Abstract
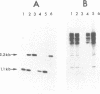
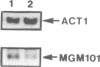
A nuclear mutation, mgm101, results in temperature sensitive loss of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The corresponding gene, MGM101, was isolated from a genomic DNA library by complementation. Sequence analysis shows that MGM101 encodes a positively charged protein of 269 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 30 kDa. This analysis also reveals that MGM101 is adjacent to the ribosomal protein gene RPS7A on chromosome X and hybridization indicates it occurs in single copy. Creation of a null mutant by targeted disruption showed that the gene has no essential cellular function, aside from its participation in mitochondrial genome maintenance. As no counterpart has been identified in databases it is a novel protein whose role has yet to be determined. Expression of MGM101 is low on glucose medium but on galactose there is a two-fold increase in the level of the transcript.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. J., Herskowitz I. Identification of a DNA binding factor involved in cell-cycle control of the yeast HO gene. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90168-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneaud N., Ozier-Kalogeropoulos O., Li G. Y., Labouesse M., Minvielle-Sebastia L., Lacroute F. A family of low and high copy replicative, integrative and single-stranded S. cerevisiae/E. coli shuttle vectors. Yeast. 1991 Aug-Sep;7(6):609–615. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Cell cycle control of the yeast HO gene: cis- and trans-acting regulators. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. J., Fukuhara H. A gene fusion system using the aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase gene of the kanamycin-resistance transposon Tn903: use in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Sep 30;69(2):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90429-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. A close relative of the nuclear, chromosomal high-mobility group protein HMG1 in yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7864–7868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. Identification and isolation of the gene encoding the small subunit of ribonucleotide reductase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: DNA damage-inducible gene required for mitotic viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2783–2793. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foury F. Cloning and sequencing of the nuclear gene MIP1 encoding the catalytic subunit of the yeast mitochondrial DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20552–20560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foury F., Lahaye A. Cloning and sequencing of the PIF gene involved in repair and recombination of yeast mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1441–1449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Kelly J. L., Lehman I. R. Yeast RPO41 gene product is required for transcription and maintenance of the mitochondrial genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3391–3394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Pfanner N., Nicholson D. W., Neupert W. Mitochondrial protein import. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):1–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J., Donald K. A., Griffiths D. E., Donald G. DMSO-enhanced whole cell yeast transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5791–5791. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. A., Fangman W. L. Mitochondrial DNA maintenance in yeast requires a protein containing a region related to the GTP-binding domain of dynamin. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):380–389. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisowsky T., Michaelis G. A nuclear gene essential for mitochondrial replication suppresses a defect of mitochondrial transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):218–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00337714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin M., Baltscheffsky H., Ronne H. Yeast PPA2 gene encodes a mitochondrial inorganic pyrophosphatase that is essential for mitochondrial function. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12168–12172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Pape L. K., Tzagoloff A. Mitochondrial protein synthesis is required for maintenance of intact mitochondrial genomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2087–2092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlon C. S., Ludescher R. D., Walter S. K. Production of petites by cell cycle mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective in DNA synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 31;169(2):189–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00271670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Brown T. A., Trumpower B. L. A rapid and simple method for preparation of RNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3091–3092. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skelly P. J., Clark-Walker G. D. Conversion at large intergenic regions of mitochondrial DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1530–1537. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Synetos D., Dabeva M. D., Warner J. R. The yeast ribosomal protein S7 and its genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3008–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyck E., Foury F., Stillman B., Brill S. J. A single-stranded DNA binding protein required for mitochondrial DNA replication in S. cerevisiae is homologous to E. coli SSB. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3421–3430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05421.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. W., Chan C. S., Tye B. K., Petes T. D. Unusual DNA sequences associated with the ends of yeast chromosomes. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):157–160. doi: 10.1038/310157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]