Abstract
cDNA clones for Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein L32 have been isolated and sequenced. The deduced amino acid sequence indicates that L32 is a basic protein of 110 amino acids, has a molecular weight of 12,603 and is homologous to the rat ribosomal protein L35. Using the cDNA clone as a probe to follow the expression of this gene during Xenopus development, it has been shown that the pattern of accumulation of this mRNA follows the one previously described for other ribosomal protein mRNAs during oogenesis and embryogenesis. The analysis of the utilization of L32 mRNA during embryogenesis shows that this is controlled by the translational regulation typical of other ribosomal protein mRNAs.
Full text
PDF
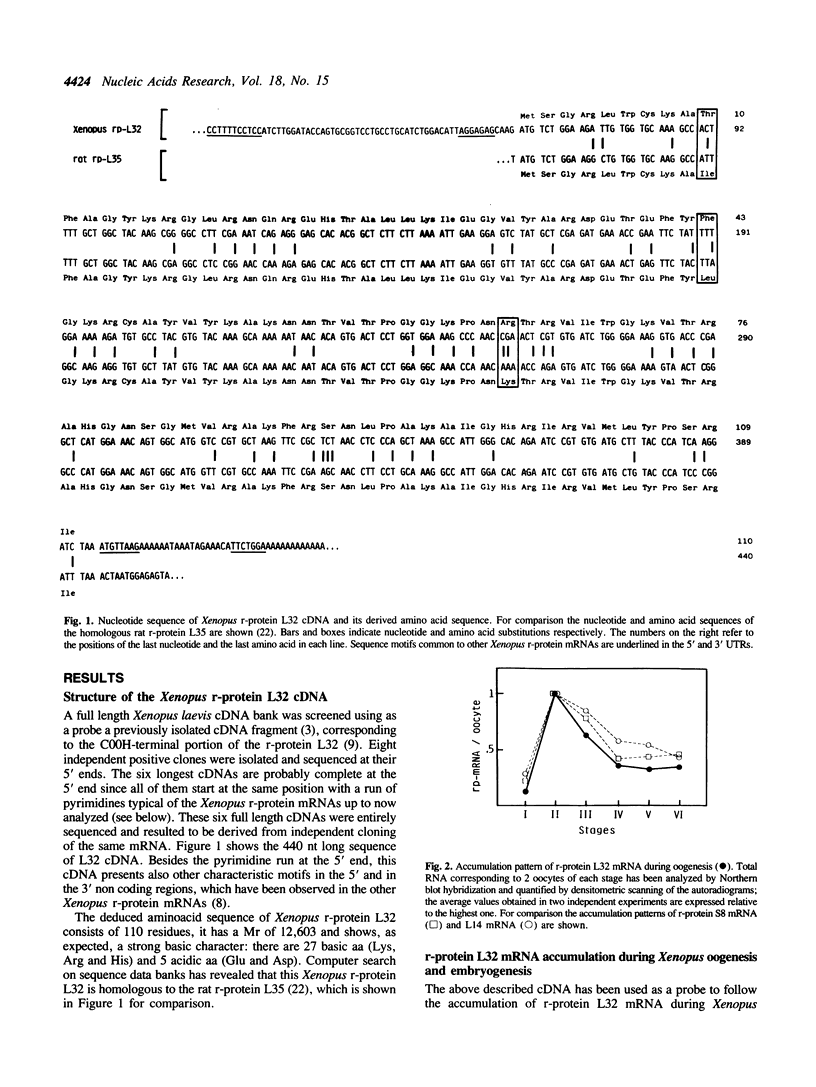
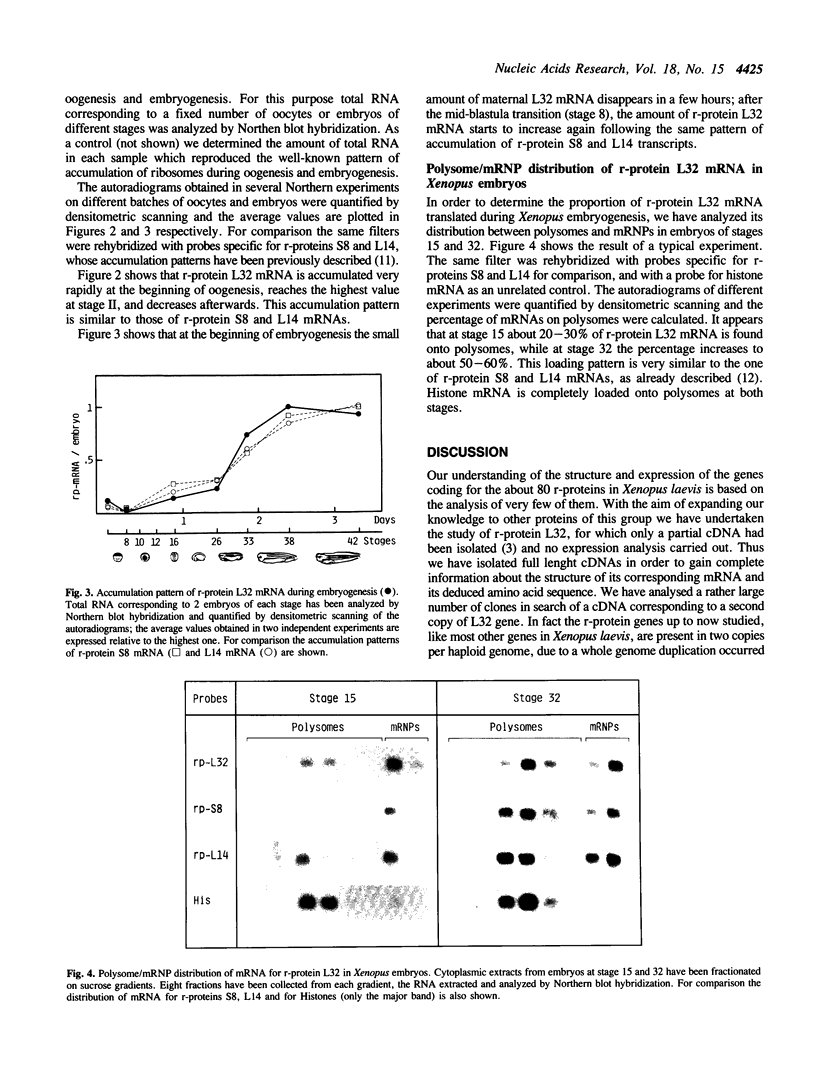

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaldi F., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Luo Z. X., Pierandrei-Amaldi P. Nucleotide sequences of cloned cDNA fragments specific for six Xenopus laevis ribosomal proteins. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amaldi F., Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Pierandrei-Amaldi P. Expression of ribosomal protein genes and regulation of ribosome biosynthesis in Xenopus development. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 May;14(5):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum E. Z., Wormington W. M. Coordinate expression of ribosomal protein genes during Xenopus development. Dev Biol. 1985 Oct;111(2):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90500-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beccari E., Mazzetti P., Mileo A., Bozzoni I., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F. Sequences coding for the ribosomal protein L14 in Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis; homologies in the 5' untranslated region are shared with other r-protein mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7633–7646. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beccari E., Mazzetti P. The nucleotide sequence of the ribosomal protein L14 gene of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1870–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Luo Z. X., Amaldi F. Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes: isolation of recombinant cDNA clones and study of the genomic organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1069–1086. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Fragapane P., Annesi F., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F., Beccari E. Expression of two Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes in injected frog oocytes. A specific splicing block interferes with the L1 RNA maturation. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):987–1005. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loreni F., Ruberti I., Bozzoni I., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F. Nucleotide sequence of the L1 ribosomal protein gene of Xenopus laevis: remarkable sequence homology among introns. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3483–3488. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariottini P., Amaldi F. The 5' untranslated region of mRNA for ribosomal protein S19 is involved in its translational regulation during Xenopus development. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):816–822. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariottini P., Bagni C., Annesi F., Amaldi F. Isolation and nucleotide sequences of cDNAs for Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein S8: similarities in the 5' and 3' untranslated regions of mRNAs for various r-proteins. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Amaldi F. Ribosomal protein production in normal and anucleolate Xenopus embryos: regulation at the posttranscriptional and translational levels. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):317–323. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Bozzoni I., Cardinali B. Expression of the gene for ribosomal protein L1 in Xenopus embryos: alteration of gene dosage by microinjection. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):23–31. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Campioni N., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Amaldi F. Expression of ribosomal-protein genes in Xenopus laevis development. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst E., Kressmann A., Birnstiel M. L. Expression of sea urchin histone genes in the oocyte of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):709–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz F., Spohr G. Isolation and characterization of sarcomeric actin genes expressed in Xenopus laevis embryos. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):349–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Wakasugi K., Kuwano Y., Ishikawa K., Ogata K. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA specific for rat ribosomal protein L35a. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):523–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M. Developmental expression and 5S rRNA-binding activity of Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein L5. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5281–5288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M. Expression of ribosomal protein genes during Xenopus development. Dev Biol (N Y 1985) 1988;5:227–240. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-6817-9_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




