Abstract
The short chain fatty acid (SCFA) butyrate, a product of fermentation of dietary fiber in the human colon, is found to exert multiple regulatory processes in colon carcinogenesis. The aim of this study was to find out whether butyrate affects the tumor-promoting genes osteopontin (OPN) and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, their respective proteins and/or their functional activity in matched normal, adenoma and tumor colon tissues obtained from 20 individuals at colon cancer surgery. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction experiments showed increased levels of OPN and COX-2 messenger RNA in tumor tissues when compared with the adjacent normal samples (P < 0.001). The addition of butyrate reduced OPN and COX-2 mRNA expression in all tissue types compared with the related medium controls (tumor: P < 0.05). In tumor samples, a downregulation of up to median 35% (COX-2) and 50% (OPN) was observed, respectively. Thereby, tumors with lower levels of OPN basal expression were more sensitive to inhibition and vice versa for COX-2 in normal tissue. At the protein and enzyme level, which were determined by using western blot and enzyme immunometric assays, the impact of the SCFA was not clearly visible anymore. The active proteins of OPN and COX-2 (determined by prostaglandin E2) were found to correlate with their respective mRNA expression only in 50–63% of analyzed donors.
For the first time, our data reveal new insights into the chemoprotective potential of butyrate by showing the suppression of OPN and COX-2 mRNA in primary human colon tissue with the strongest effects observed in tumors.
Introduction
Colorectal cancer is the third most frequent malignancy in men and the second in women worldwide (1). The tumors develop in a multistep process over years or decades and occur as sporadic colon cancer predominantly in the aging population.
Dietary fiber is believed to lower the risk of colon carcinogenesis (2,3). The indigestible plant ingredients are fermented by the colonic microflora resulting in the formation of short chain fatty acids (SCFA) such as acetate, propionate and butyrate which seem to contribute to this impact. Besides its physiological relevance as an energy source, butyrate revealed chemopreventive properties against colorectal carcinogenesis via induction of apoptosis and differentiation, inhibition of proliferation and modulation of stress and detoxification-related genes (4–6). These apparent opposite effects of butyrate on normal and malignant colon cells are described as ‘butyrate paradox’ in the literature (7).
Presently, only few data is available concerning the impact of butyrate on tumor-promoting genes and their analog proteins which are often modified during the development of cancer. Osteopontin (OPN) and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 are substantially involved in tumor growth and spreading and therefore represent promising targets in cancer therapy (8,9). OPN is a secreted glycosylated phosphoprotein located in the extracellular matrix. As an adhesion protein mediating cell attachment via interactions with integrins and CD44 variants and as a cytokine, it is acting physiologically in diverse cellular processes like immune response, bone mineralization and survival (10). In accordance with the pathological stage and patient’s survival, OPN was found in elevated levels in a variety of cancers (e.g. breast, lung, colon) (11,12) where it is implicated in tumor cell invasion and metastasis (13,14).
COX-2, the inducible and partly constitutive expressed isoform of COXs, is involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins that are particularly active in pathophysiological processes, like inflammation, pain, fever and tumor development (15). Over 70% of colorectal carcinomas and a subset of adenomas showed elevated levels of this protein (16,17). The expression of COX-2 and its principal metabolite prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) promote tumor growth by influencing characteristic attributes of cancer cells including invasion, angiogenesis and apoptosis (18).
A suppression of OPN and COX-2 messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein has been associated with a decreased metastatic spread, an inhibition of cell growth and an induction of apoptosis (9,19,20). Much of this work has employed colon cancer cell lines or animal models just as studies with butyrate. The aim of the present study was therefore to investigate the impact of a physiologically relevant dose of butyrate on gene expression and protein/enzyme levels of OPN and COX-2 in human colon tissues with different malignity degree ex vivo. The outcomes shall provide new insights whether surgical colon cancer tissue responds to butyrate in a manner similar to colon cancer cell lines and build a bridge to clinical research.
Material and methods
Patient material
Colon tumor and respective normal tissues were obtained from 20 patients with colorectal cancer who underwent surgical resection at the University Hospital of Jena. Five of them also displayed benign adenomas which were additionally resected. The study was approved by the ethical committee of the University of Jena (no. 1601-08/05) and all patients gave their informed consent. The group consisted of 8 men and 12 women with a mean age of 70.5 ± 13.2 years. None of the patients has received chemotherapy or radiation prior to surgery. After removal the tissue samples were stored in Hank’s balanced salt solution (8.0 g/l NaCl, 0.4 g/l KCl, 0.06 g/l Na2HPO4 × 2 H2O, 0.06 g/l K2HPO4, 1 g/l glucose, 0.35 g/l NaHCO3 and 4.8 g/l N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid ; pH 7.2), transported on ice to the laboratory and prepared immediately. The colon epithelium was separated from the normal colon tissue by perfusion-supported mechanical disaggregation (21), whereas adenoma and tumor tissues were cut into small pieces of approximately 0.3–0.5 cm2. Tissue strips were either frozen in liquid nitrogen alone or submerged in RNA later (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and stored at −80°C until cytosol or RNA was being extracted. Pathological examination of the colon tissues assessed tumor stage and grading according to the Union for International Cancer Control classification (Table I).
Table I.
Clinicopathological data of the patients analyzed in this study
| Patient and tumor characteristics | Number of patients |
| Mean age (years) ± SD | 70.5 ± 13.2 |
| Gender | 12 females, 8 males |
| Tumor stage | |
| I | 2 |
| II | 6 |
| III | 8 |
| IV | 3 |
| Tumor grading | |
| 1 | — |
| 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 7 |
| 4 | 1 |
One of the donors was only found with adenoma. In case of another patient, the tumor grading was not reported.
Treatment of colon tissue with butyrate
Simultaneously, strips from normal, adenoma and cancerous colon tissue were placed into six-well plates (two to three strips per well) and treated either with 0 mM (control) or 10 mM butyrate (diluted in primary cell culture medium) under sterile conditions at 37°C in a 95% humidified incubator (5% CO2). The medium consisted of minimal essential medium with Earle’s salts enriched with 20% fetal calf serum, 2 mM glutamine, 100 μg/ml gentamycin, 2.5 μg/ml fungizone, 10 ng/ml epidermal growth factor, 5 μg/ml insulin, 5 μg/ml transferrin and 5 ng/ml sodium selenite according to Rogler et al. (22). After incubation for 12 h, the tissue strips used for protein analyses were washed in Hank’s balanced salt solution and frozen in liquid nitrogen. Samples for gene expression studies were additionally submerged in RNA later.
RNA isolation and complementary DNA preparation
After homogenization of the tissue strips in RLT Plus buffer with the Polytron homogenizer 2100 (Kinematica AG, Littau/Lucerne, Switzerland), total RNA was isolated by using the RNeasy Plus Mini Kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The RNA was eluted in 25 μl RNase-free water and quantified spectrophotometrically with the NanoDrop®ND-1000 (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE). RNA integrity was checked before complementary DNA synthesis with the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA). Depending on the amount, 100–2500 ng of total RNA was reverse transcribed in a 20 μl reaction mix with Oligo(dT)12–18 primers using the SuperScript II First Strand cDNA Synthesis System (Invitrogen, Darmstadt, Germany). Subsequently, the remaining RNA was removed by RNase H (New England Biolabs, Frankfurt/Main, Germany) treatment.
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
The efficiency of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was verified for all primer pairs by previous experiments and was in the acceptable range of 95–105%. Two microliters complementary DNA (5–30 ng RNA equivalents) prepared from different starting concentrations of total RNA were used in a 25 μl PCR mix containing iQ SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad, Munich, Germany), RNase-free water and 10 pmol gene-specific primers: COX-2 forward, 5′-CGCTCAGCCATACAGCAA-3′ and reverse, 5′-GAATCCTGTCCGGGTACAATC-3′; OPN forward, 5′-TGGAAGTTCTGAGGAAAAGCAG-3′ and reverse, 5′-GGCTTTCGTTGGACTTACTTG-3′; β-actin forward, 5′-AGAGCCTCGCCTTTGCCGAT-3′ and reverse, 5′-CCCACGATGGAGGGGAAGAC-3′; β-glucuronidase (GUS) forward, 5′-TGCAGGTGATGGAAGAAGTG-3′ and reverse, 5′-TTGCTCACAAAGGTCACAGG-3′.
Quantitative PCR experiments were performed using the iCycler iQ Real time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad). After an initial denaturation step of 2 min at 95°C, the amplification was carried out in 40 cycles involving denaturation (at 94°C for 30 s), annealing (at 60°C for 30 s) and extension (at 72°C for 30 s). The specificity of the PCR products was confirmed by a subsequent melting curve analysis. All samples were analyzed in duplicate.
The expression of the targets was normalized to the geometric average of two reference genes (β-actin, GUS) based on the equation of Pfaffl et al. (23) involving efficiency (E) and quantification cycle (Cq). Since the reaction efficiencies of all primer pairs were close to 100%, E was set to 2.
Western blot analysis
For detection of protein, equally treated colon tissue material of the same donors used for mRNA analysis was examined. Because of difficulties in OPN detection in previous experiments, only COX-2 protein expression was measured. Our investigations indicate that high protein amounts (≥40 μg) were necessary to verify COX-2 protein. Since cytosolic protein contents of the samples used in this study were often low (range 300–4900 μg/ml), the detection of COX-2 was restricted to a few donors.
Butyrate-treated (10 mM) and non-treated paired normal, adenoma and tumor tissues were homogenized with the Polytron homogenizer 2100 in cold lysis buffer (50 mM KH2PO4, 1 mM Na2EDTA, 0.1% Triton X-100 and 1 mM Pefabloc; pH 7) and centrifuged (16 000g, 10 min, 4°C). Total protein contents were determined according to Bradford (24). For western blot analysis, 30–50 μg of total protein was mixed with 5× concentrated loading buffer (250 mM Tris–HCl pH 6.8; 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate; 50% glycerol; 0.1% bromphenol blue and 0.5 M dithiothreitol), separated by discontinuous sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (stacking gel: 4%; separating gel: 12%) and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Whatman, Florham Park, NJ). The membrane was blocked with 3% nonfat dried milk powder (β-actin: 5%; AppliChem, Darmstadt, Germany) and incubated with the following primary and secondary antibodies: rabbit anti-COX-2 (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), mouse anti-β-actin (Sigma-Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany), rabbit anti-mouse IgG-HRP (Dako, Hamburg, Germany) and goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (Dako). By using enhanced chemiluminescence (Amersham Biosciences, Buckinghamshire, UK), proteins were finally visualized and band intensities were quantified by densitometric measurement using Quantity One software, version 4.1 (Bio-Rad).
Determination of OPN and PGE2 levels in cell culture supernatants
After 12 h butyrate treatment of colon epithelial tissues, cell culture media of all samples were collected and centrifuged (3900g, 10 min, 4°C) before being stored at −80°C. OPN and PGE2 contents in the supernatants were determined by using commercially available enzyme immunoassay kits according to the manufacturer’s manuals (OPN: Assay Designs, Ann Arbor, MI; PGE2: Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI). Levels expressed as nanograms per microliter were normalized to the total protein content of the cultured tissue.
Statistical evaluation
Statistical analysis was performed by the nonparametric Wilcoxon matched pairs test or the Kruskal–Wallis test using GraphPad Prism Software 5 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA), comparing two and multiple groups, respectively. The relation between two parameters was evaluated by the Spearman’s rank correlation test. Gender differences were identified by the Mann–Whitney test. All results reached significance when P < 0.05.
Results
Basal COX-2 and OPN mRNA expression
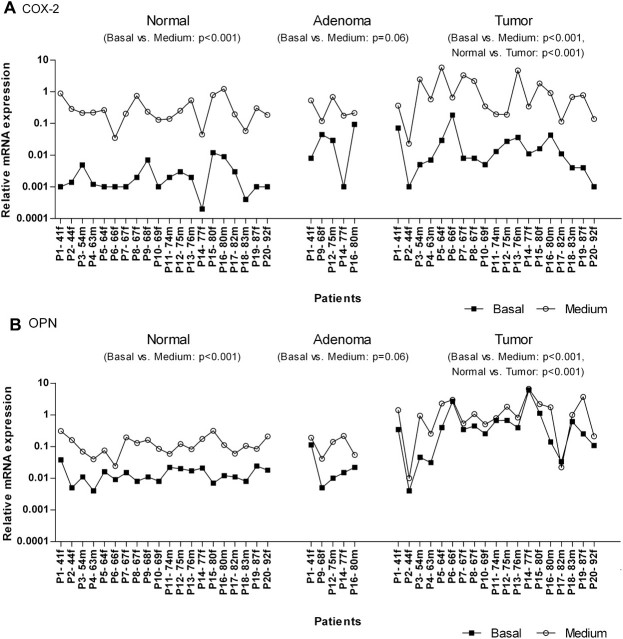
In this study, colon tissue material of 20 patients in total was used to examine basal mRNA expression levels of known tumor markers. The analysis revealed that COX-2 mRNA was elevated in tumor as compared with normal colon tissue (P < 0.001, Figure 1A). Expression changes ranged from 0.72- to 278-fold (median of 6-fold). The OPN mRNA level was also increased in nearly all malignant tissues (except one, P2) when compared with the related normal counterparts (P < 0.001, Figure 1B). Thereby, OPN transcripts were present in 3- to 299-fold higher amounts by showing a median increase of 23-fold. Among the analyzed patients, some individuals were marked by extremely high OPN (P6, P14, P15) and/or COX-2 mRNA levels (P6) in tumor tissue (fold changes >100) which indicates a patient-specific expression. However, due to the limited number of patients possessing premalignant lesions, the expression of both targets was not significantly (COX-2: P = 0.43, OPN: P = 0.58) changed in adenoma tissues when compared with the corresponding normal samples (Figure 1A and B).
Fig. 1.
Relative mRNA expression of COX-2 (A) and OPN (B) and the influence of cell culturing in paired normal, adenoma and tumor colon tissue of 20 individual patients. mRNA levels were quantified before (0 h, closed squares) and after the treatment with medium (12 h, open circles) in a humidified incubator (37°C, 5% CO2) by using quantitative real-time PCR. Data are sorted by age of the patients (P), the small letter discriminates further between male (m) and female (f). For better visualization, basal levels and medium effects were each connected by a line.
Considering clinicopathological parameters, we demonstrated that gene expression of COX-2 and OPN were not correlated with tumor stage and grading (data not shown). But in contrast to COX-2, OPN was observed to be increased by median 41-fold during the progression of benign adenomas to malign tumors (P < 0.05). The influence of age and gender was evaluated in normal as well as in tumor tissue (data not shown). Males tended to express more COX-2 in normal colon tissue compared with females (P = 0.12). No difference between both groups was noted for OPN. Furthermore, neither the transcript amount of COX-2 nor those of OPN was age-related in any of the tissue types.
Effect of incubation on COX-2 and OPN mRNA expression
The primary cell culture medium served as solvent for the SCFA and therefore was used as a negative control. The incubation (12 h) with medium alone caused a multi-fold induction of both targets in normal as well as in the cancerous colon tissues. Thereby, COX-2 expression was most affected by showing a median increase of 150-fold in normal (P < 0.001) and 81-fold in tumor colon tissue (P < 0.001) compared with the respective untreated counterparts (basal; Figure 1A). An induction of COX-2 could also be observed in the premalignant adenoma tissue, which nevertheless appeared less susceptible than the other ones (median fold change 23, P = 0.06; Figure 1A).
In contrast, OPN gene expression was not altered so dramatically (Figure 1B). The incubation of normal and adenoma tissue strips in medium resulted in a comparable increase of OPN mRNA (normal: median fold change 8.65, P < 0.001; adenoma: median fold change 7.65, P = 0.06), whereas this influence was less apparent in tumor tissue (median fold change 2.08, P < 0.001).
Effect of butyrate on COX-2 and OPN mRNA expression
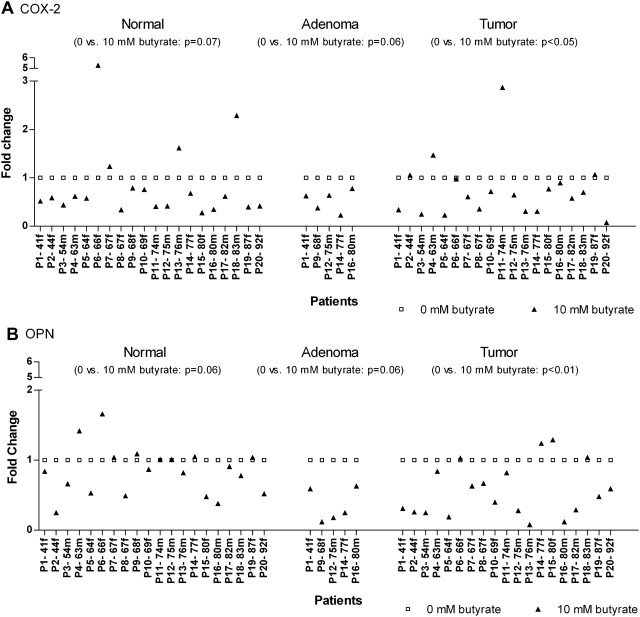
To ascertain the effect of butyrate, the expression of butyrate-treated tissues had to be compared with the expression of the respective medium controls. The data indicate a modulation of mRNA expression of COX-2 and OPN in tissues of different stage of transformation in response to butyrate (Figure 2).
Fig. 2.
Effect of butyrate (filled triangles) on COX-2 (A) and OPN (B) mRNA expression in matched normal, adenoma and tumor colon tissue of 20 individual donors. Relative OPN and COX-2 mRNA levels were determined after butyrate treatment (10 mM, 12 h) by quantitative real-time PCR and compared with the respective medium controls (open squares) which were set to 1. Results are listed by age of the patients (P), the small letter discriminates further between male (m) and female (f).
COX-2 mRNA expression was tendentially reduced by butyrate in normal colon tissues when compared with the related non-treated controls (medium, P = 0.07). The majority of patients (16 of 20) exhibited a decreased transcript level by median 41% (fold change 0.59). In adenoma and tumor tissues, similar results could be observed whereby the reduction of COX-2 mRNA expression in the malignant group achieved significance (median fold change 0.65, P < 0.05). Here, 14 of 20 donors showed decreased transcript levels after butyrate treatment, whereas all adenoma samples were found with reduced COX-2 mRNA levels (median fold change 0.63, P = 0.06). When the effects of butyrate in normal and tumor tissue were compared, the applied Wilcoxon matched pairs test confirmed that no differential regulation of COX-2 is present (Figure 2A).
The influence of butyrate on OPN gene expression was significantly depending on the tissue type. Although butyrate only insignificantly suppressed the medium-induced OPN mRNA increase by median 14% in normal colon mucosa (fold change 0.86), the amount of transcripts was downregulated by almost half in the malignant tumors (median fold change 0.48). Here, the expression of nearly all patients (15 of 20) exhibited a fold change <1 after butyrate treatment indicating a decreased gene expression. The rest appeared to be insensitive to the SCFA. In the pre-stage of tumor, adenoma, OPN gene expression was observed to be even more affected by butyrate as in the fully blown carcinomas. All the benign tissues of the five donors investigated showed a butyrate-suppressed expression by median 75% (fold change 0.25, P = 0.06) (Figure 2B).
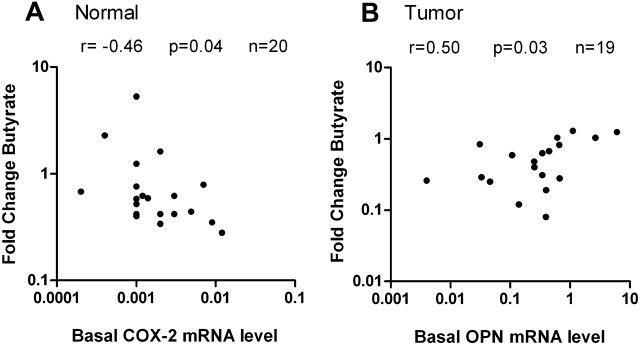
Considering the clinicopathological characteristics of patients, no correlation between gender, age, tumor stage or grading and the individual effect of butyrate was found (data not shown). Further correlation analyses revealed that both genes appeared to be altered depending on their basal expression and the tissue type. The initial transcript amount of COX-2 in normal colon epithelium (no effect in adenoma and tumor) correlated negative with the respective fold change after butyrate treatment (P < 0.05, r = −0.46, Figure 3A). This means that normal epithelia with higher levels of COX-2 expression were more sensitive to inhibition by butyrate as those with lower expression. In transformed tissue, an inverse correlation was found for OPN. Here, levels of OPN expression were more downregulated by the SCFA when the initial expression was low than at originally high expression (P < 0.05, r = 0.50, Figure 3B). Similar findings were also made in adenoma tissue (P = 0.08, r = 0.90, data not shown).
Fig. 3.
Influence of the initial transcript level on the effect of butyrate in colon tissue. Both parameters, each determined by quantitative real-time PCR in paired normal, adenoma and tumor tissue of 20 individual colon cancer patients (closed circles), were plotted against each other and significant outcomes of the Spearman correlation are presented. (A) In normal tissue, COX-2 was more strongly downregulated by butyrate at original high expression. (B) In contrast to COX-2, butyrate suppressed OPN gene expression in tumor more effectively when originally less mRNA was present.
Effect of butyrate on COX-2 protein expression
Since basal expression levels of COX-2 protein were inconsistent in normal and tumor tissues and not meaningful when compared with the gene expression results (data not shown), we have focused on the analysis of COX-2 levels after in vitro culturing. Generally, only moderate changes of COX-2 protein expression were observed in response to butyrate. Data of six patients showed median fold changes of 1.30 in normal tissue and 0.87 in cancerous tissue. A comparison of the gene and protein expression outcomes of these six donors revealed no correlation (data not shown). The western blot analysis showed either less, no or adverse effects at COX-2 protein level in normal as well as in tumor colon tissue. Nevertheless, we suppose a link between the response to butyrate and age of the patients. Combining the data of normal and tumor tissue, the protein fold change (effect of butyrate compared with related medium control) was observed to be above the mRNA fold change after butyrate treatment with increasing age of donors indicating a posttranscriptional regulation of COX-2 mRNA (r = 0.47, P = 0.15).
Effect of butyrate on secreted PGE2 and OPN levels
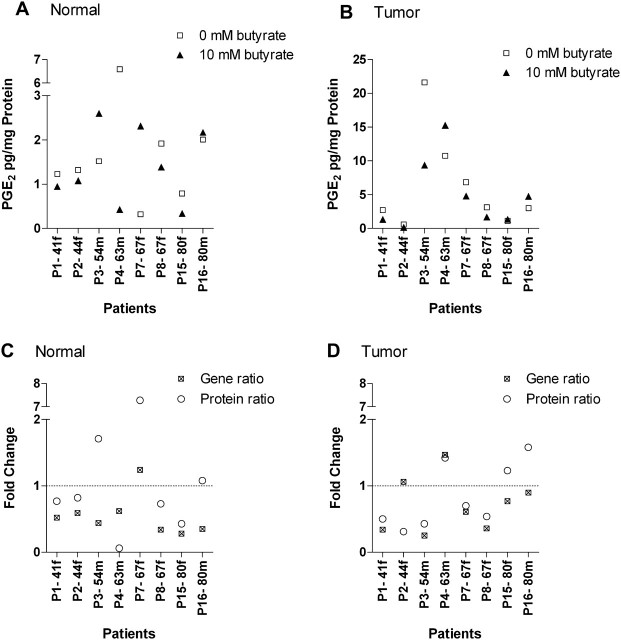
Because of problems in respect of the detection of COX-2 protein by western blot due to insufficient total protein amounts, the functional consequence of a possible downregulation by butyrate was examined by measuring the amount of PGE2, the main mediator of COX-2, using enzyme immunoassay. The assay was performed with patient material (n = 8) which mainly showed a decreased COX-2 mRNA expression after butyrate incubation.
PGE2 was well detectable in the cell culture supernatants (300–4000 pg/ml) derived from normal colon tissues treated with medium. After normalization to the total tissue protein content, similar high levels were observed in the media with exception of one donor (P4) showing a remarkably higher PGE2 concentration than the others (Figure 4A). Exposure of normal tissue to butyrate (10 mM) had only a marginal influence on PGE2 contents (median fold change: 0.80; Figure 4A). Solely two donors with strong modified PGE2 levels (fold changes 0.06 and 7.28) were identified after treatment with the SCFA.
Fig. 4.
Effect of butyrate on PGE2 levels derived from normal (A) and tumor colon tissue (B) of individual patients (n = 8). PGE2 concentrations were determined in cell culture supernatants of butyrate-treated (10 mM, 12 h) and non-treated tissues (0 mM, 12 h) by enzyme immunoassay. A comparison of PGE2 protein and the respective COX-2 mRNA expression after butyrate treatment is illustrated in (C) (normal) and (D) (tumor). Both parameters, expressed as ratios in relation to the corresponding controls (fold change), were not correlating according to the performed Spearman test. In all graphs, data are plotted according to age of the patients (P) in ascending order, the small letter discriminates further between male (m) and female (f).
The respective tumor samples released median 1.63-fold more PGE2 into the medium (Figure 4A and B) as the normal counterparts (range of raw values: 3000–10 000 pg/ml). The influence of the SCFA was controversial: half of the patients exhibited a reduced tumor-derived PGE2 level, whereas the rest showed slightly increased levels (median fold change 0.62; Figure 4B). In adenoma samples, no meaningful results were obtained (data not shown).
A comparison of PGE2 levels and the respective COX-2 mRNA expression revealed no significant correlation in both tissues (Figure 4C and D). In general, the COX-2 transcript amount was more strongly affected by butyrate than the PGE2 protein level in most of the analyzed patients. However, in normal tissue, four of eight donors showed a tendential relation between COX-2 gene and PGE2 protein expression data. A comparable correlation was also found in the tumor tissue (63%).
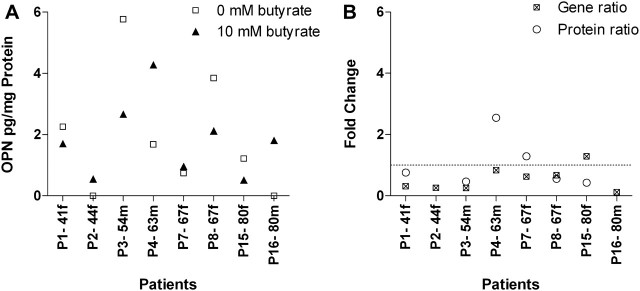
In contrast, OPN protein levels were much more difficult to detect since the kit used was not as sensitive as the PGE2 enzyme immunoassay. OPN derived from colon tumor samples ranged from 700 to almost 3000 pg/ml. In the cell culture supernatants of normal tissues, the glycosylated phosphoprotein was entirely below the detection limit. After OPN levels had been normalized to the total protein content of the tissue, no general expression pattern was obvious after the treatment with butyrate (Figure 5A). Half of the patients showed a reduced OPN abundance, whereas the rest exhibited increased or unaltered levels. A correlation analysis according to Spearman revealed no relation between OPN mRNA and protein. Only four of eight patients showed an approximate conformity with the respective gene expression (Figure 5B). In contrast to COX-2, a divergent relation regarding the butyrate effect and age of donors is assumed. Younger patients showed stronger decreased mRNA levels in relation to their protein expression in tumor tissue after butyrate treatment. This effect is probably diminished or even inverted with ongoing age of patients indicating a different posttranscriptional mechanism as those regulating COX-2 mRNA expression (r = −0.67, P = 0.18).
Fig. 5.
Effect of butyrate on tumor-derived OPN levels (A) in individual patients (n = 8). OPN concentrations were determined in cell culture media of butyrate-treated (10 mM, 12 h) and non-treated (0 mM, 12 h) tissues by enzyme immunoassay. In cell culture supernatants of adjacent normal tissues, OPN was below the detection limit. Additionally, no tumor-derived OPN was found in cell culture supernatants of patient 2 and 16. A comparison (B) of OPN protein and the respective mRNA revealed no relation according to the performed Spearman test. Data are arranged by age of the patients (P) in ascending order, the small letter indicates further males (m) and females (f).
Discussion
Basal expression levels
The overexpression of OPN and COX-2 mRNA observed in colon cancer is in line with previous results (11,25), but a marked increase of both genes and/or their respective proteins during progression of malignant transformation as reported by Agrawal et al. (26) and Soumaoro et al. (17) who concentrated only on basal expression levels was not found. The relative small number of donors used in this study and the unequal distribution of tumor stages can probably be attributed to the missing correlation between expression of OPN or COX-2 mRNA and tumor stages.
Besides clinical parameters, promoter polymorphisms (27), taking of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g. aspirin) (28) or specific eating habits (29) may account for the interindividual differences of COX-2 expression in normal as well as in transformed tissue. A reported promoter polymorphism (30) and mutated ras (31) or p53 (32) proteins might be explain the different expression levels of OPN.
Influence of culturing on expression levels
After resection of colon tissue, an acute stress situation is occurring up to the end of the experiment. OPN and COX-2 mRNA were dramatically increased during culturing of the epithelial tissue strips in medium, with highest expression alterations in normal tissues. In the literature, OPN expression is reported to be frequently upregulated in response to various stressors (33). Thereby, the protein acts as a survival factor protecting cells from undergoing apoptosis via distinct pathways (34). Single components of the cell culture medium may enhance COX-2 and OPN expression in addition. Fetal calf serum is most probably the major inducing supplement (35,36) complemented by others (37–39). In consideration of the exogenous circumstances and medium composition, we suppose a synergistic effect leading to the increase of OPN and COX-2 mRNA. Therefore, assessment of the butyrate effects requires the comparison with a medium control.
Influence of butyrate on expression levels
Adding a physiological relevant dose of butyrate (10 mM) (40) inhibited the medium-induced OPN mRNA expression in tumor colon tissue dependent on the initial transcript amount. A similar suppression had been observed in adenoma and normal tissue with varying sensitivity to butyrate. However, these modifications did not correlate with the respective protein expression of OPN (r = −0.03). A previous study which indeed detected opposite effects of butyrate on OPN had been shown a similar variation between OPN gene (20-fold increase) and protein expression (3-fold increase) in MCE301 mouse colonic epithelial cells after 48 h butyrate (2 mM) treatment (41). Based on these results and our own, we hypothesize a time lag between transcription and translation or translation and posttranslational modifications, respectively. To definitely confirm or exclude this, kinetic studies of OPN at all expression levels have to be performed, prospectively. OPN is activated at the transcriptional level by several signaling pathways and transcription factors that are associated with cancer progression (14). Furthermore, the protein is extensively regulated at the posttranslational level by phosphorylation and O-glycosylation (42). These modifications are cell type specific and crucial for the biological activity of OPN (43).
Besides regulatory mechanisms, it also should be considered that different pieces of the same tissue were used for the various analyses, as observed in other studies. Due to the heterogeneity of tumors, it might be that different areas show variable effects to butyrate. This fact is especially interesting in the case of OPN since the protein which is equally produced by tumor cells and immune cells performs apparently divergent functions depending on the cell type (44).
A further aspect that should be considered when interpreting the results is the cleavage of OPN protein by thrombin under specific physiological circumstances in vivo (e.g. tissue injury or inflammation). Since we have to assume that a certain part of OPN has been cleaved without false sample handling, this part would not be detected from our and most other offered kits that measure only uncleaved OPN (45). Cleavage of full-length OPN plays apparently an important role in the regulation of OPN function (46) and hence should not be left unconsidered.
The underlying mechanism by which butyrate is modifying OPN gene expression is still obscure. But, a recently published study by Sharma et al. (47) provided new insights into the potential features of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors regarding the experimentally induced OPN transcription which is associated with HDAC1. Since butyrate as a known HDAC inhibitor has been reported to inhibit HDAC1 activity in HeLa cancer cells, we assume a downregulation of OPN gene expression by its HDAC inhibitory activity. Nevertheless, the precise mechanism of action has to be elucidated in further experiments.
Moreover, in agreement with other in vitro studies (48), we observed a suppression of COX-2 (mRNA) expression through butyrate with significant outcome in colon tumor tissue. In normal colon mucosa, an inhibitory effect of butyrate was found with rising number of COX-2 transcripts that indirectly confirms the anti-inflammatory potential of the SCFA. The effects of butyrate at the expression levels of COX-2 as well as OPN mRNA in normal colon epithelium were similar to those in tumor tissue which is probably attributable to the altered metabolic phenotype of colon mucosa, seeming histologically normal (49). It should be kept in mind that this phenotype does not correspond to that of healthy volunteers anymore when working with these tissue specimens.
Some discordance appeared when relating the expression of mRNA to COX-2 protein synthesis and PGE2 production. Only 4 of 12 normal and tumor tissues in total showed relative consistent mRNA and protein amounts. In contrast to our study, others have observed simultaneous changes after previous cytokine stimulation (48) of colon cancer cell lines, affecting all expression levels. Since we measured all parameters solely after 12 h, we cannot definitely rule out the possibility that there was insufficient time for the reduced mRNA levels to translate into reduced levels of protein and enzyme expression, respectively. To exclude or prove a time lag between transcription and translation, protein expression should also be investigated at a subsequent date, prospectively. This will be possible by further improving our primary cell culture where to date the maximum duration for culturing is 12 h. Additionally, the presence of serum in the cell culture medium might interfere with the regulation of COX-2 (50) and possibly accounts for the ambiguity. Therefore, caution should be taken when interpreting these results.
Alternatively, it has to be considered that COX-2 can be regulated at several levels, including transcription, mRNA stability and mRNA translation. Butyrate has been reported to inhibit the transcription elongation step but not transcription initiation or mRNA stability via the 3′-untranslated region (51). In colon cells, transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of COX-2 gene expression is hypothesized as a possible decisive checkpoint, if deregulated leading to the constitutive overexpression of the protein as detected in cancer cells (52). Besides a direct action, the complex regulation of COX-2 offers also the possibility to target alternative pathways/mechanisms, which may finally modulate COX-2 functions. Butyrate has further been shown, for example, to modulate inflammatory mediators, such as nuclear factor-kappaB or tumor necrosis factor-α (53) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (54), which are involved in the transcriptional activation of COX-2 and trigger its expression in the early phases of carcinogenesis. Based on these facts and our results, we conclude that COX-2 might be prior targeted by butyrate in inflammatory processes and in the pre-stages of cancer that are associated with loss of transcriptional control of COX-2. With progression of tumor development, the effectiveness of butyrate to inhibit COX-2 expression seemingly decreases due to a predominantly posttranscriptional regulation of the gene (increase of mRNA stability) in the later stages of cancer (52). Even if the impact of the SCFA on COX-2 might be limited and thus its use to specific lesions, we do not generally doubt the effectiveness of butyrate as an anticancer/anti-inflammatory agent since a variety of other proteins/pathways which are dysregulated in colon cancer, rank among butyrate’s targets.
Besides COX-2, the production of PGE2 is further regulated by the complex interaction of phospholipase A2, microsomal prostaglandin E synthase and 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase. All downstream enzymes in the COX pathway were found either up- or downregulated in colorectal cancer and represent additional targets for decreasing the level of PGE2 (55–57). The activities of these enzymes have been observed to be functionally coupled and inducible by inflammatory cytokines (58,59). In agreement with Pugh and Thomas (60), who demonstrated increased levels of PGE2 in colonic polyps and adenocarcinomas, we detected a higher PGE2 release by tumors in the media when comparing with normal mucosa after in vitro culturing. Supplementation of the medium with butyrate was followed only by a minor insignificant decrease of PGE2 levels in normal as well as in transformed tissues. Similar observations were also made by other groups.
To explain the lack of correlation between COX-2 mRNA levels and PGE2 synthesis, biological factors (heterogeneity of the tumor, complex regulation of PGE2) and the experimental design of the study have to be considered. A study of Sherratt et al. (61) indicated that no generalized co-regulation of COX-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase is existing despite the functional coupling of both genes. Depending on the chemopreventive agent, COX-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase can be differentially regulated resulting in opposed effects at the level of COX-2 mRNA expression and PGE2 production. In contrast, a positive correlation between the protein expression levels of COX-2 and phospholipase A2 was found in colon carcinomas (56), supposing a co-regulation. The missing stimulation of colon tissues by arachidonic acid (AA) provides an additional possibility that might explain the missing correlation between the abundance of COX-2 mRNA and PGE2. To ensure the availability of free AA, exogenous AA is added in many experimental approaches. The experimental design what we have chosen did not allow the supply of AA since the tissue material was limited and therefore also used for analysis of further targets. AA is essential for the production of PGE2 and can induce phospholipase A2 as well as COX-2 that is accompanied by an increased level of PGE2 (62). Alternatively, serum has also been reported to have a stimulative effect on PGE2 production (58). Even if this stimulus is probably too low to release sufficient amounts of AA, it is more likely that the minor impact of butyrate is due to the marginal effects observed at the protein expression level of COX-2 since the inflammatory enzyme catalyzes the rate-limiting step in prostaglandin biosynthesis.
In summary, for the first time, the present study shows the butyrate-initiated decrease of OPN and COX-2 mRNA in human colon tissues with different degree of transformation derived from individual donors. In this regard, only a few cell line studies exist so far, postulating occasionally contrary effects of butyrate. However, at the functional level, only minor insignificant reductions of OPN and PGE2 levels appeared in this study. Based on these results, the use of butyrate as a single anticancer drug seems to be limited and further investigations are needed to define its impact on the synthesis of OPN and PGE2 which are crucial for the development of colon cancer.
Funding
German Research Foundation (PO 284/8-2).
Acknowledgments
We thank Kerstin Kalmring-Raspe, Dr Wiebke Schlörmann, Birgit Reumann and Rosalie Ridzewski for technical assistance and their helpful encouragement. Additionally, we express our gratitude to Christine Drake who edited the language of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement: None declared.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- AA
arachidonic acid
- COX-2
cyclooxygenase-2
- HDAC
histone deacetylase
- mRNA
messenger RNA
- OPN
osteopontin
- PCR
polymerase chain reaction
- PGE2
prostaglandin E2
- SCFA
short chain fatty acid
References
- 1.Ferlay J, et al. Globocan 2008, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 10. Lyon, France.: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2010. http://globocan.iarc.fr. (08 February 2011, date last accessed) [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bingham SA, et al. Dietary fibre in food and protection against colorectal cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC): an observational study. Lancet. 2003;361:1496–1501. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(03)13174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.World Cancer Research Fund and American Institute for Cancer Research. Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity and the Prevention of Cancer: A Global Perspective. Washington, DC: American Institute for Cancer Research; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Beyer-Sehlmeyer G, et al. Butyrate is only one of several growth inhibitors produced during gut flora-mediated fermentation of dietary fibre sources. Br. J. Nutr. 2003;90:1057–1070. doi: 10.1079/bjn20031003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pool-Zobel BL, et al. Butyrate may enhance toxicological defence in primary, adenoma and tumor human colon cells by favourably modulating expression of glutathione S-transferases genes, an approach in nutrigenomics. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:1064–1076. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Scharlau D, et al. Mechanisms of primary cancer prevention by butyrate and other products formed during gut flora-mediated fermentation of dietary fibre. Mutat. Res. 2009;682:39–53. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2009.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gibson PR, et al. Colonic epithelial cell activation and the paradoxical effects of butyrate. Carcinogenesis. 1999;20:539–544. doi: 10.1093/carcin/20.4.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Oshima M, et al. Suppression of intestinal polyposis in Apc delta716 knockout mice by inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) Cell. 1996;87:803–809. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81988-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wai PY, et al. Osteopontin silencing by small interfering RNA suppresses in vitro and in vivo CT26 murine colon adenocarcinoma metastasis. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:741–751. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mazzali M, et al. Osteopontin–a molecule for all seasons. QJM. 2002;95:3–13. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/95.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fedarko NS, et al. Elevated serum bone sialoprotein and osteopontin in colon, breast, prostate, and lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001;7:4060–4066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rohde F, et al. Expression of osteopontin, a target gene of de-regulated Wnt signaling, predicts survival in colon cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2007;121:1717–1723. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.McAllister SS, et al. Systemic endocrine instigation of indolent tumor growth requires osteopontin. Cell. 2008;133:994–1005. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wai PY, et al. Osteopontin: regulation in tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008;27:103–118. doi: 10.1007/s10555-007-9104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Funk CD. Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: advances in eicosanoid biology. Science. 2001;294:1871–1875. doi: 10.1126/science.294.5548.1871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.McLean MH, et al. COX-2 expression in sporadic colorectal adenomatous polyps is linked to adenoma characteristics. Histopathology. 2008;52:806–815. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2008.03038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Soumaoro LT, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression: a significant prognostic indicator for patients with colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004;10:8465–8471. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Greenhough A, et al. The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:377–386. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lev-Ari S, et al. Celecoxib and curcumin synergistically inhibit the growth of colorectal cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005;11:6738–6744. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhao J, et al. Down-regulation of osteopontin suppresses growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via induction of apoptosis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:956–968. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.05.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schaeferhenrich A, et al. Putative colon cancer risk factors damage global DNA and TP53 in primary human colon cells isolated from surgical samples. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003;41:655–664. doi: 10.1016/s0278-6915(02)00328-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rogler G, et al. Establishment of long-term primary cultures of human small and large intestinal epithelial cells. Lab. Invest. 1998;78:889–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pfaffl MW. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:e45. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.9.e45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kargman SL, et al. Expression of prostaglandin G/H synthase-1 and -2 protein in human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1995;55:2556–2559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Agrawal D, et al. Osteopontin identified as lead marker of colon cancer progression, using pooled sample expression profiling. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:513–521. doi: 10.1093/jnci/94.7.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Papafili A, et al. Common promoter variant in cyclooxygenase-2 represses gene expression: evidence of role in acute-phase inflammatory response. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002;22:1631–1636. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.0000030340.80207.c5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhang ZH, et al. Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 with sodium butyrate and NSAIDs on colorectal adenoma/carcinoma cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004;10:2954–2957. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.2954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pajari AM, et al. Role of red meat and arachidonic acid in protein kinase C activation in rat colonic mucosa. Nutr. Cancer. 1998;32:86–94. doi: 10.1080/01635589809514724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schultz J, et al. The functional -443T/C osteopontin promoter polymorphism influences osteopontin gene expression in melanoma cells via binding of c-Myb transcription factor. Mol. Carcinog. 2009;48:14–23. doi: 10.1002/mc.20452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chambers AF, et al. Induction of expression of osteopontin (OPN; secreted phosphoprotein) in metastatic, ras-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. Anticancer Res. 1992;12:43–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Morimoto I, et al. Identification of the osteopontin gene as a direct target of TP53. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002;33:270–278. doi: 10.1002/gcc.10020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang KX, et al. Osteopontin: role in immune regulation and stress responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008;19:333–345. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2008.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Courter D, et al. The RGD domain of human osteopontin promotes tumor growth and metastasis through activation of survival pathways. PLoS One. 2010;5:e9633. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lee SH, et al. Selective expression of mitogen-inducible cyclooxygenase in macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:25934–25938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nagasaki T, et al. Osteopontin gene expression and protein synthesis in cultured rat mesangial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997;233:81–85. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.6399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mann JR, et al. Repression of prostaglandin dehydrogenase by epidermal growth factor and snail increases prostaglandin E2 and promotes cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6649–6656. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ozaki N, et al. Identification of genes involved in gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats–a toxicogenomic investigation. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010;62:555–566. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2009.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Takemoto M, et al. Enhanced expression of osteopontin by high glucose in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999;258:722–726. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.0701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hamer HM, et al. Review article: the role of butyrate on colonic function. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008;27:104–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tabuchi Y, et al. Identification of genes responsive to sodium butyrate in colonic epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002;293:1287–1294. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00365-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Christensen B, et al. Post-translationally modified residues of native human osteopontin are located in clusters: identification of 36 phosphorylation and five O-glycosylation sites and their biological implications. Biochem. J. 2005;390:285–292. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Christensen B, et al. Cell type-specific post-translational modifications of mouse osteopontin are associated with different adhesive properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:19463–19472. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703055200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Crawford HC, et al. Distinct roles of osteopontin in host defense activity and tumor survival during squamous cell carcinoma progression in vivo. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5206–5215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Anborgh PH, et al. New dual monoclonal ELISA for measuring plasma osteopontin as a biomarker associated with survival in prostate cancer: clinical validation and comparison of multiple ELISAs. Clin. Chem. 2009;55:895–903. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2008.117465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Senger DR, et al. Adhesive properties of osteopontin: regulation by a naturally occurring thrombin-cleavage in close proximity to the GRGDS cell-binding domain. Mol. Biol. Cell. 1994;5:565–574. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.5.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sharma P, et al. Transcriptional regulation of human osteopontin promoter by histone deacetylase inhibitor, trichostatin A in cervical cancer cells. Mol. Cancer. 2010;9:178. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tong X, et al. Butyrate suppresses Cox-2 activation in colon cancer cells through HDAC inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004;317:463–471. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.03.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Chen LC, et al. Alteration of gene expression in normal-appearing colon mucosa of APC(min) mice and human cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3694–3700. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.DeWitt DL, et al. Serum and glucocorticoid regulation of gene transcription and expression of the prostaglandin H synthase-1 and prostaglandin H synthase-2 isozymes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1993;306:94–102. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tong X, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 regulation in colon cancer cells: modulation of RNA polymerase II elongation by histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:15503–15509. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411978200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dixon DA. Regulation of COX-2 expression in human cancers. Prog. Exp. Tumor Res. 2003;37:52–71. doi: 10.1159/000071363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Usami M, et al. Butyrate and trichostatin A attenuate nuclear factor kappaB activation and tumor necrosis factor alpha secretion and increase prostaglandin E2 secretion in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nutr. Res. 2008;28:321–328. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2008.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Jung JW, et al. Ras/MAP kinase pathways are involved in Ras specific apoptosis induced by sodium butyrate. Cancer Lett. 2005;225:199–206. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2004.11.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Backlund MG, et al. 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase is down-regulated in colorectal cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:3217–3223. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411221200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Panel V, et al. Cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 expression in human colon adenocarcinoma is correlated with cyclooxygenase-2 expression and contributes to prostaglandin E2 production. Cancer Lett. 2006;243:255–263. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.11.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Seo T, et al. Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase protein levels correlate with prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Virchows Arch. 2009;454:667–676. doi: 10.1007/s00428-009-0777-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Murakami M, et al. Functional coupling between various phospholipase A2s and cyclooxygenases in immediate and delayed prostanoid biosynthetic pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:3103–3115. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.5.3103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Murakami M, et al. Regulation of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by inducible membrane-associated prostaglandin E2 synthase that acts in concert with cyclooxygenase-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:32783–32792. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003505200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Pugh S, et al. Patients with adenomatous polyps and carcinomas have increased colonic mucosal prostaglandin E2. Gut. 1994;35:675–678. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sherratt PJ, et al. Positive and negative regulation of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis in human colorectal carcinoma cells by cancer chemopreventive agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003;66:51–61. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hughes-Fulford M, et al. Arachidonic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid, induces cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 in prostate carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:1520–1526. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]