Full text
PDF
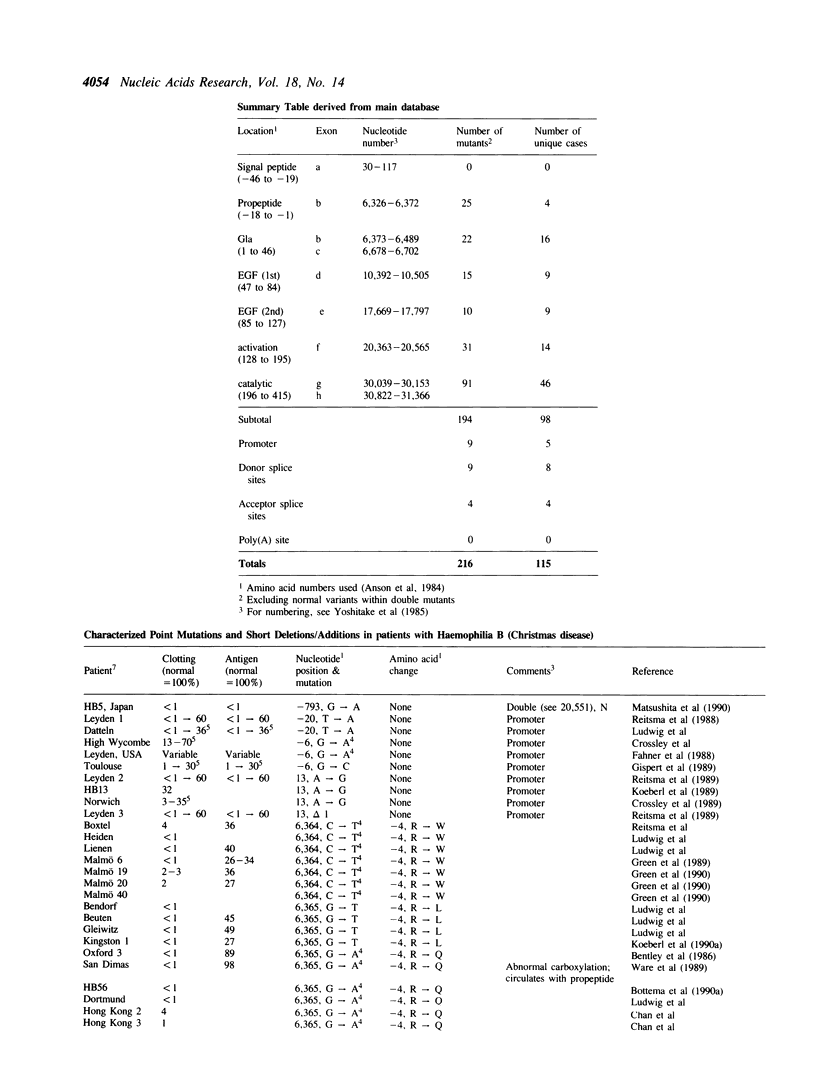
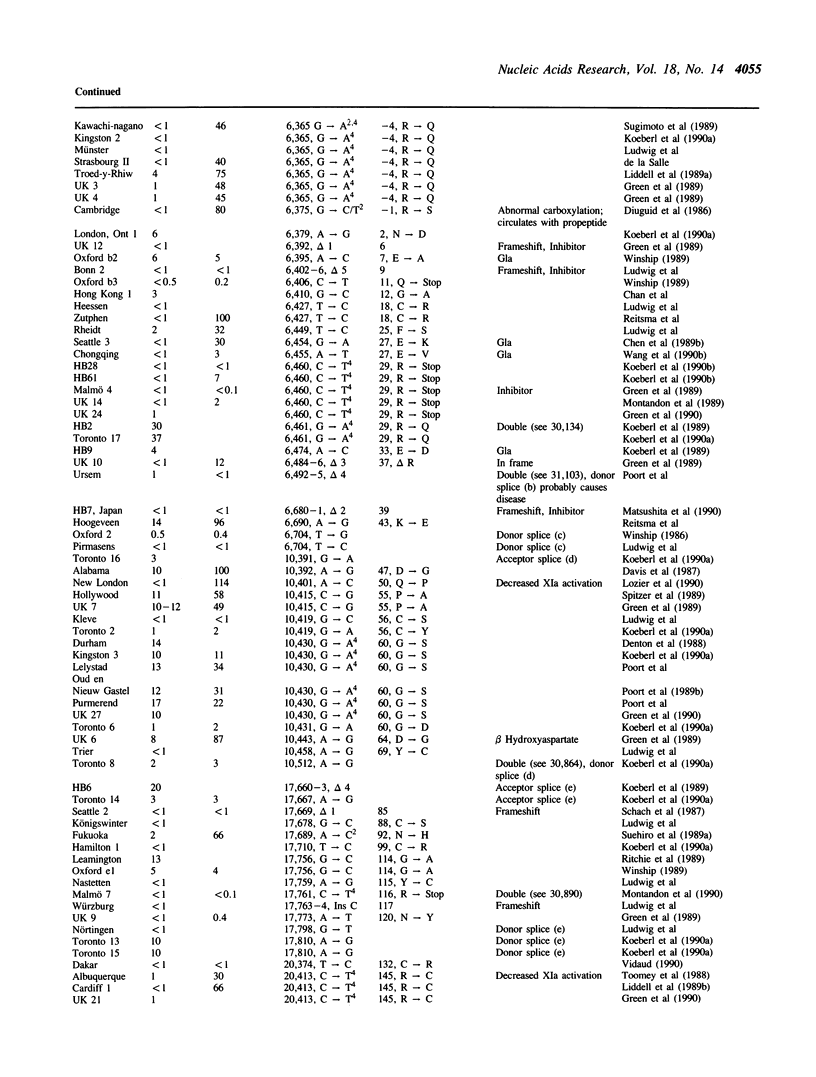
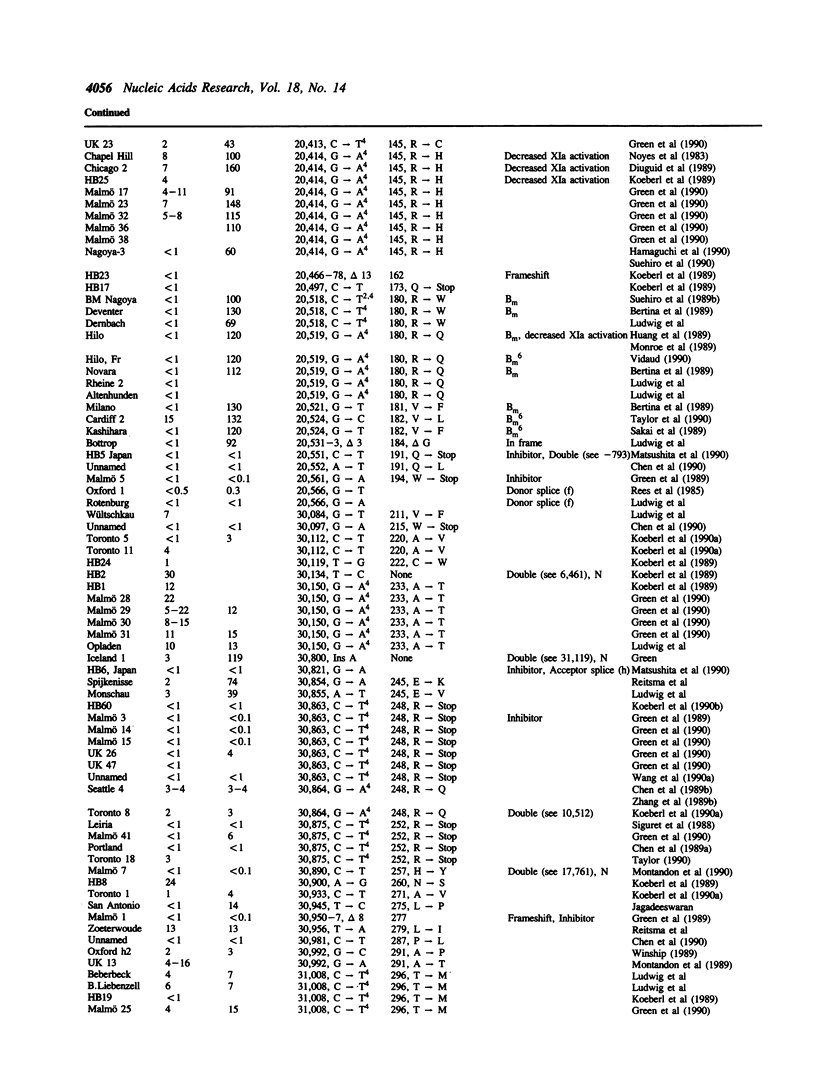
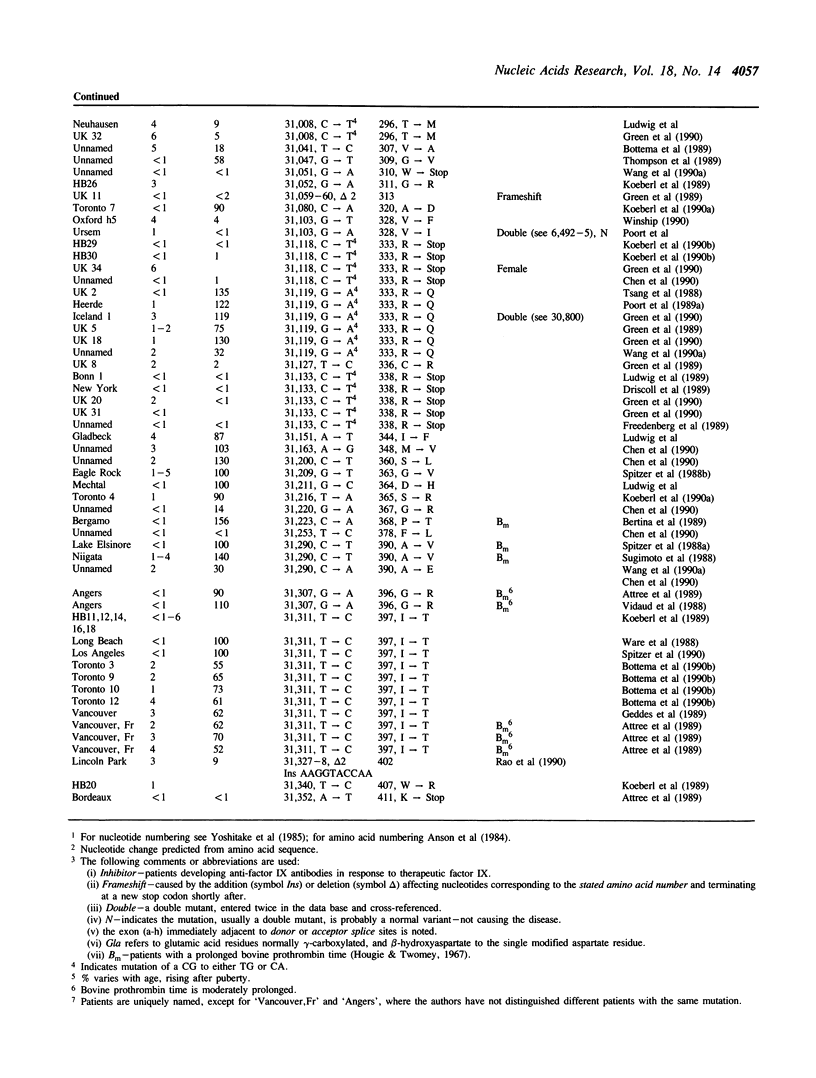


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attree O., Vidaud D., Vidaud M., Amselem S., Lavergne J. M., Goossens M. Mutations in the catalytic domain of human coagulation factor IX: rapid characterization by direct genomic sequencing of DNA fragments displaying an altered melting behavior. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):266–272. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90330-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. K., Rees D. J., Rizza C., Brownlee G. G. Defective propeptide processing of blood clotting factor IX caused by mutation of arginine to glutamine at position -4. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottema C. D., Koeberl D. D., Sommer S. S. Direct carrier testing in 14 families with haemophilia B. Lancet. 1989 Sep 2;2(8662):526–529. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90653-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Scott C. R., Schoof J., Lovrien E. W., Kurachi K. Factor IXPortland: a nonsense mutation (CGA to TGA) resulting in hemophilia B. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):567–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Thompson A. R., Zhang M., Scott C. R. Three point mutations in the factor IX genes of five hemophilia B patients. Identification strategy using localization by altered epitopes in their hemophilic proteins. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):113–118. doi: 10.1172/JCI114130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley M., Brownlee G. G. Disruption of a C/EBP binding site in the factor IX promoter is associated with haemophilia B. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):444–446. doi: 10.1038/345444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. M., McGraw R. A., Ware J. L., Roberts H. R., Stafford D. W. Factor IXAlabama: a point mutation in a clotting protein results in hemophilia B. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):140–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton P. H., Fowlkes D. M., Lord S. T., Reisner H. M. Hemophilia B Durham: a mutation in the first EGF-like domain of factor IX that is characterized by polymerase chain reaction. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1407–1411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diuguid D. L., Rabiet M. J., Furie B. C., Liebman H. A., Furie B. Molecular basis of hemophilia B: a defective enzyme due to an unprocessed propeptide is caused by a point mutation in the factor IX precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5803–5807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll M. C., Bouhassira E., Aledort L. M. A codon 338 nonsense mutation in the factor IX gene in unrelated hemophilia B patients: factor IX338 New York. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):737–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes V. A., Le Bonniec B. F., Louie G. V., Brayer G. D., Thompson A. R., MacGillivray R. T. A moderate form of hemophilia B is caused by a novel mutation in the protease domain of factor IXVancouver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4689–4697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. M., Bentley D. R., Mibashan R. S., Nilsson I. M., Giannelli F. Molecular pathology of haemophilia B. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. M., Montandon A. J., Bentley D. R., Ljung R., Nilsson I. M., Giannelli F. The incidence and distribution of CpG----TpG transitions in the coagulation factor IX gene. A fresh look at CpG mutational hotspots. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3227–3231. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handford P. A., Baron M., Mayhew M., Willis A., Beesley T., Brownlee G. G., Campbell I. D. The first EGF-like domain from human factor IX contains a high-affinity calcium binding site. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):475–480. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. N., Kasper C. K., Roberts H. R., Stafford D. W., High K. A. Molecular defect in factor IXHilo, a hemophilia Bm variant: Arg----Gln at the carboxyterminal cleavage site of the activation peptide. Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):718–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeberl D. D., Bottema C. D., Buerstedde J. M., Sommer S. S. Functionally important regions of the factor IX gene have a low rate of polymorphism and a high rate of mutation in the dinucleotide CpG. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Sep;45(3):448–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeberl D. D., Bottema C. D., Sarkar G., Ketterling R. P., Chen S. H., Sommer S. S. Recurrent nonsense mutations at arginine residues cause severe hemophilia B in unrelated hemophiliacs. Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;84(5):387–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00195805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddell M. B., Lillicrap D. P., Peake I. R., Bloom A. L. Defective propeptide processing and abnormal activation underlie the molecular pathology of factor IX Troed-y-Rhiw. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jun;72(2):208–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddell M. B., Peake I. R., Taylor S. A., Lillicrap D. P., Giddings J. C., Bloom A. L. Factor IX Cardiff: a variant factor IX protein that shows abnormal activation is caused by an arginine to cysteine substitution at position 145. Br J Haematol. 1989 Aug;72(4):556–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb04323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier J. N., Monroe D. M., Stanfield-Oakley S., Lin S. W., Smith K. J., Roberts H. R., High K. A. Factor IX New London: substitution of proline for glutamine at position 50 causes severe hemophilia B. Blood. 1990 Mar 1;75(5):1097–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig M., Schwaab R., Eigel A., Horst J., Egli H., Brackmann H. H., Olek K. Identification of a single nucleotide C-to-T transition and five different deletions in patients with severe hemophilia B. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;45(1):115–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe D. M., McCord D. M., Huang M. N., High K. A., Lundblad R. L., Kasper C. K., Roberts H. R. Functional consequences of an arginine180 to glutamine mutation in factor IX Hilo. Blood. 1989 May 1;73(6):1540–1544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon A. J., Green P. M., Giannelli F., Bentley D. R. Direct detection of point mutations by mismatch analysis: application to haemophilia B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3347–3358. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes C. M., Griffith M. J., Roberts H. R., Lundblad R. L. Identification of the molecular defect in factor IX Chapel Hill: substitution of histidine for arginine at position 145. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4200–4202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poort S. R., Briët E., Bertina R. M., Reitsma P. H. A Dutch family with moderately severe hemophilia B (factor IXHeerde) has a missense mutation identical to that of factor IX London 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3614–3614. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poort S. R., Briët E., Bertina R. M., Reitsma P. H. A Dutch pedigree with mild hemophilia B with a missense mutation in the first EGF domain (factor IXOud en Nieuw Gastel). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5869–5869. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. J., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Haemophilia B caused by a point mutation in a donor splice junction of the human factor IX gene. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):643–645. doi: 10.1038/316643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Bertina R. M., Ploos van Amstel J. K., Riemens A., Briët E. The putative factor IX gene promoter in hemophilia B Leyden. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):1074–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Mandalaki T., Kasper C. K., Bertina R. M., Briët E. Two novel point mutations correlate with an altered developmental expression of blood coagulation factor IX (hemophilia B Leyden phenotype). Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):743–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Yoshioka A., Yamamoto K., Niinomi K., Fujimura Y., Fukui H., Miyata T., Iwanaga S. Blood clotting factor IX Kashihara: amino acid substitution of valine-182 by phenylalanine. J Biochem. 1989 May;105(5):756–759. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schach B. G., Yoshitake S., Davie E. W. Hemophilia B (factor IXSeattle 2) due to a single nucleotide deletion in the gene for factor IX. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1023–1028. doi: 10.1172/JCI113155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siguret V., Amselem S., Vidaud M., Assouline Z., Kerbiriou-Nabias D., Piétu G., Goossens M., Larrieu M. J., Bahnak B., Meyer D. Identification of a CpG mutation in the coagulation factor-IX gene by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. Br J Haematol. 1988 Dec;70(4):411–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb02509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer S. G., Warn-Cramer B. J., Kasper C. K., Bajaj S. P. Replacement of isoleucine-397 by threonine in the clotting proteinase factor IXa (Los Angeles and Long Beach variants) affects macromolecular catalysis but not L-tosylarginine methyl ester hydrolysis. Lack of correlation between the ox brain prothrombin time and the mutation site in the variant proteins. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 1;265(1):219–225. doi: 10.1042/bj2650219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suehiro K., Kawabata S., Miyata T., Takeya H., Takamatsu J., Ogata K., Kamiya T., Saito H., Niho Y., Iwanaga S. Blood clotting factor IX BM Nagoya. Substitution of arginine 180 by tryptophan and its activation by alpha-chymotrypsin and rat mast cell chymase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21257–21265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto M., Miyata T., Kawabata S., Yoshioka A., Fukui H., Iwanaga S. Factor IX Kawachinagano: impaired function of the Gla-domain caused by attached propeptide region due to substitution of arginine by glutamine at position -4. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jun;72(2):216–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto M., Miyata T., Kawabata S., Yoshioka A., Fukui H., Takahashi H., Iwanaga S. Blood clotting factor IX Niigata: substitution of alanine-390 by valine in the catalytic domain. J Biochem. 1988 Dec;104(6):878–880. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. R., Bajaj S. P., Chen S. H., MacGillivray R. T. "Founder" effect in different families with haemophilia B mutation. Lancet. 1990 Feb 17;335(8686):418–418. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang T. C., Bentley D. R., Mibashan R. S., Giannelli F. A factor IX mutation, verified by direct genomic sequencing, causes haemophilia B by a novel mechanism. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3009–3015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N. S., Zhang M., Thompson A. R., Chen S. H. Factor IX Chongqing: a new mutation in the calcium-binding domain of factor IX resulting in severe hemophilia B. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Feb 19;63(1):24–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J., Davis L., Frazier D., Bajaj S. P., Stafford D. W. Genetic defect responsible for the dysfunctional protein: factor IXLong Beach. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):820–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship P. R. Haemophilia B caused by mutation of a potential thrombin cleavage site in factor IX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1310–1310. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitake S., Schach B. G., Foster D. C., Davie E. W., Kurachi K. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human factor IX (antihemophilic factor B). Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3736–3750. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M., Chen S. H., Scott C. R., Thompson A. R. The factor IX BamHI polymorphism: T-to-G transversion at the nucleotide sequence -561. The BamHI/MSPI haplotypes in blacks and Caucasians. Hum Genet. 1989 Jun;82(3):283–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00291171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


