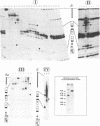
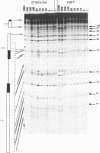
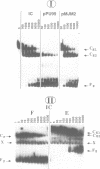
Abstract
Starting from a crude E. coli extract, two activities which specifically protect highly repetitive bacterial DNA sequences (called PU for Palindromic Unit or REP for Repetitive Extragenic Palindromic sequence) against a digestion with Exonuclease III have been purified. We show that one of these activities is due to the DNA polymerase I (Pol I). This constitutes the first indication for a specific interaction between Pol I and a duplex DNA. This interaction requires the presence of PU. It was confirmed and analyzed by native gel electrophoresis and DNase I footprinting experiments. The other activity contained at least five polypeptides. Its binding to PU DNA sequences was confirmed by native gel electrophoresis. Implications for the possible origin and functions of PU are discussed.
Full text
PDF
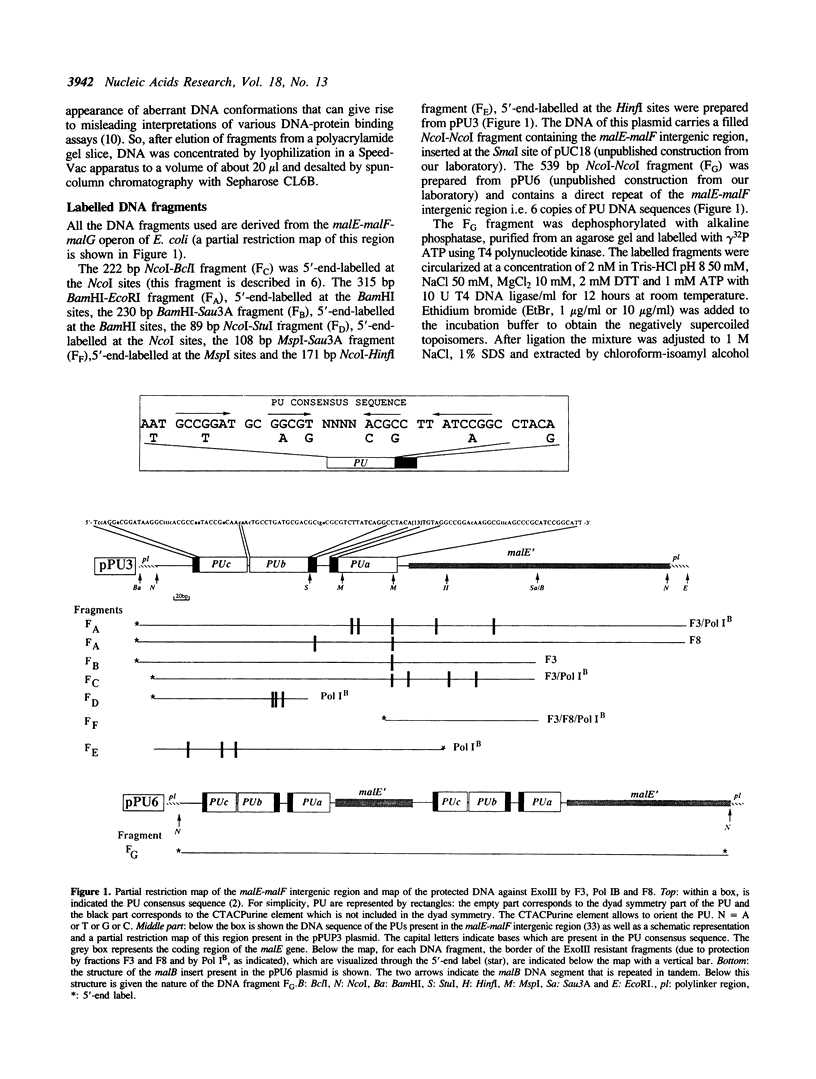
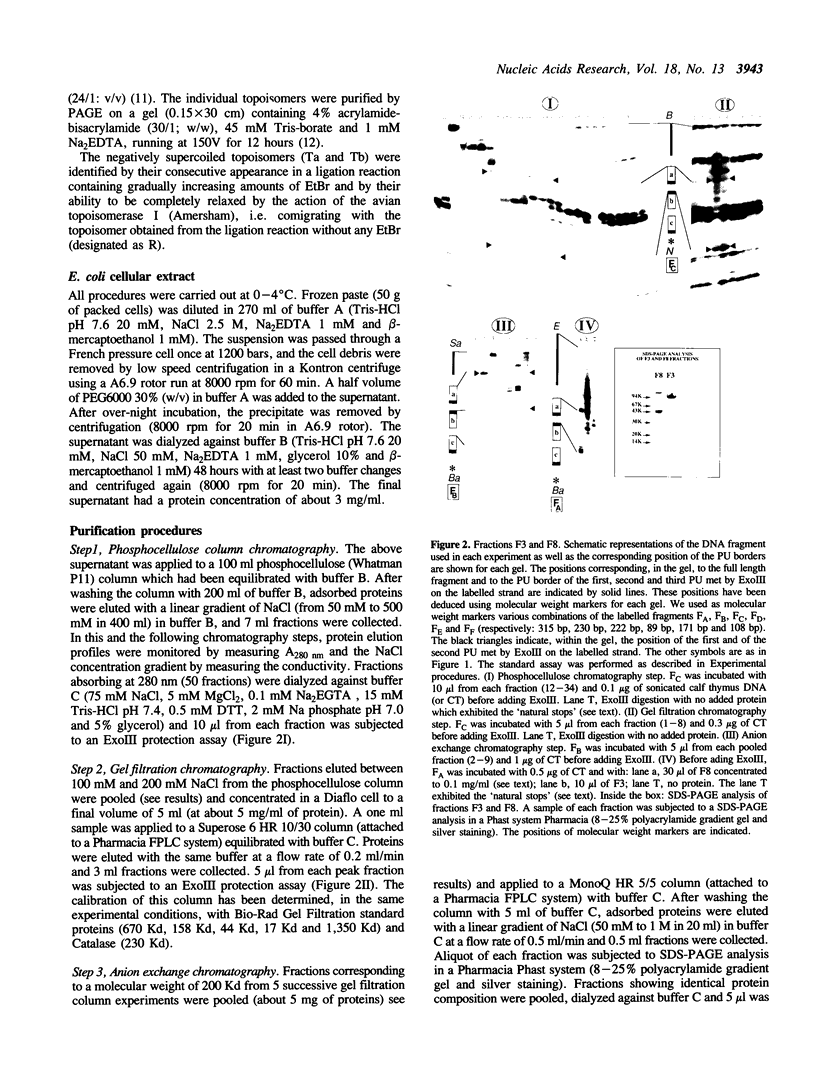



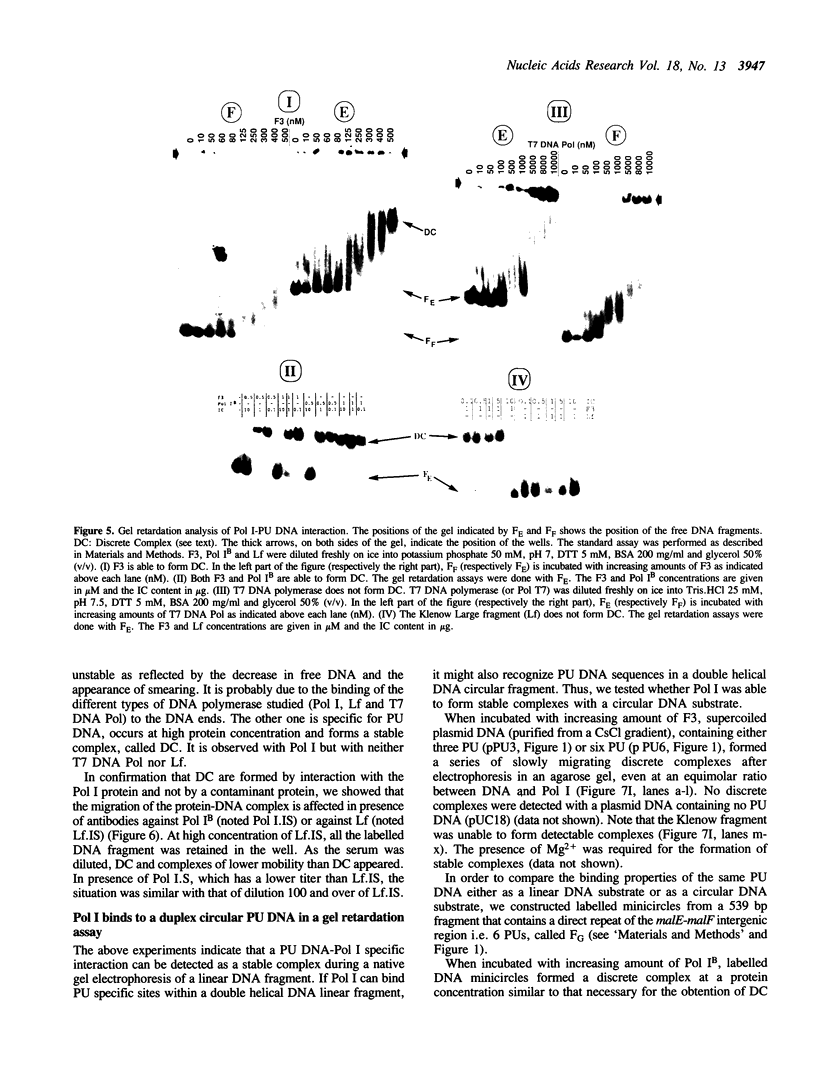

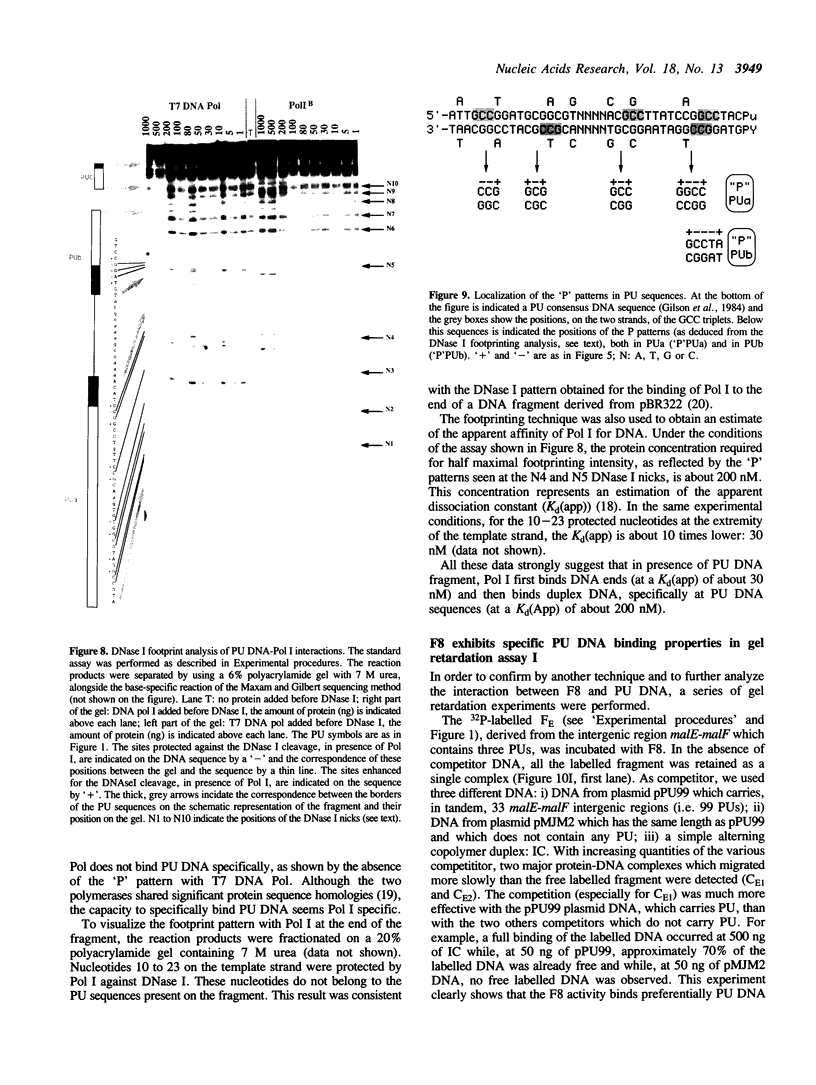



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan S., Chen H., Sun Y., Moses R. E. Alternate pathways of DNA replication in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 20;951(2-3):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J. Gel retardation at low pH resolves trp repressor-DNA complexes for quantitative study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):975–979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Lilley D. M. The anomalous gel migration of a stable cruciform: temperature and salt dependence, and some comparisons with curved DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5765–5774. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund P. T., Kelly R. B., Kornberg A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXXI. Binding of deoxyribonucleic acid to deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):3045–3052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froshauer S., Beckwith J. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for malF protein, an inner membrane component of the maltose transport system of Escherichia coli. Repeated DNA sequences are found in the malE-malF intercistronic region. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10896–10903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Clément J. M., Brutlag D., Hofnung M. A family of dispersed repetitive extragenic palindromic DNA sequences in E. coli. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1417–1421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Perrin D., Clement J. M., Szmelcman S., Dassa E., Hofnung M. Palindromic units from E. coli as binding sites for a chromoid-associated protein. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):323–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Perrin D., Saurin W., Hofnung M. Species specificity of bacterial palindromic units. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):371–373. doi: 10.1007/BF02603122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Ames G. F., Barnes W. M., Clement J. M., Hofnung M. A novel intercistronic regulatory element of prokaryotic operons. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):760–762. doi: 10.1038/298760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., McLaren R. S., Newbury S. F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences, mRNA stability and gene expression: evolution by gene conversion? A review. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):3–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce C. M., Kelley W. S., Grindley N. D. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli polA gene and primary structure of DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1958–1964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Magnesium ion-dependent triple-helix structure formed by homopurine-homopyrimidine sequences in supercoiled plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3781–3785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Meese K. Topoisomer gel retardation: detection of anti-Z-DNA antibodies bound to Z-DNA within supercoiled DNA minicircles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):21–37. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollis D. L., Brick P., Hamlin R., Xuong N. G., Steitz T. A. Structure of large fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I complexed with dTMP. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):762–766. doi: 10.1038/313762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollis D. L., Kline C., Steitz T. A. Domain of E. coli DNA polymerase I showing sequence homology to T7 DNA polymerase. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):818–819. doi: 10.1038/313818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papanicolaou C., Ripley L. S. Polymerase-specific differences in the DNA intermediates of frameshift mutagenesis. In vitro synthesis errors of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I and its large fragment derivative. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):335–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Kleinberger T., Livingston D. M. Mapping of SV40 DNA replication origin region binding sites for the SV40 T antigen by protection against exonuclease III digestion. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P., Wickner W. Genetic mapping of the Escherichia coli leader (signal) peptidase gene (lep): a new approach for determining the map position of a cloned gene. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):569–572. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.569-572.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. J., Ames G. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Higgins C. F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: a major component of the bacterial genome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svaren J., Inagami S., Lovegren E., Chalkley R. DNA denatures upon drying after ethanol precipitation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8739–8754. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Ames G. F. DNA gyrase binds to the family of prokaryotic repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8850–8854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zivanovic Y., Goulet I., Prunell A. Properties of supercoiled DNA in gel electrophoresis. The V-like dependence of mobility on topological constraint. DNA-matrix interactions. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):645–660. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90282-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]