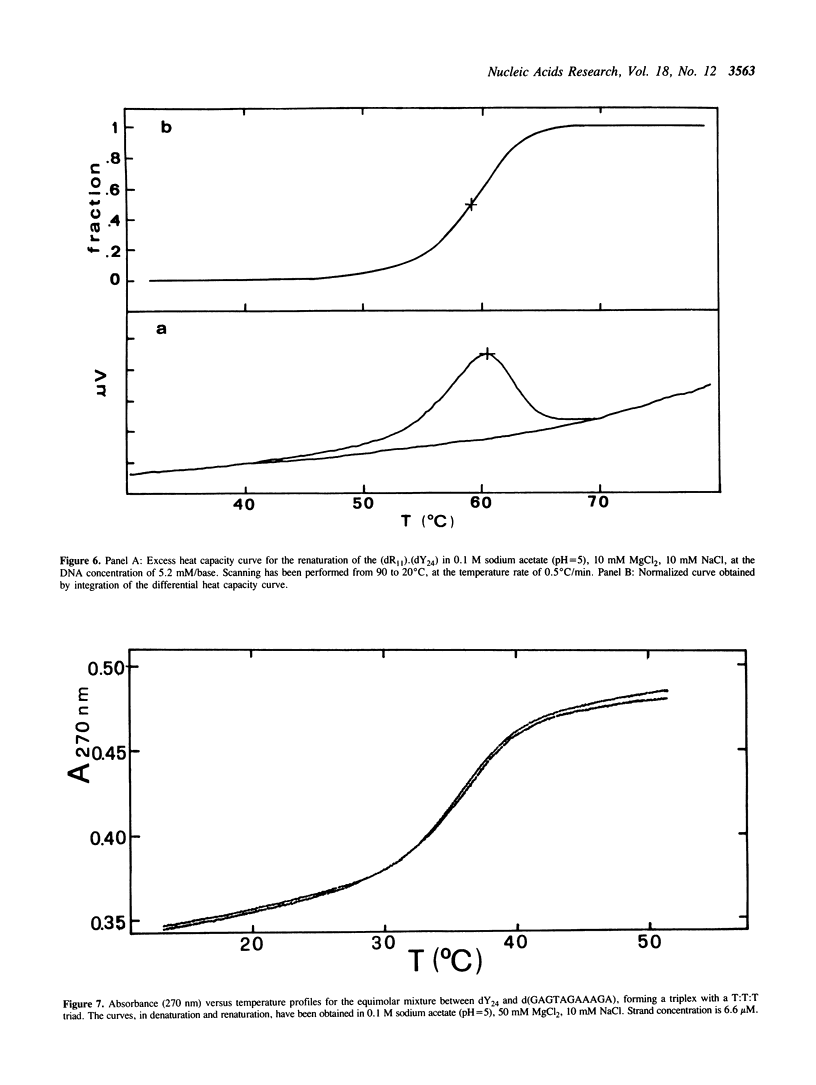
The equimolar mixture of d(CTCTTCTTTCTTTTCTTTCTTCTC) (dY24) and d(GAGAAGAAAGA) (dR11) [designated (dY24).(dR11)], forms at pH = 5 a DNA triplex, which mimicks the H-DNA structure. The DNA triplex was identified by the following criteria: (i) dY24 and dR11 co-migrate in a poly-acrylamide gel, with a mobility and a retardation coefficient comparable to those observed for an 11-triad DNA triplex, previously characterized in our laboratories (1); (ii) the intercalator ethidium bromide shows a poor affinity for (dR11).(dY24) at pH = 5, and a high affinity at pH = 8; (iii) the (dR11).(dY24) mixture is not a substrate for DNase I at pH = 5; (iv) the CD spectrum of (dR11).(dY24), at pH = 5, is consistent with those previously reported for triple-stranded DNA. The (dR11).(dY24) mixture exhibits a thermally induced co-operative transition, which appears to be monophasic, reversible and concentration dependent. This transition is attributed to the disruption of the DNA triplex into single strands. The enthalpy change of the triplex-coil transition was measured by DSC (delta Hcal = 129 +/- 6 kcal/mol) and, assuming a two-state model, by analysis of UV-denaturation curves (average of two methods delta HUV = 137 +/- 13 kcal/mol). Subtracting from delta Hcal of triplex formation the contributions due to the Watson-Crick helix and to the protonation of the C-residues, we found that each pyrimidine binding into the major groove of the duplex, through a Hoogsteen base pair, is accompanied by an average delta H = -5.8 +/- 0.6 kcal/mol. The effect on the stability of the (dR11).(dY24) triplex due to the substitution of a T:A:T triad with a T:T:T one was also investigated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albergo D. D., Marky L. A., Breslauer K. J., Turner D. H. Thermodynamics of (dG--dC)3 double-helix formation in water and deuterium oxide. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1409–1413. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Selsing E. Structures for the polynucleotide complexes poly(dA) with poly (dT) and poly(dT) with poly(dA) with poly (dT). J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behe M. J. The DNA sequence of the human beta-globin region is strongly biased in favor of long strings of contiguous purine or pyrimidine residues. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7870–7875. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Sederoff R. R., Paterson M. C. Distribution of polypyrimidine . polypurine segments in DNA from diverse organisms. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):301–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Frank R., Blöcker H., Marky L. A. Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3746–3750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank R., Köster H. DNA chain length markers and the influence of base composition on electrophoretic mobility of oligodeoxyribonucleotides in polyacrylamide-gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(6):2069–2087. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.6.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition of the major groove of DNA by oligodeoxynucleotides via triple helix formation. Footprinting studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11431–11440. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Alkema D., Sinclair A., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Contributions of dangling end stacking and terminal base-pair formation to the stabilities of XGGCCp, XCCGGp, XGGCCYp, and XCCGGYp helixes. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4533–4539. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wells R. D. Intramolecular DNA triplexes in supercoiled plasmids. II. Effect of base composition and noncentral interruptions on formation and stability. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5950–5956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Dahlberg J. E. Single strands, triple strands, and kinks in H-DNA. Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1791–1796. doi: 10.1126/science.3175620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. Human U1 RNA genes contain an unusually sensitive nuclease S1 cleavage site within the conserved 3' flanking region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7288–7292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Magnesium ion-dependent triple-helix structure formed by homopurine-homopyrimidine sequences in supercoiled plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3781–3785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Johnson D. A., Morgan A. R. Complexes formed by (pyrimidine)n . (purine)n DNAs on lowering the pH are three-stranded. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3073–3091. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Johnson D. A., Morgan A. R. Complexes formed by (pyrimidine)n . (purine)n DNAs on lowering the pH are three-stranded. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3073–3091. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Woodsworth M. L., Latimer L. J., Morgan A. R. Poly(pyrimidine) . poly(purine) synthetic DNAs containing 5-methylcytosine form stable triplexes at neutral pH. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6603–6614. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):667–669. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C., Thiele D. Poly(dG).poly(dC) at neutral and alkaline pH: the formation of triple stranded poly(dG).poly(dG).poly(dC). Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Mar;5(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.3.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marky L. A., Breslauer K. J. Calculating thermodynamic data for transitions of any molecularity from equilibrium melting curves. Biopolymers. 1987 Sep;26(9):1601–1620. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Uhlenbeck O. C., Doty P. Self-complementary oligoribonucleotides: adenylic acid-uridylic acid block copolymers. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):201–215. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Massoulié J., Guschlbauer W. Synthetic polynucleotides. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1967;6:83–141. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60525-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkin S. M., Lyamichev V. I., Drushlyak K. N., Dobrynin V. N., Filippov S. A., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. DNA H form requires a homopurine-homopyrimidine mirror repeat. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):495–497. doi: 10.1038/330495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Wells R. D. Specificity of the three-stranded complex formation between double-stranded DNA and single-stranded RNA containing repeating nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal P., Feigon J. Triple-strand formation in the homopurine:homopyrimidine DNA oligonucleotides d(G-A)4 and d(T-C)4. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):637–640. doi: 10.1038/339637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Maling B. Physical and chemical characterization of two- and three-stranded adenine-thymine and adenine-uracil homopolymer complexes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):359–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Estimation of molecular radius, free mobility, and valence using polyacylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Mar;40(1):95–134. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarocchi M. T., Courtois Y., Guschlbauer W. Protonated polynucleotide structures. Specific complex formation between polycytidylic acid and guanosine or guanylic acids. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jul;14(3):411–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Collier D. A., Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wohlrab F. The chemistry and biology of unusual DNA structures adopted by oligopurine.oligopyrimidine sequences. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):2939–2949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de los Santos C., Rosen M., Patel D. NMR studies of DNA (R+)n.(Y-)n.(Y+)n triple helices in solution: imino and amino proton markers of T.A.T and C.G.C+ base-triple formation. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7282–7289. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]