To the Editor: Myiasis is an infestation of human tissue by the larval stage of flies of the order Diptera. There are 3 clinical manifestations of myiasis: localized furuncular myiasis typically caused by Dermatobia hominis, Cordylobia anthropophaga, Wohlfahrtia vigil, and Cuterebra spp.; creeping dermal myiasis caused by Gasterophilus spp. and Hypoderma spp.; and wound and body cavity myiasis caused by Cochliomyia hominivorax, Chrysomya bezziana, and Wohlfahrtia magnifica (1). The Tumbu fly (C. anthropophaga) and the human botfly (D. hominis) are the most common vectors for myiasis in Africa and the tropical Western Hemisphere, respectively (2). The genus Cordylobia also contains 2 less common species (C. ruandae and C. rodhaini) (3). Infection with C. rodhaini (Lund’s fly) is less common.
A review of the literature showed only 7 reports of C. rodhani myiasis in travelers from countries such as Australia (3), Italy (4), Canada (5), France (6), and Israel (7). All travelers were infested after travel to eastern and western regions of central Africa. In humans, the skin lesion starts as a painful red papule that gradually enlarges and develops into a furuncle. Typically, the center of the lesion has an opening, through which the larva breaths and discharges its waste products. Cutaneous myiasis is usually an uncomplicated and self-limiting disease. The flies have adapted to tropical environments, and spread to areas in which this disease is not endemic is unlikely.
In the emergency department, cellulitis or furuncular lesions are common with a broad differential diagnosis. With the introduction of bedside ultrasonography in the emergency department, ultrasonographic evaluation of soft tissue infections is more accurate than clinical examination in detecting abscesses (8,9). Ultrasonographic examination of soft tissue infections enables more accurate localization of an associated abscess and the potential to more specifically identify etiology such as a foreign body (10). We report a rare case of cutaneous myiasis caused by C. rodhaini larvae in a traveler returning from tropical Africa.
The patient was a 26-year-old woman who came to the emergency department at Toronto East General Hospital with a 10-day history of a painful red lesion on her left upper arm. She had first assumed it to be an insect bite, but during the preceding few days the swelling had greatly increased. She had no constitutional symptoms other than a persisting mild cough for which she had taken a 5-day course of amoxicillin ≈2 weeks before coming to the hospital. Her medical history was noncontributory. She reported that 7 days earlier she had returned from a 1-month trip to Ethiopia. During her stay in Ethiopia, she had been primarily in rural areas but did not report contact with sick persons. Her vital signs were normal.
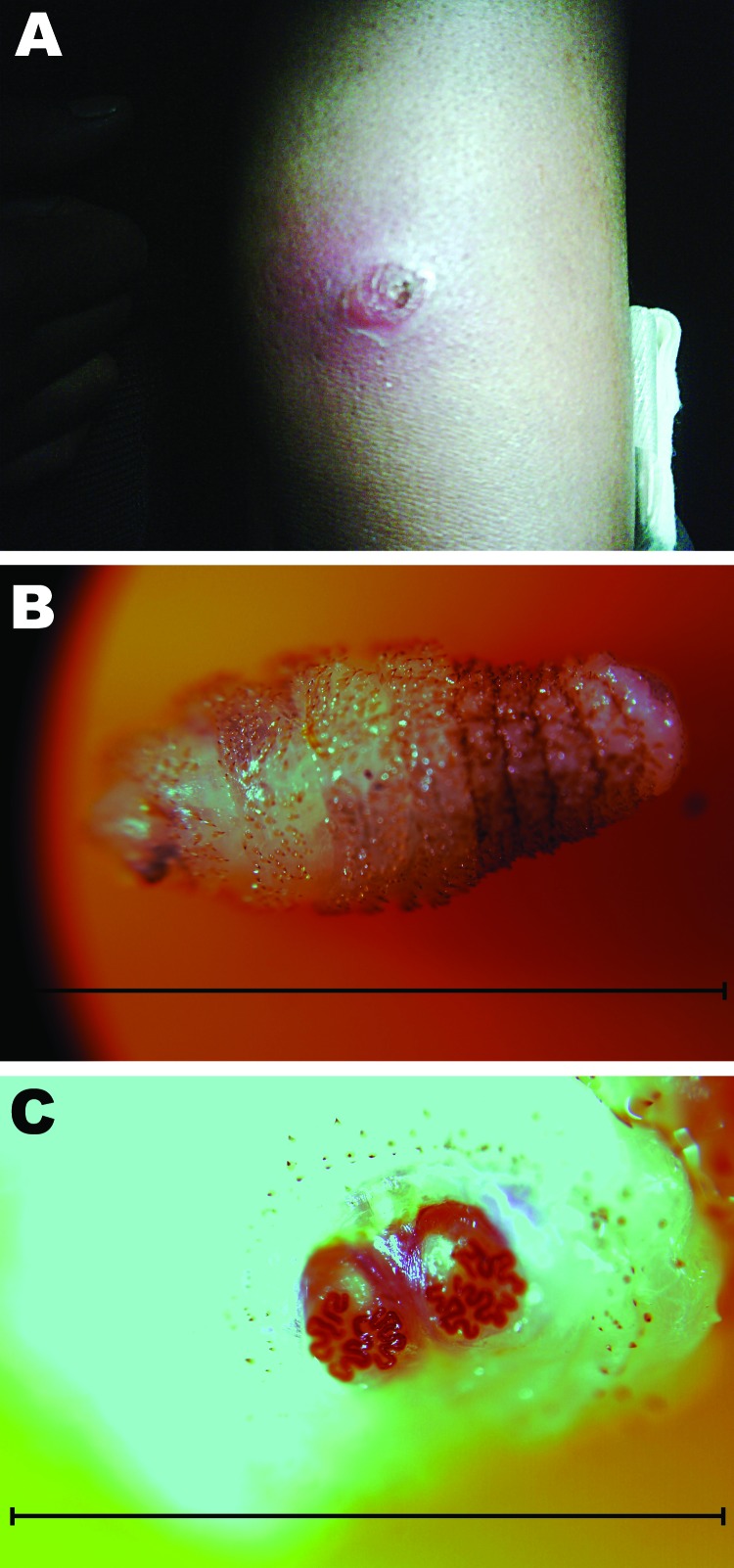
Physical examination showed a 2.5-cm2 erythematous area on the lateral aspect of the upper arm (Figure, panel A). There was a 1-mm central punctum and local tenderness. Discharge, streaking, or proximal adenopathy were not present. Other results of the examination were noncontributory. Results of a complete blood count and liver function tests were within reference ranges. Results of a chest radiographic were normal.
Figure.
A) Lateral aspect of the upper arm of a 26-year-old woman showing cutaneous myiasis and an erythematous lesion 2.5 cm in diameter, Canada. B) Cordylobia rodhaini larva (length ≈1 cm) isolated from the erythematous lesion. Scale bar = 10 mm. C) Characteristic posterior spiracles of a C. rodhaini larva. Scale bar = 3 mm.
Bedside ultrasonography was performed to assess possible abscess. During ultrasonography, the patient reported a biting sensation and increased pain in the area of the lesion. Ultrasonographic images of the lesion showed an area of spontaneous movement just below the skin, suggestive of cutaneous myiasis (Video).
Video.
Ultrasonographic image of a lesion on the upper arm of a 26-year-old woman who returned to Canada from Ethiopia, showing an area of spontaneous movement just below the skin, suggestive of cutaneous myiasis.
Direct Video Link: http://streaming.cdc.gov/vod.php?id=23c872c98cac849c2d2d01ae4229456620111201171809133
Treatment for myiasis can be conservative or surgical. Surgical treatment consists of mechanical removal of the larva. After consultation with infectious disease specialists, we covered the lesion with standard lubricating jelly and Op Site Flexfix transparent adhesive (Smith and Nephew, St. Laurent, Quebec, Canada) to obtain a seal. Approximately 45 minutes later, a 1-cm, white–yellow larvae emerged from the area and was removed intact with the dressing (Figure, panel B). C. rodhaini was identified by its characteristic posterior spiracles and the pattern of the larvae (Figure, panel C). Another occlusive dressing was applied before patient discharge. At follow-up 4 days later, the lesion was no longer symptomatic and the patient refused further treatment.
Physicians should consider myiasis in patients who have a furuncular lesion after returning from tropical countries. Bedside ultrasonography rapidly confirmed the diagnosis of myiasis, enabling immediate and appropriate treatment. Travelers should be aware of this potential infestation with the less common Lund’s fly and not only avoid direct contact with clothes left outside but also avoid direct contact with infested material (5).
Acknowledgments
We thank clinical laboratory staff and public health departments for expert assistance.
Suggested citation for this article: Hannam P, Khairnar K, Downey J, Powis J, Ralevski F, Pillai DR. Cutaneous myiasis in traveler returning from Ethiopia [letter]. Emerg Infect Dis [serial on the Internet]. 2011 Dec [date cited]. http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid1712.111062
Current affiliation: Calgary Laboratory Services, Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
References
- 1.Maguire JH, Spielman A. Ectoparasite infestations and arthropod bites and stings. In: Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Isselbacher KJ, Wilson JD, Martin JB, Kasper DL, et al, editors. New York: McGraw Hill; 1998. p. 2250. [Google Scholar]
- 2.White GB. Flies causing myiasis. In: Cook GC, Zumla AJ, editors. Manson’s tropical diseases. London: W.B. Saunders; 1996. p. 1661–3. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Geary MJ, Hudson BJ, Russell RC, Hardy A. Exotic myiasis with Lund’s fly (Cordylobia rodhaini). Med J Aust. 1999;171:654–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pampiglione S, Schiavon S, Candiani G, Fioravanti ML. Clinical and parasitological observations on a case of disseminated furuncular myiasis caused by Cordylobia rodhaini in a man in Ethiopia [in Italian]. Parassitologia. 1991;33:159–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Scholten TH, Hicks RJ. Myiasis by Cordylobia rodhaini contracted in Africa and diagnosed in Canada. Can J Public Health. 1973;64:488–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kremer M, Lenys J, Basset M, Rombourg H, Molet B. 2 cases of Cordylobia rhodaini myiasis contracted in Cameroon and diagnosed in Alsace [in French]. Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 1970;63:592–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tamir J, Haik J, Schwartz E. Myiasis with Lund’s fly (Cordylobia rodhaini) in travelers. J Travel Med. 2003;10:293–5. 10.2310/7060.2003.2732 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tayal VS, Hasan N, Norton HJ, Tomaszewski CA. The effect of soft tissue ultrasound on the management of cellulitis in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2006;13:384–8. 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2006.tb00314.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Squire BT, Fox JC, Anderson C. ABSCESS: applied bedside sonography for convenient evaluation of superficial soft tissue infections. Acad Emerg Med. 2005;12:601–6. 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2005.tb00913.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Banerjee B, Das RK. Sonographic detection of foreign bodies of the extremities. Br J Radiol. 1991;64:107–12. 10.1259/0007-1285-64-758-107 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]