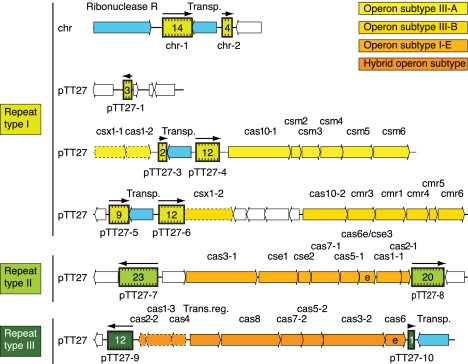
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of the genomic organization of T. thermophilus HB8 CRISPRs and CRISPR-associated (Cas) genes on the chromosome and plasmid pTT27. CRISPRs are indicated by colored boxes in different shades of green, one for each repeat-sequence type. The number of spacers for each CRISPR is given within each box. Transcriptional direction is indicated by black arrows above the boxes. Open reading frames are shown as boxes with arrowheads indicating their transcriptional direction. Genes unrelated to CRISPRs are white; CRISPR-associated genes are colored and named (on top) according to the classification and nomenclature of the proteins in the CRISPR-Cas systems (Makarova et al. 2011a,b; K. Makarova, pers. comm.). For clarity we added a serial number for paralogous genes (e.g., cas1-1, cas1-2, etc.). The four different colors correspond to four CRISPR-Cas system subtypes: light yellow indicates III-A (Mtube); yellow, III-B (RAMP); light orange, I-E (Ecoli); and orange, a hybrid of I-A (Aperm) and I-B (Tneap-Hmari). The gene Csx1-2 (dotted box) was colored according to its adjacent subtype, although it was not originally classified as part of this subtype. Two genes (cse3 and cas6) are marked by the letter “e,” indicating that these Cas proteins are orthologous to Cas proteins that are known to be involved in endonucleolytic cleavage of CRISPR transcripts. Transposons (Transp.) as well as a ribonuclease close to the CRISPRs are indicated by blue boxes with arrowheads indicating transcription direction. One transcriptional regulator associated with CRISPR-Cas systems is displayed as well (Trans.reg.).