Abstract
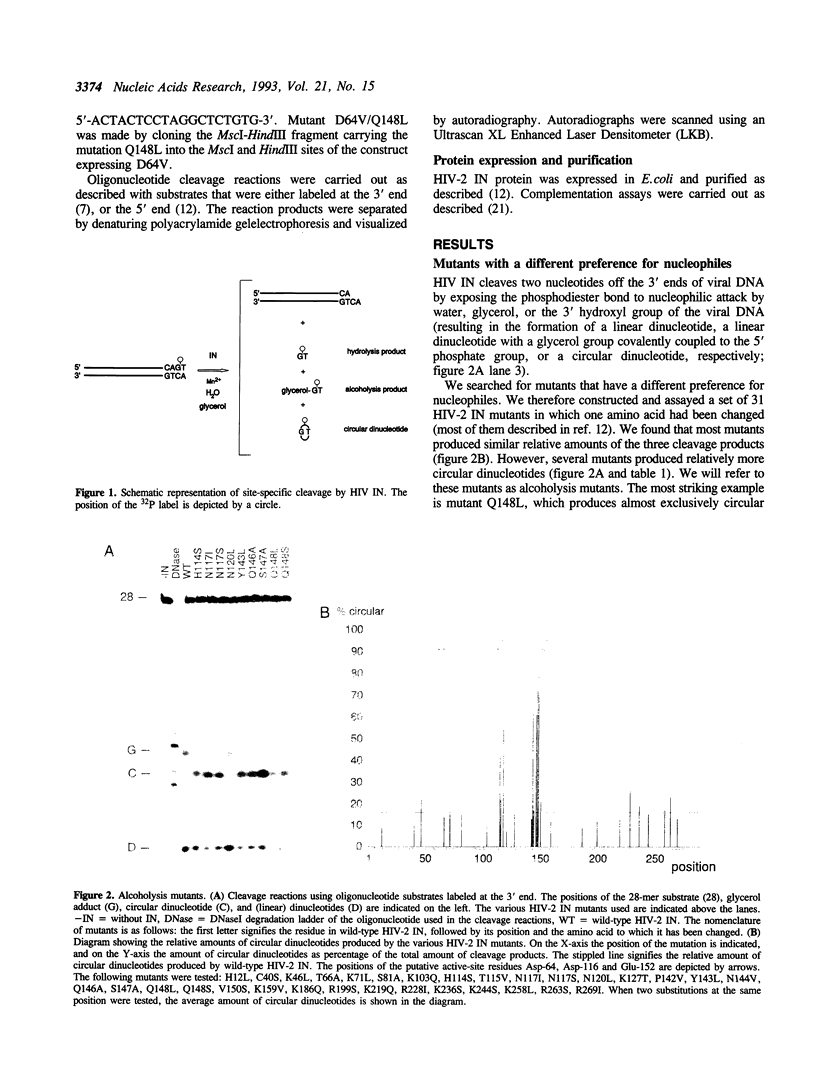
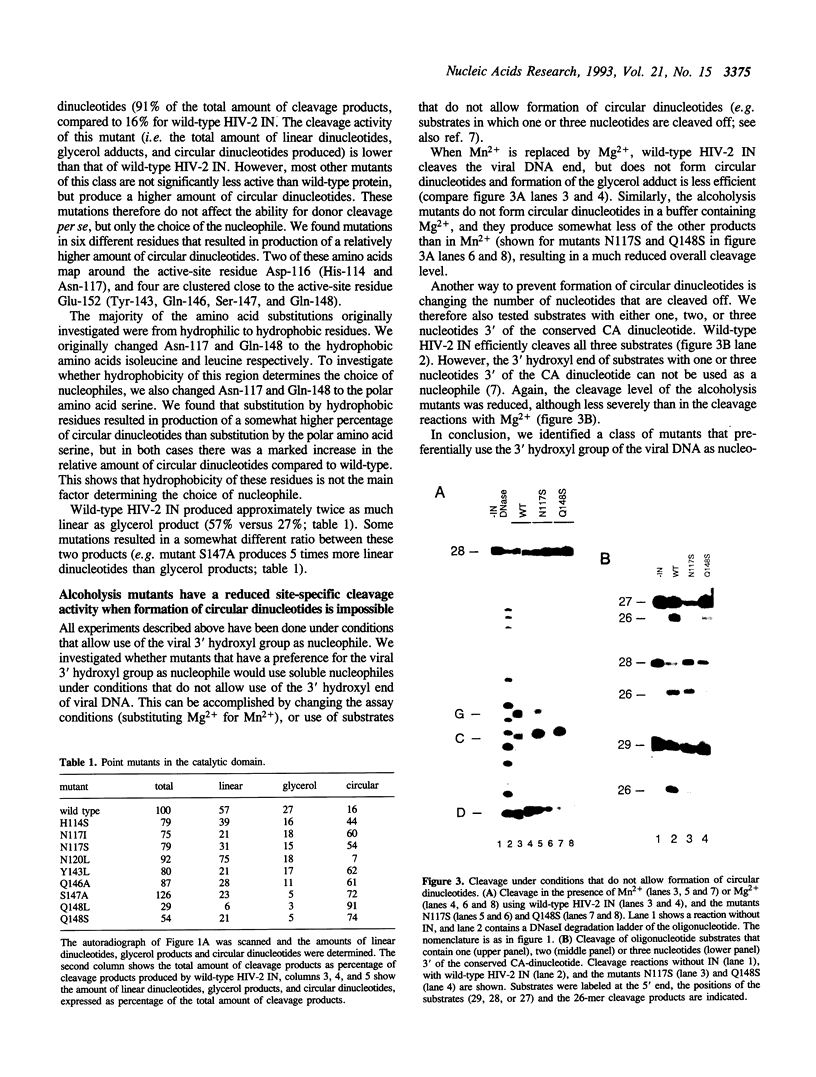
The human immunodeficiency virus integrase (HIV IN) protein cleaves two nucleotides off the 3' end of viral DNA and subsequently integrates the viral DNA into target DNA. IN exposes a specific phosphodiester bond near the viral DNA end to nucleophilic attack by water or other nucleophiles, such as glycerol or the 3' hydroxyl group of the viral DNA molecule itself. Wild-type IN has a preference for water as the nucleophile; we here describe a class of IN mutants that preferentially use the 3' hydroxyl group of viral DNA as nucleophile. The amino acids that are altered in this class of mutants map near the putative active-site residues Asp-116 and Glu-152. These results support a model in which multiple amino acid side-chains are involved in presentation of the (soluble) nucleophile. IN is probably active as an oligomeric complex, in which the subunits have non-equivalent roles; we here report that nucleophile selection is determined by the subunit that supplies the active site.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beese L. S., Steitz T. A. Structural basis for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I: a two metal ion mechanism. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):25–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Activities of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integration protein in vitro: specific cleavage and integration of HIV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1339–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. W., Lee J., Jayaram M. DNA cleavage in trans by the active site tyrosine during Flp recombination: switching protein partners before exchanging strands. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90228-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Vincent K. A., Ellison V., Brown P. O. Reversal of integration and DNA splicing mediated by integrase of human immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.1738845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Fujiwara T., Bushman F. The IN protein of Moloney murine leukemia virus processes the viral DNA ends and accomplishes their integration in vitro. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):829–837. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90126-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drelich M., Wilhelm R., Mous J. Identification of amino acid residues critical for endonuclease and integration activities of HIV-1 IN protein in vitro. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90499-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Craigie R. Identification of conserved amino acid residues critical for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase function in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6361–6369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6361-6369.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Mizuuchi K., Craigie R. HIV-1 DNA integration: mechanism of viral DNA cleavage and DNA strand transfer. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90297-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayet O., Ramond P., Polard P., Prère M. F., Chandler M. Functional similarities between retroviruses and the IS3 family of bacterial insertion sequences? Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1771–1777. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. S., Coleman J., Merkel G. W., Laue T. M., Skalka A. M. Retroviral integrase functions as a multimer and can turn over catalytically. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16037–16040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Merkel G., Kulkosky J., Leis J., Skalka A. M. The avian retroviral IN protein is both necessary and sufficient for integrative recombination in vitro. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90290-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan E., Mack J. P., Katz R. A., Kulkosky J., Skalka A. M. Retroviral integrase domains: DNA binding and the recognition of LTR sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):851–860. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkosky J., Jones K. S., Katz R. A., Mack J. P., Skalka A. M. Residues critical for retroviral integrative recombination in a region that is highly conserved among retroviral/retrotransposon integrases and bacterial insertion sequence transposases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2331–2338. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt A. D., Shiue L., Varmus H. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of HIV-1 integrase demonstrates differential effects on integrase functions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2113–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer M., Billich A. The N-terminal region of HIV-1 integrase is required for integration activity, but not for DNA-binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):874–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91708-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Fyfe J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus integration protein expressed in Escherichia coli possesses selective DNA cleaving activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5119–5123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Oude Groeneger A. M., Plasterk R. H. Identification of the catalytic and DNA-binding region of the human immunodeficiency virus type I integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 25;21(6):1419–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.6.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Yeheskiely E., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Plasterk R. H. Site-specific hydrolysis and alcoholysis of human immunodeficiency virus DNA termini mediated by the viral integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6691–6698. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D. C., Groeneger A. A., Plasterk R. H. Mutational analysis of the integrase protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9598–9602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






