Abstract
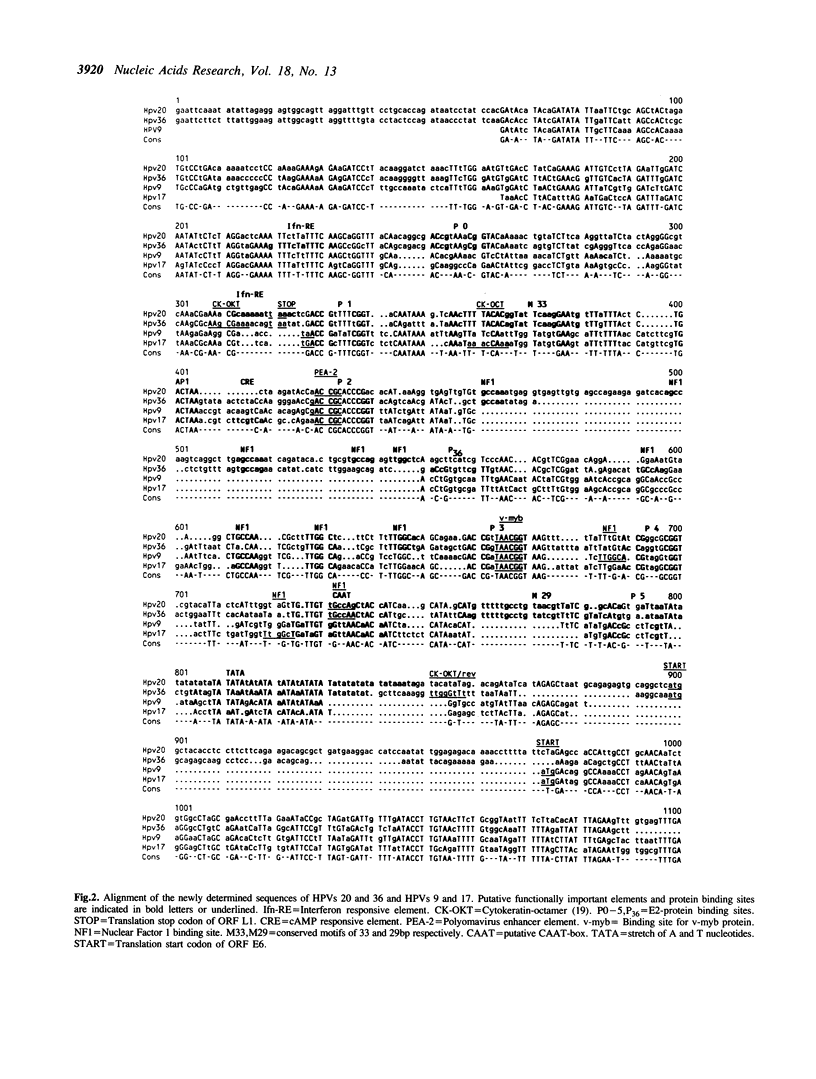
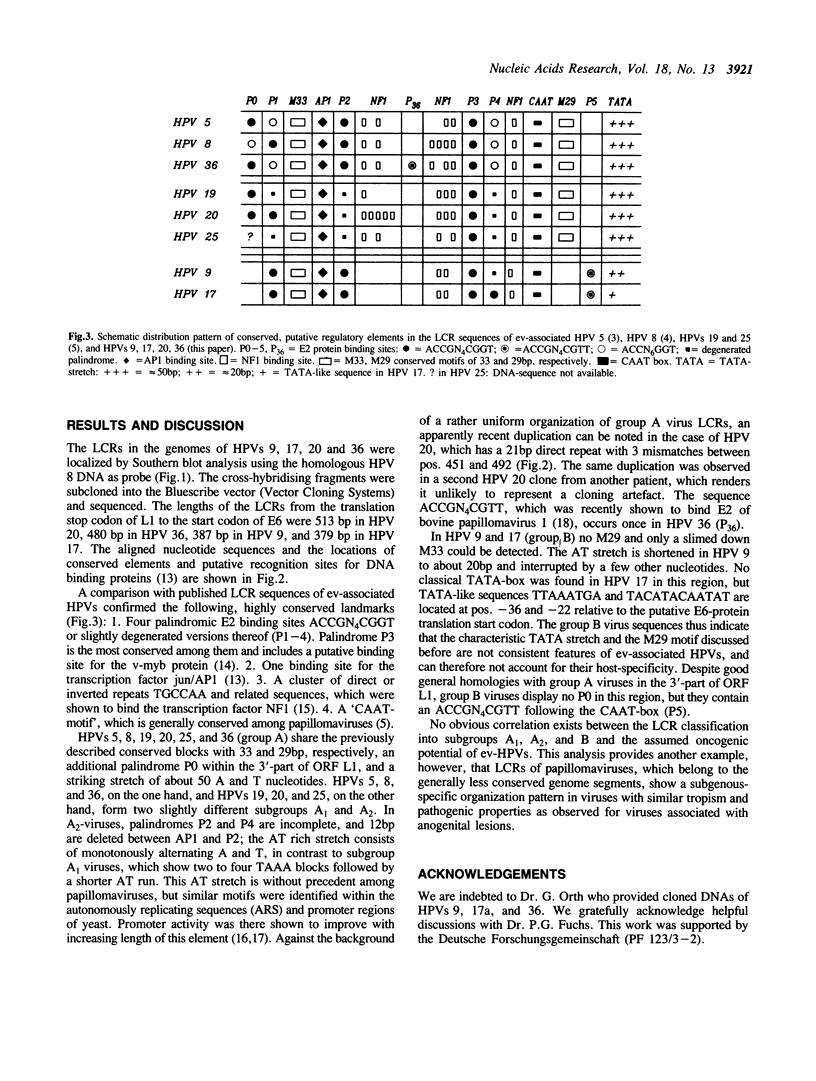
The regulatory regions of the human papillomaviruses (HPVs) 9, 17, 20, and 36 were mapped, sequenced, and aligned. They revealed an arrangement of putative protein binding sites specific for the epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated HPVs. Three subgroups could be differentiated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blessing M., Zentgraf H., Jorcano J. L. Differentially expressed bovine cytokeratin genes. Analysis of gene linkage and evolutionary conservation of 5'-upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):567–575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. G., Iftner T., Weninger J., Pfister H. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis-associated human papillomavirus 8: genomic sequence and comparative analysis. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):626–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.626-634.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassenmaier A., Lammel M., Pfister H. Molecular cloning and characterization of the DNAs of human papillomaviruses 19, 20, and 25 from a patient with epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):1019–1023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.1019-1023.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Yeo-Gloss M., Meisterenst M., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L., Bernard H. U. Clusters of nuclear factor I binding sites identify enhancers of several papillomaviruses but alone are not sufficient for enhancer function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3519–3533. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima M., Favre M., Jablonska S., Obalek S., Orth G. Characterization of a new type of human papillomavirus (HPV) related to HPV5 from a case of actinic keratosis. Virology. 1986 Oct 30;154(2):389–394. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremsdorf D., Favre M., Jablonska S., Obalek S., Rueda L. A., Lutzner M. A., Blanchet-Bardon C., Van Voorst Vader P. C., Orth G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the genomes of nine newly recognized human papillomavirus types associated with epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):1013–1018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.1013-1018.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremsdorf D., Jablonska S., Favre M., Orth G. Biochemical characterization of two types of human papillomaviruses associated with epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):436–447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.436-447.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krubke J., Kraus J., Delius H., Chow L., Broker T., Iftner T., Pfister H. Genetic relationship among human papillomaviruses associated with benign and malignant tumours of patients with epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3091–3103. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J., Bream G., Stenlund A., Botchan M. Specific recognition nucleotides and their DNA context determine the affinity of E2 protein for 17 binding sites in the BPV-1 genome. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):510–526. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Naturally occurring poly(dA-dT) sequences are upstream promoter elements for constitutive transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8419–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachow K. R., Ostrow R. S., Faras A. J. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of human papillomavirus type 5. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers E. M. Heterogeneity of the human papillomavirus group. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4898–4903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4898-4903.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


