Abstract
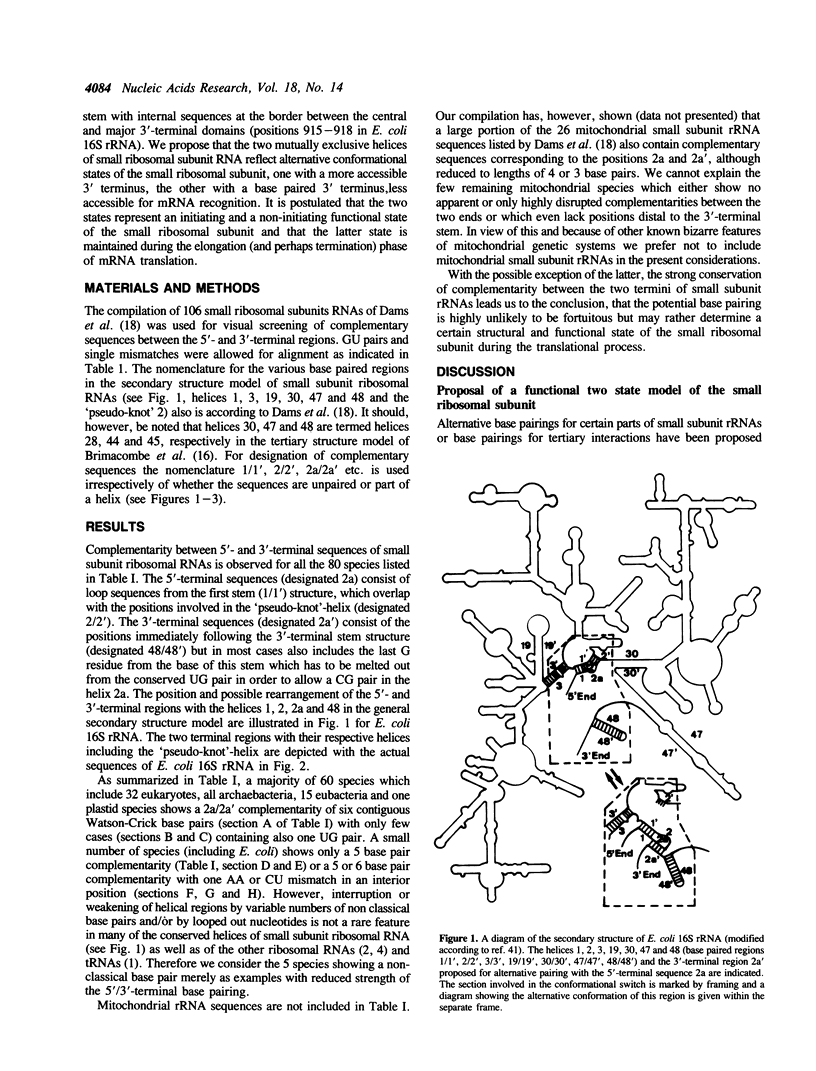
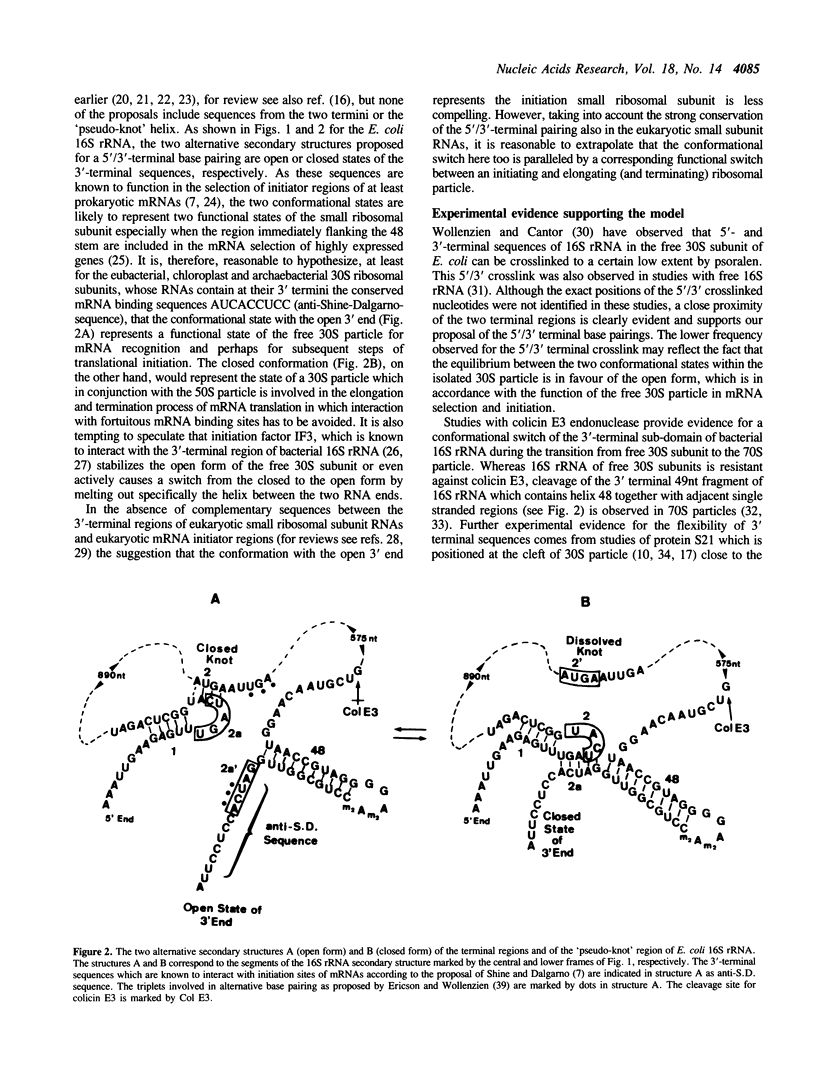
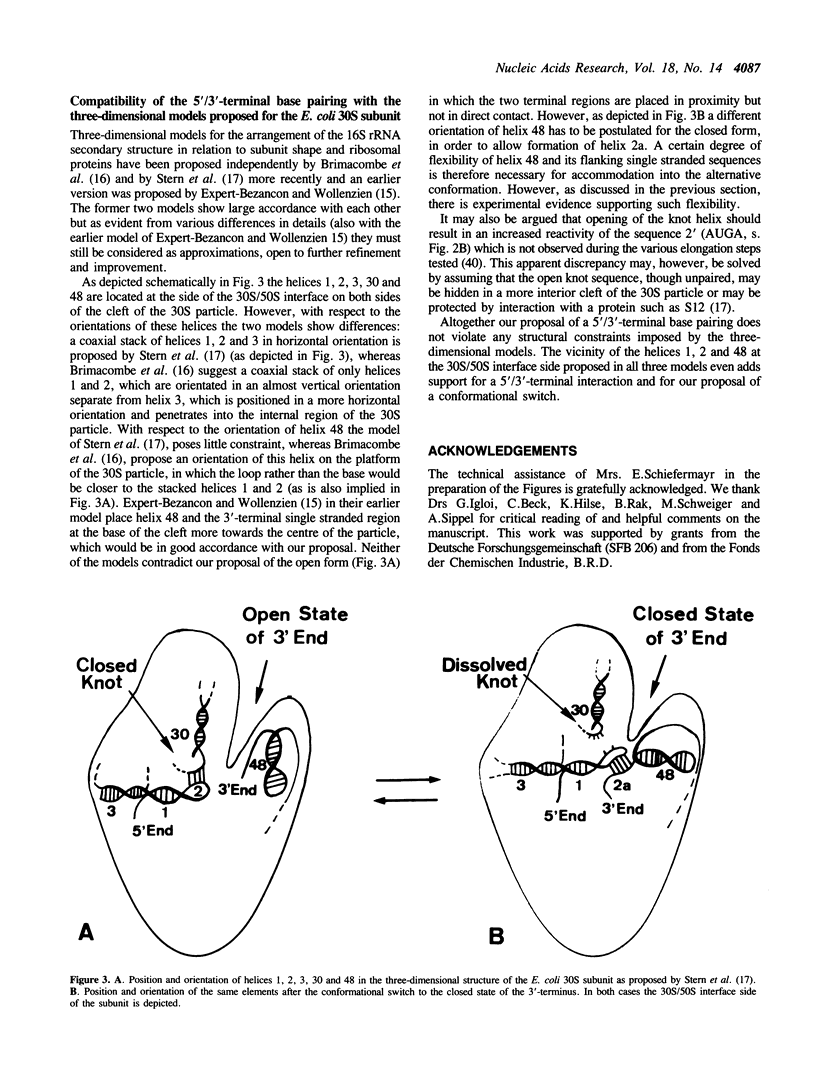
The compiled sequences of small subunit ribosomal RNAs have been screened for base complementary between 5'- and 3'-terminal regions. Highly conserved complementary sequences are found which allow formation of a helix between the two ends of 5 or 6 base pairs. This helix is composed of sequences from the loop region of the first 5'-terminal stem and from sequences immediately distal to the last stem (the Me2A-stem) of the 3' terminus and therefore allows a coaxial stacking with either of these two flanking stems. Formation of the 5'/3'-helical arrangement is, however, only possible at the cost of dissolving the 'pseudo-knot' helix between the 5'-terminal region and the internal region of small subunit RNA. It is postulated that the mutually exclusive conformational states are in dynamic equilibrium and that they correlate with distinct functional states of the small ribosomal subunit. The 'pseudo-knot' containing conformation with the 3'-terminal sequences more exposed is likely to represent the initiating state, whereas the 5'/3' terminal paired 'closed' conformation may represent the elongating state in which interaction with fortuitous ribosomal binding sequences of mRNAs is avoided.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backendorf C., Ravensbergen C. J., Van der Plas J., van Boom J. H., Veeneman G., Van Duin J. Basepairing potential of the 3' terminus of 16S RNA: dependence on the functional state of the 30S subunit and the presence of protein S21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1425–1444. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon T. Inactivation of ribosomes in vitro by colicin E 3 and its mechanism of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):549–552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. M. Inactivation of ribosomes by colicin E3 in vitro: Requirement for 50 S ribosomal subunits. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 15;22(1):73–75. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Atmadja J., Stiege W., Schüler D. A detailed model of the three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA in situ in the 30 S subunit. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):115–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capel M. S., Engelman D. M., Freeborn B. R., Kjeldgaard M., Langer J. A., Ramakrishnan V., Schindler D. G., Schneider D. K., Schoenborn B. P., Sillers I. Y. A complete mapping of the proteins in the small ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1403–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.3317832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F. Sequence and structural features associated with translational initiator regions in yeast--a review. Gene. 1987;59(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dams E., Hendriks L., Van de Peer Y., Neefs J. M., Smits G., Vandenbempt I., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16 (Suppl):r87–173. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.suppl.r87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson D., Spitnik-Elson P. A three-dimensional model of domain III of the Escherichia coli small ribosomal subunit. Biochimie. 1987 Sep;69(9):991–999. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90233-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson G., Wollenzien P. An RNA secondary structure switch between the inactive and active conformations of the Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal subunit. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):540–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Expert-Bezançon A., Wollenzien P. L. Three-dimensional arrangement of the Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotz C., Zwieb C., Brimacombe R., Edwards K., Kössel H. Secondary structure of the large subunit ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli, Zea mays chloroplast, and human and mouse mitochondrial ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3287–3306. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Fox G. E. A compilation of large subunit RNA sequences presented in a structural format. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16 (Suppl):r175–r269. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.suppl.r175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselman T., Camp D. G., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic evidence for tertiary interactions in 16S-like ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2215–2221. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. F., Cantor C. R. Mapping the location of psoralen crosslinks on RNA by mung bean nuclease sensitivity of RNA.DNA hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1381–1385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James B. D., Olsen G. J., Liu J. S., Pace N. R. The secondary structure of ribonuclease P RNA, the catalytic element of a ribonucleoprotein enzyme. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lührmann R., Stöffler-Meilicke M., Stöffler G. Localization of the 3' end of 16S rRNA in Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunits by immuno electron microscopy. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):369–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00293924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Intermediate states in the movement of transfer RNA in the ribosome. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):142–148. doi: 10.1038/342142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Van Stolk B. J., Douthwaite S., Noller H. F. Interconversion of active and inactive 30 S ribosomal subunits is accompanied by a conformational change in the decoding region of 16 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):483–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochalova L. V., Shatsky I. N., Bogdanov A. A., Vasiliev V. D. Topography of rna in the ribosome localization of the 16 s rna 5' end by immune electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):637–650. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom O. W., Deng H. Y., Dabbs E. R., Hardesty B. Binding of S21 to the 50S subunit and the effect of the 50S subunit on nonradiative energy transfer between the 3' end of 16S RNA and S21. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5069–5076. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen G. B., Stockwell P. A., Hill D. F. Messenger RNA recognition in Escherichia coli: a possible second site of interaction with 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3957–3962. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleij C. W., Rietveld K., Bosch L. A new principle of RNA folding based on pseudoknotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1717–1731. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatsky I. N., Evstafieva A. G., Bystrova T. F., Bogdanov A. A., Vasiliev V. D. Topography of RNA in the ribosome: location of the 3'-end of 5 S RNA on the central protuberance of the 50 S subunit. FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 17;121(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81274-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitnik-Elson P., Elson D., Avital S., Abramowitz R. Long range RNA-RNA interactions in the 30 S ribosomal subunit of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4719–4738. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Hartmann T., Meissner F., Moll J., Vorderwülbecke T. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987;15 (Suppl):r53–188. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.suppl.r53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Weiser B., Noller H. F. Model for the three-dimensional folding of 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):447–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90588-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter G., Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A., Kössel H. Identification of an rRNA operon promoter from Zea mays chloroplasts which excludes the proximal tRNAValGAC from the primary transcript. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):599–604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03672.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler-Meilicke M., Stöffler G., Odom O. W., Zinn A., Kramer G., Hardesty B. Localization of 3' ends of 5S and 23S rRNAs in reconstituted subunits of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5538–5542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Stöffler-Meilicke M. Immunoelectron microscopy of ribosomes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:303–330. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanaraj T. A., Pandit M. W. An additional ribosome-binding site on mRNA of highly expressed genes and a bifunctional site on the colicin fragment of 16S rRNA from Escherichia coli: important determinants of the efficiency of translation-initiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):2973–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. Nuclease mapping of the secondary structure of the 49-nucleotide 3' terminal cloacin fragment of Escherichia coli 16s RNA and its interactions with initiation factor 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2035–2052. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G. Architecture of prokaryotic ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:35–65. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenzien P. L., Cantor C. R. Gel electrophoretic technique for separating crosslinked RNAs. Application to improved electron microscopic analysis of psoralen crosslinked 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 25;159(1):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenzien P. L., Murphy R. F., Cantor C. R., Expert-Bezançon A., Hayes D. H. Structure of the Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA. Psoralen crosslinks and N-acetyl-N'-(p-glyoxylylbenzoyl)cystamine crosslinks detected by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):67–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Complementary sequences 1700 nucleotides apart form a ribonuclease III cleavage site in Escherichia coli ribosomal precursor RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3593–3597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin J., Kurland C. G., Dondon J., Grunberg-Manago M. Near neighbors of IF3 bound to 30S ribosomal subunits. FEBS Lett. 1975 Nov 15;59(2):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80394-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


