Abstract
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, stimulation of the Neiguan spot has been utilized to treat palpitations and symptoms related to different cardiovascular diseases. We evaluated whether acupuncture might exert an antiarrhythmic effect on patients with paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation (AF). Two sets of data are reviewed. The first included patients with persistent AF who underwent electrical cardioversion to restore sinus rhythm. The second included patients with symptomatic paroxysmal AF. All subjects had normal ventricular function. Acupuncture treatment consisted of 10 acupuncture sessions on a once a week basis with puncturing of the Neiguan, Shenmen and Xinshu spots. In patients with persistent AF, the recurrence rate after acupuncture treatment was similar to that observed in patients on amiodarone, but significantly smaller than that measured after sham acupuncture treatment or in the absence of any antiarrhythmic drugs. In a small group of patients with paroxysmal AF, acupuncture resulted in a significant reduction in the number and duration of symptomatic AF episodes. In conclusion, we observed that acupuncture of the Neiguan spot was associated with an antiarrhythmic effect, which was evident in patients with both persistent and paroxysmal AF. These preliminary data, observed in 2 small groups of AF patients, need to be validated in a larger population but strongly suggest that acupuncture may be an effective non-invasive and safe antiarrhythmic tool in the management of these patients.
Keywords: Chinese medicine, Antiarrhythmic drugs, Autonomic mechanisms, Atrial arrhythmias
INTRODUCTION
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common clinical arrhythmia with a relevant socioeconomic impact. Patients with AF have symptoms such as palpitations and shortness of breath; they have reduced exercise capacity and are subject to a higher risk of thromboembolic events[1-3]. AF diagnosis is relatively simple when a permanent form is present, but is much more complicated when it is paroxysmal. Indeed, up to 25% of cryptogenic strokes may be due to paroxysmal or undiagnosed AF. Management of AF patients is also difficult because of uncertainties about the optimal therapeutic strategy[4], and the limited efficacy and safety of the most common antiarrhythmic drugs[3,5]. More recent approaches, such as the use of radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary vein firing to reduce arrhythmia triggering or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy targeting the atrial substrate, remain controversial because of the uncertainty of patient selection criteria and the limited efficacy in controlled trials[6-9].
In the last 20 years[1-3], a general consensus has been reached on the fact that AF is not only a simple electrocardiographic diagnosis but rather a clinical disorder in which different factors act as triggers or substrate modifiers and affect the medical history of AF patients (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
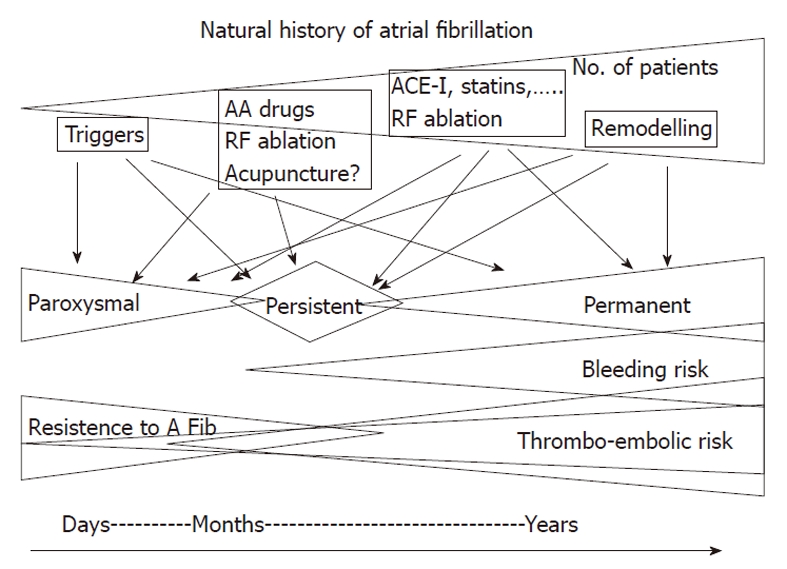
Schematic representation of the temporal changes of the factors that favor or oppose to atrial fibrillation. Initial (left side) triggers play a major proarrhythmic role and need to be targeted by therapeutic interventions. With time and the change from paroxysmal to persistent atrial fibrillation (AF), both triggers and structural alterations become critical and both have to be targeted by therapy. Finally, when structural alterations become extensive and not reversible, AF becomes permanent. The timing of this journey varies from patient to patient and is likely to be related to cardiac and non-cardiac factors. RF: Radio frequency; AA: Antiarrhythmic; ACE-I: Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor.
The complexity of the picture and the interaction among different factors may therefore explain the difficulty in managing AF patients and the need for new or alternative therapeutic options[10]. In traditional Chinese medicine[11], stimulation of the Neiguan spot on the meridian of the Minister of the Heart has been extensively used to treat nausea and vomiting. It is also considered to be an essential point in the treatment of cardiovascular pathologies, specifically with regard to disorders of rhythm as well as of the coronary blood flow. Recently also in Western literature, reports have been published supporting the clinical efficacy of acupuncture to treat arterial hypertension[12] and to reduce chest pain[13,14].
We have previously reported[15] that acupuncture might prevent the recurrence in patients with persistent AF. In the present review we also report the antiarrhythmic effects of Chinese acupuncture therapy in patients with paroxysmal or persistent AF.
PATIENT POPULATIONS
From our outpatient arrhythmia clinic, we enrolled 2 sets of patients. All had preserved ventricular function (defined as left ventricular ejection fraction > 45%). Subjects with ischemic, dilated or valvular cardiomyopathy, New York Heart Association functional class III-IV, signs of acute or chronic inflammatory disease, malignancies, significant renal or hepatic failure and thyreotoxicosis were excluded.
The first set[15] consisted of patients with persistent AF who underwent electrical cardioversion to restore sinus rhythm. All were on anticoagulant therapy and were randomized to acupuncture, sham acupuncture and no antiarrhythmic therapy. A group of patients on amiodarone was considered as a reference group. The second set of patients consisted of 31 subjects with frequent symptomatic paroxysmal AF episodes present for at least a 6-mo period. Most received antiarrhythmic drugs (Table 1). At enrolment, patients were given a chart to annotate the occurrence and duration of paroxysmal symptomatic episodes. All patients of this latter group as well as patients with persistent AF randomized to acupuncture underwent 10 acupuncture sessions of 15-20 min duration on a once a week basis in the following spots (Figure 2): PC-6 (Neiguan in modern Chinese language), which is reported to have a modulating effect on the autonomic nervous system, with a mainly vagomimetic and sympathicolytic action[16-18]; HT-7 (Shenmen in modern Chinese language), which is reported to have a calming and sedative effect on cardiac excitability[19]; BL-15 (Xinshu in modern Chinese language), which is reported to have a modulating effect on the autonomic nervous system[20].
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of patients with symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
| Sex (M/F) (%M) | 17/14 (55) |
| Age (yr) | 32-78 |
| LVEF (%) | 54 (52-64) |
| LA diameter | 37 (35-42) |
| Duration AF (yr) | 7 (2-12) |
| Hypertension (%) | 18 (58) |
| Diabetes (%) | 9 (29) |
| Medication (%) | |
| None | 7 (23) |
| Flecainide | 7 (23) |
| Amiodarone | 3 (10) |
| Propiophenone | 10 (32) |
| Sotalol | 2 (6) |
| Verapamil | 2 (6) |
LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fraction; LA: Left atrial; AF: Atrial fibrillation.
Figure 2.
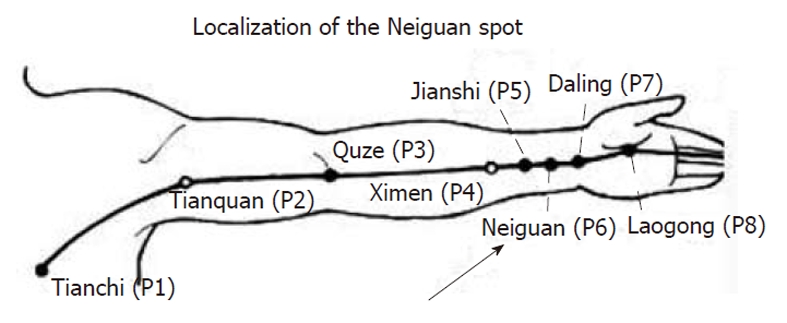
Insertion point for acupuncture. The PC-6 (Neiguan in modern Chinese language) spot situated in the heart meridian is indicated by an arrow.
The effects of acupuncture were evaluated in a 12 mo follow-up period in both sets of patients.
ANTIARRHYTHMIC EFFECTS OF ACUPUNCTURE
In all patients with persistent AF[15], electrical cardioversion restored sinus rhythm without complications. During the following 12-mo observation period, 35 of 80 patients enrolled in the study experienced a recurrence of AF with a cumulative incidence of 43.8%. In comparison with controls, Neiguan spot puncturing was associated with a significant reduction in the AF recurrence rate. The cumulative proportion of patients with AF recurrences was 35% in the active acupuncture group, 27% in the reference group of patients treated with amiodarone, and was significantly smaller than in patients with no antiarrhythmic drugs (54%) or treated with sham acupuncture (69%).
As indicated in Figure 3, there was a significant difference between the 2 active treatment groups (amiodarone or acupuncture) and the 2 control groups (sham acupuncture and no antiarrhythmic drugs). Among clinical or echocardiographic parameters, only left atrial diameter, history of hypertension and left ventricular ejection fraction were significantly associated with AF recurrence.
Figure 3.
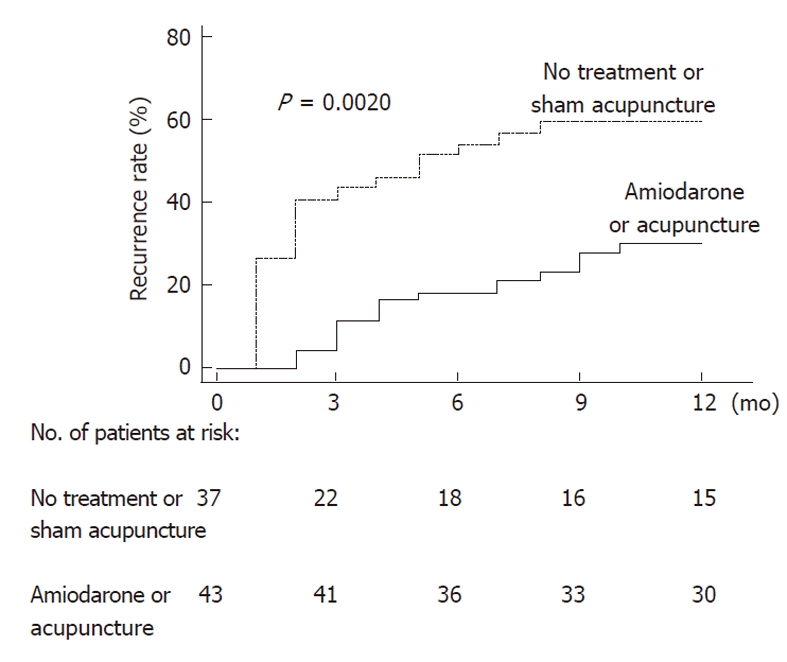
Cumulative recurrence rate. Kaplan and Meier plots of recurrence of atrial fibrillation after electrical cardioversion in patients receiving amiodarone or acupuncture (solid line) compared with no treatment or sham acupuncture (dotted line).
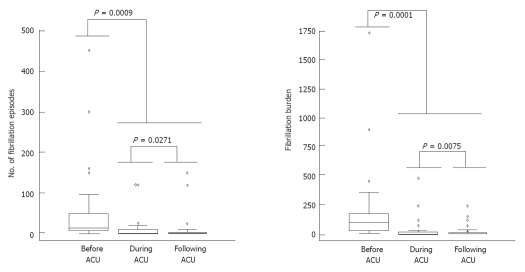
When considering patients with paroxysmal AF, we measured the number and duration of symptomatic episodes in order to determine the arrhythmic burden (average number and duration in minutes of AF episodes for each patient) and compared the control period with the first 2 mo after acupuncture and an additional 10 mo follow-up period. As illustrated in Figure 4, acupuncture was associated with a significant reduction in the number of AF episodes from a median of 15 [interquartile range (IQR), 6-50] to 2 (IQR, 1-10; P = 0.0018) and in AF burden from 100 (IQR, 30-180) to 6 (IQR, 1-20; P = 0.0002). The antiarrhythmic effect of acupuncture persisted during the 10-mo follow-up period.
Figure 4.
Number of atrial fibrillation episodes and atrial fibrillation burden in the period before, immediately after and during follow-up of acupuncture treatment in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Comparison of the different experimental conditions was made using Friedman’s non-parametric analysis of variance for repeated measurements. ACU: Acupuncture.
Acupuncture treatment did not cause bleeding, hematoma or infection. No pain or vaso-vagal reactions were reported with needle insertion.
HOW TO EXPLAIN THE OBSERVED RESULTS
Possible effects of Neiguan puncturing
These findings indicate that acupuncture of the Neiguan spot exerts an antiarrhythmic effect similar to that of amiodarone in patients with persistent AF and is additive to common antiarrhythmic drugs in patients with symptomatic paroxysmal AF. Although these results deserve confirmation in a larger patient population, they are, in our opinion, of relevant physiopathological and clinical interest and open new perspectives in the management of AF patients in relation to traditional and Western medicine.
In the Traditional Chinese Medical Doctrine[11,21], AF, like most supraventricular arrhythmias, is related to Heart Yin deficiency in the absence of structural disorders or to Heart Yang deficiency in the presence of a cardiac disease. The Neiguan spot is located in the portion of the heart meridian situated in the forearm and is responsible for blood flow and pulse rate control. Its malfunction has been associated with anxiety and restlessness and cardiac pain.
In the Western world, puncturing of the Neiguan spot has been used to treat chest pain, sickness and vomiting during chemo-embolization procedures[22] and to limit the symptoms related to fullness-tension in the chest and palpitations[23]. Reductions in the electrocardiographic signs of myocardial ischemia and plasma levels of endothelin have also been reported[23,24].
Electroacupuncture of the Neiguan spot has also been associated with an effect on the autonomic nervous system and, in particular on the sympatho-vagal interaction[25,26]. In one of the first studies, Kong et al[27] was able to restore a more physiological sympatho-vagal balance after acupuncture by measuring heart rate variability. More recently, however, in a systematic review[28] in which the effects of acupuncture on heart rate variability were studied in different patient populations and experimental conditions, contrasting results were observed. For example in healthy subjects, acupuncture determined a significant attenuation of signs of sympathetic activation and reduced vagal modulation induced by a stress state in comparison to sham acupuncture[29]. Other studies, however, failed to detect similar changes in heart rate variability parameters when subjects were exposed to mental stress testing or other stressors[28]. On the other hand, Flachskampf et al[12], reported that 6 wk of acupuncture significantly lowered median 24-h ambulatory blood pressure and that the effect was no longer present after cessation of acupuncture treatment.
The possibility that acupuncture may exert its antiarrhythmic effect through an action on the autonomic nervous system is therefore a plausible hypothesis although not tested in our studies. Indeed, several clinical and experimental reports have indicated that an imbalance of autonomic control mechanisms due to either an increase in vagal or sympathetic neural activity directed to the heart may favor the initiation and maintenance of AF episodes[1,2]. In patients who developed AF during Holter recordings[30,31], signs of either an increased vagal or sympathetic modulation of the sinus node were commonly detected in the minutes preceding AF initiation: a finding that in our opinion, suggests that an imbalance between the two branches of the autonomic nervous system rather than a specific predominance of one component is the most important pro-arrhythmic factor.
The possibility that the antiarrhythmic effect of acupuncture might be related to a stabilization of sympathetic and vagal control mechanisms rather than to a direct antiadrenergic or vagomimetic effect is therefore appealing and is substantiated by recent experimental findings. In fact, whereas direct high threshold cardiac vagal ganglia stimulation has been associated with a pro-fibrillatory effect[32,33], bilateral low-level vago-sympathetic nerve stimulation has been found to suppress effectively high-frequency stimulation-induced focal AF at atrial and pulmonary vein sites[34-36]. Whether acupuncture of Neiguan spot might exert similar effects on cardiac autonomic ganglia remains to be determined and at the moment it is an interesting hypothesis.
Antiarrhythmic effects of acupuncture
We observed that the antiarrhythmic efficacy of acupuncture was similar to that of amiodarone in patients with persistent AF and additive to traditional antiarrhythmic drugs in patients with symptomatic paroxysmal AF. Of interest were the findings that, in the former group, acupuncture matched the efficacy of the most active available antiarrhythmic drug[37] and that sham-acupuncture patients had an AF recurrence rate similar to that of patients with no antiarrhythmic therapy. We interpreted this result as indirect evidence of the fact that only specific spot puncturing rather than simple needling was the mechanism responsible for acupuncture efficacy, thus making it unlikely a placebo effect as frequently suspected in Western medicine.
When we consider patients treated with acupuncture, few additional considerations appear of interest. In patients with persistent AF, the antiarrhythmic effect of acupuncture was particularly evident in the first weeks after cardioversion, i.e., the period with the highest recurrence rate[38] where autonomic mechanisms may play a major pro-arrhythmic role[39]. Unfortunately, our study does not allow us to infer the possibility that, in patients with early AF recurrence but already on antiarrhythmic drugs, acupuncture might exert an additive antiarrhythmic action. This possibility, however, is suggested by the results obtained in patients with paroxysmal AF. Most of these patients were on propiophenone, flecainide or amiodarone. Puncturing of the Neiguan spot resulted in a significant reduction of the arrhythmic burden that persisted during the whole follow-period. Even taking into account the small number of patients treated with acupuncture and the fact that only symptomatic episodes were measured, one could hypothesize that acupuncture could enhance the antiarrhythmic efficacy of these drugs by a combination effect on atrial electrical properties and autonomic mechanisms.
Finally, it has to be mentioned that acupuncture was safe, without any pro-arrhythmic effect and with limited cost. All these factors should be considered when evaluating the efficacy of therapeutic intervention for an epidemic disease as AF.
These data were obtained in 2 small study populations and the recurrence rate was documented during control visits or by the patients’ perception of symptoms. In particular, when considering data obtained in patients with paroxysmal AF, it must be pointed out that the numbers were small and that patients were treated with different antiarrhythmic drugs, and no sham acupuncture was used to rule out a placebo effect. Nevertheless, the persistency of the antiarrhythmic effect of acupuncture on symptomatic AF during the 10-mo follow-up period make this possibility unlikely. It must be also stated that for economic reasons we were unable to use a trans-telephonic monitoring system or internal or external loop recorders to detect asymptomatic or brief self-terminating AF episodes. Finally, this was a single center study with an active acupuncture team led by a cardiologist with a recognized training in traditional Chinese Medicine.
Footnotes
Peer reviewer: Dr. Rui Providência, Coimbra’s Hospital Center and University, Urbanização Quinta das Lágrimas, 3040-375 Coimbra, Portugal
S- Editor Cheng JX L- Editor Cant MR E- Editor Li JY
References
- 1.Allessie MA, Boyden PA, Camm AJ, Kléber AG, Lab MJ, Legato MJ, Rosen MR, Schwartz PJ, Spooner PM, Van Wagoner DR, et al. Pathophysiology and prevention of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2001;103:769–777. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.5.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fuster V, Rydén LE, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ, Curtis AB, Ellenbogen KA, Halperin JL, Le Heuzey JY, Kay GN, Lowe JE, et al. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: full text: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2001 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation) developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association and the Heart Rhythm Society. Europace. 2006;8:651–745. doi: 10.1093/europace/eul097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY, Schotten U, Savelieva I, Ernst S, Van Gelder IC, Al-Attar N, Hindricks G, Prendergast B, et al. Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: the Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2010;31:2369–2429. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wyse DG, Waldo AL, DiMarco JP, Domanski MJ, Rosenberg Y, Schron EB, Kellen JC, Greene HL, Mickel MC, Dalquist JE, et al. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1825–1833. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lafuente-Lafuente C, Mouly S, Longás-Tejero MA, Mahé I, Bergmann JF. Antiarrhythmic drugs for maintaining sinus rhythm after cardioversion of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:719–728. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.7.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen SA, Davies W, Iesaka Y, Kalman J, Kim YH, Klein G, Natale A, Packer D, et al. Prevalence and causes of fatal outcome in catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:1798–1803. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pisters R, Nieuwlaat R, de Vos CB, Crijns HJ. Comprehensive upstream treatment for atrial fibrillation, when and how? Europace. 2009;11:397–399. doi: 10.1093/europace/eup050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Smit MD, Van Gelder IC. Upstream therapy of atrial fibrillation. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2009;7:763–778. doi: 10.1586/erc.09.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pratt CM, Reiffel JA, Ellenbogen KA, Naccarelli GV, Kowey PR. Efficacy and safety of prescription omega-3-acid ethyl esters for the prevention of recurrent symptomatic atrial fibrillation: a prospective study. Am Heart J. 2009;158:163–169.e1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2009.05.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dobrev D, Nattel S. New antiarrhythmic drugs for treatment of atrial fibrillation. Lancet. 2010;375:1212–1223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Qiu M. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion. London: Churchill Livingstone; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Flachskampf FA, Gallasch J, Gefeller O, Gan J, Mao J, Pfahlberg AB, Wortmann A, Klinghammer L, Pflederer W, Daniel WG. Randomized trial of acupuncture to lower blood pressure. Circulation. 2007;115:3121–3129. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.661140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Richter A, Herlitz J, Hjalmarson AA. Effect of acupuncture in patients with angina pectoris. Europ Heart J. 1991;12:175–178. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kim W, Jeong MH, Ahn YK. Acupuncture for chest pain. Heart. 2004;90:1062. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2003.032185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lomuscio A, Belletti S, Battezzati PM, Lombardi F. Efficacy of acupuncture in preventing atrial fibrillation recurrences after electrical cardioversion. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2011;22:241–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2010.01878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Abad-Alegria F, Pomaron C, Aznar C, Munoz C, Adelantado S: Objective assessment of the sympatholytic action of Neiguan acupoint. Am J Chin Med. 2001;29:201–210. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X0100023X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Huang ST, Chen GY, Lo HM, Lin JG, Kuo CD: Increase in the Vagal Modulation by Acupuncture at Neiguan Point in the Healthy Subjects. Am J Chin Med. 2005;33:157–164. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X0500276X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wu JH, Chen HY, Chang YJ, Wu HC, Chang WD, Chu YJ, Jiang JA. Study of autonomic nervous activity of night shift workers treated with laser acupuncture. Photomed Laser Surg. 2009;27:273–279. doi: 10.1089/pho.2007.2235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Insoo J, Kiho C, Sangkwan M. A Study on the Central Neural Pathway of the Heart, Nei-Kuan (EH-6) and Shen-Men (He-7) with Neural Tracer in Rats. Am J Chin Med. 2003;31:591–609. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X03001314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mayor DF. Die Shu- und Mu-Akupunkturpunkte und ihre segmentale Innervation. Deutsche Zeitschrift fur Akupunktur. 2008;51:26–36. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Enquin Z. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion. Shanghai: Publishing House of Shanghai College of Traditional Chinese Medicine; 1990. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liu S, Chen Z, Hou J, Wang J, Wang J, Zhang X. Magnetic disk applied on Neiguan point for prevention and treatment of cisplatin-induced nausea and vomiting. J Tradit Chin Med. 1991;11:181–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lin H. Specific therapeutic effect of Neiguan on heart disease. Int J of Clinical Acupuncture. 1998;9:303–305. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chiu YJ, Chi A, Reid IA. Cardiovascular and endocrine effects of acupuncture in hypertensive patients. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1997;19:1047–1063. doi: 10.3109/10641969709083204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lai Z, Cao Q, Chen S, Han Z. Role of amygdaloid nucleus in the correlation between the heart and the acupoint neiguan in rabbits. J Tradit Chin Med. 1991;11:128–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Syuu Y, Matsubara H, Kiyooka T, Hosogi S, Mohri S, Araki J, Ohe T, Suga H. Cardiovascular beneficial effects of electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC-6) acupoint in anesthetized open-chest dog. Jpn J Physiol. 2001;51:231–238. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.51.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kong SM, Li SX, Han YA, Zang YW, Li CX. Heart rate power spectral analysis during homeostatic action of neiguan acupoint--role played by the cardial vagus nerve. J Tradit Chin Med. 1988;8:271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee S, Lee MS, Choi JY, Lee SW, Jeong SY, Ernst E. Acupuncture and heart rate variability: a systematic review. Auton Neurosci. 2010;155:5–13. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2010.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Li Z, Wang C, Mak AF, Chow DH. Effects of acupuncture on heart rate variability in normal subjects under fatigue and non-fatigue state. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2005;94:633–640. doi: 10.1007/s00421-005-1362-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bettoni M, Zimmermann M. Autonomic tone variations before the onset of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2002;105:2753–2759. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000018443.44005.d8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lombardi F, Tarricone D, Tundo F, Colombo F, Belletti S, Fiorentini C. Autonomic nervous system and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a study based on the analysis of RR interval changes before, during and after paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2004;25:1242–1248. doi: 10.1016/j.ehj.2004.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Danik S, Neuzil P, d’Avila A, Malchano ZJ, Kralovec S, Ruskin JN, Reddy VY. Evaluation of catheter ablation of periatrial ganglionic plexi in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2008;102:578–583. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.04.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lu Z, Scherlag BJ, Lin J, Yu L, Guo JH, Niu G, Jackman WM, Lazzara R, Jiang H, Po SS. Autonomic mechanism for initiation of rapid firing from atria and pulmonary veins: evidence by ablation of ganglionated plexi. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;84:245–252. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li S, Scherlag BJ, Yu L, Sheng X, Zhang Y, Ali R, Dong Y, Ghias M, Po SS. Low-level vagosympathetic stimulation: a paradox and potential new modality for the treatment of focal atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009;2:645–651. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.109.868331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tai CT, Chiou CW, Wen ZC, Hsieh MH, Tsai CF, Lin WS, Chen CC, Lin YK, Yu WC, Ding YA, et al. Effect of phenylephrine on focal atrial fibrillation originating in the pulmonary veins and superior vena cava. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:788–793. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(00)00792-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang Y, Scherlag BJ, Lu Z, Niu GD, Yamanashi WS, Hogan C, Fields J, Ghias M, Lazzara R, Jackman WM, et al. Comparison of atrial fibrillation inducibility by electrical stimulation of either the extrinsic or the intrinsic autonomic nervous systems. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2009;24:5–10. doi: 10.1007/s10840-008-9297-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Roy D, Talajic M, Dorian P, Connolly S, Eisenberg MJ, Green M, Kus T, Lambert J, Dubuc M, Gagné P, et al. Amiodarone to prevent recurrence of atrial fibrillation. Canadian Trial of Atrial Fibrillation Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:913–920. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200003303421302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Van Gelder IC, Crijns HJ, Van Gilst WH, Verwer R, Lie KI. Prediction of uneventful cardioversion and maintenance of sinus rhythm from direct-current electrical cardioversion of chronic atrial fibrillation and flutter. Am J Cardiol. 1991;68:41–46. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(91)90707-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lombardi F, Colombo A, Basilico B, Ravaglia R, Garbin M, Vergani D, Battezzati PM, Fiorentini C. Heart rate variability and early recurrence of atrial fibrillation after electrical cardioversion. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001:37: 157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(00)01039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]