Abstract
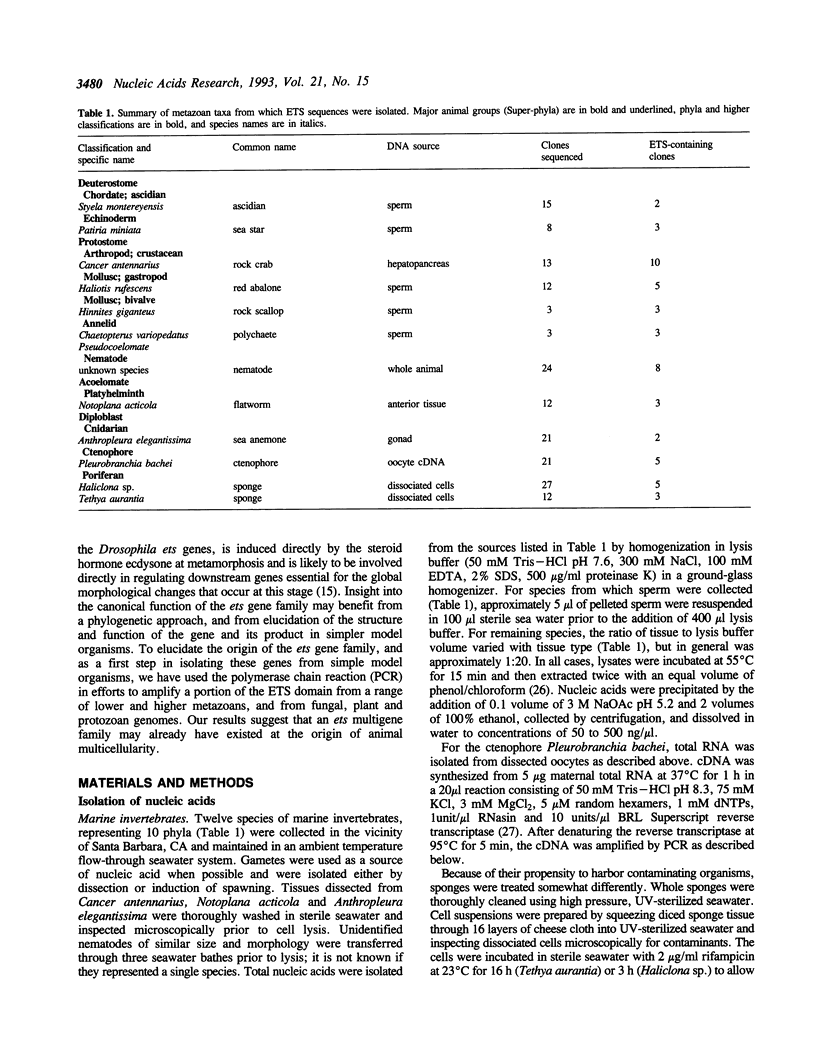
This study provides the first empirical evidence for the conservation of the ets proto-oncogene transcription factor family throughout the Metazoa. Using the polymerase chain reaction with degenerate primers corresponding to conserved sequences within the ETS DNA-binding domain, we have detected ets genes in a range of lower metazoans, including sponges, ctenophores, anemones, flatworms and nematodes, and in several higher invertebrate metazoans. Many of these sequences are significantly divergent from the original v-ets-1 oncogene, although most can be aligned with recently defined groups within the ets gene family. Multiple ETS domain sequences were detected in a number of the lower metazoan species, providing evidence for the existence of an ets multigene family at the earliest stages of metazoan evolution. In contrast, we were unable to detect any ETS sequences in fungal, plant or several protozoan DNAs. Our findings suggest that the duplication and divergence of ets proto-oncogenes responsible for generating the multigene family occurred concomitantly with the development of metazoan animals. In addition, these data corroborate other recent molecular evidence in providing strong support for the monophyletic origin of all multicellular animals, including sponges.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-David Y., Giddens E. B., Letwin K., Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):908–918. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesalski H. K., Doepner G., Tzimas G., Gamulin V., Schröder H. C., Batel R., Nau H., Müller W. E. Modulation of myb gene expression in sponges by retinoic acid. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1765–1774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulukos K. E., Pognonec P., Begue A., Galibert F., Gesquière J. C., Stéhelin D., Ghysdael J. Identification in chickens of an evolutionarily conserved cellular ets-2 gene (c-ets-2) encoding nuclear proteins related to the products of the c-ets proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):697–705. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T., Bunting M., Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Isolation and characterization of five Drosophila genes that encode an ets-related DNA binding domain. Dev Biol. 1992 May;151(1):176–191. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90225-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Q., Burdett L. A., Seth A. K., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S. Requirement of ets-2 expression for Xenopus oocyte maturation. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1416–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.2255913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Q., Kan N. C., Pribyl L., Lautenberger J. A., Moudrianakis E., Papas T. S. Molecular cloning of the ets proto-oncogene of the sea urchin and analysis of its developmental expression. Dev Biol. 1988 Feb;125(2):432–440. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross M., Dexter T. M. Growth factors in development, transformation, and tumorigenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90638-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Treisman R. Characterization of SAP-1, a protein recruited by serum response factor to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):597–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90194-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H. Spatial mechanisms of gene regulation in metazoan embryos. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):1–26. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degnan B. M., Morse D. E. Identification of eight homeobox-containing transcripts expressed during larval development and at metamorphosis in the gastropod mollusc Haliotis rufescens. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol. 1993 Feb;2(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duterque-Coquillaud M., Leprince D., Flourens A., Henry C., Ghysdael J., Debuire B., Stehelin D. Cloning and expression of chicken p54c-ets cDNAs: the first p54c-ets coding exon is located into the 40.0 kbp genomic domain unrelated to v-ets. Oncogene Res. 1988 May;2(4):335–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exposito J. Y., Le Guellec D., Lu Q., Garrone R. Short chain collagens in sponges are encoded by a family of closely related genes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21923–21928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys T. Species specific aggregation of dissociated sponge cells. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):685–686. doi: 10.1038/228685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Nojima H., Okayama H. High efficiency transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. Gene. 1990 Nov 30;96(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90336-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Urness L. D., Thummel C. S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A., Gunther C. V., Nye J. A. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1451–1453. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klämbt C. The Drosophila gene pointed encodes two ETS-like proteins which are involved in the development of the midline glial cells. Development. 1993 Jan;117(1):163–176. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K., Thompson C. C., Byers B. P., Walton E. M., McKnight S. L. Identification of Ets- and notch-related subunits in GA binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1876836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Rubin G. M. Negative control of photoreceptor development in Drosophila by the product of the yan gene, an ETS domain protein. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):609–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90430-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudet V., Niel C., Duterque-Coquillaud M., Leprince D., Stehelin D. Evolution of the ets gene family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jan 15;190(1):8–14. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautenberger J. A., Burdett L. A., Gunnell M. A., Qi S., Watson D. K., O'Brien S. J., Papas T. S. Genomic dispersal of the ets gene family during metazoan evolution. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1713–1719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Gegonne A., Coll J., de Taisne C., Schneeberger A., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. A putative second cell-derived oncogene of the avian leukaemia retrovirus E26. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):395–397. doi: 10.1038/306395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod K., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The ets gene family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jul;17(7):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90404-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majérus M. A., Bibollet-Ruche F., Telliez J. B., Wasylyk B., Bailleul B. Serum, AP-1 and Ets-1 stimulate the human ets-1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2699–2703. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau J., Le Guellec R., Leibovici M., Couturier A., Philippe M., Mechali M. Detection of proto-oncogenes in the genome of the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Oncogene. 1989 Apr;4(4):443–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray V. Improved double-stranded DNA sequencing using the linear polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8889–8889. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtha M. T., Leckman J. F., Ruddle F. H. Detection of homeobox genes in development and evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10711–10715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottilie S., Raulf F., Barnekow A., Hannig G., Schartl M. Multiple src-related kinase genes, srk1-4, in the fresh water sponge Spongilla lacustris. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1625–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ares J., Ghosal D., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3553–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Dailey G. M., Tjian R. Novel Jun- and Fos-related proteins in Drosophila are functionally homologous to enhancer factor AP-1. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4265–4273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl L. J., Watson D. K., McWilliams M. J., Ascione R., Papas T. S. The Drosophila ets-2 gene: molecular structure, chromosomal localization, and developmental expression. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl L. J., Watson D. K., Schulz R. A., Papas T. S. D-elg, a member of the Drosophila ets gene family: sequence, expression and evolutionary comparison. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1175–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Huebner K., Isobe M., ar-Rushdi A., Croce C. M., Reddy E. S. elk, tissue-specific ets-related genes on chromosomes X and 14 near translocation breakpoints. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):66–70. doi: 10.1126/science.2539641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Papas T. S., Reddy E. S. erg, a human ets-related gene on chromosome 21: alternative splicing, polyadenylation, and translation. Science. 1987 Aug 7;237(4815):635–639. doi: 10.1126/science.3299708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray D., Bosselut R., Ghysdael J., Mattei M. G., Tavitian A., Moreau-Gachelin F. Characterization of Spi-B, a transcription factor related to the putative oncoprotein Spi-1/PU.1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4297–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray D., Culine S., Tavitain A., Moreau-Gachelin F. The human homologue of the putative proto-oncogene Spi-1: characterization and expression in tumors. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schummer M., Scheurlen I., Schaller C., Galliot B. HOM/HOX homeobox genes are present in hydra (Chlorohydra viridissima) and are differentially expressed during regeneration. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1815–1823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Wolff C. M., Baltzinger M., Hirtzlin J., Senan F., Meyer D., Ghysdael J., Stéhelin D., Befort N., Remy P. Characterization of Xenopus laevis cDNA clones of the c-ets-1 proto-oncogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5298–5298. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tei H., Nihonmatsu I., Yokokura T., Ueda R., Sano Y., Okuda T., Sato K., Hirata K., Fujita S. C., Yamamoto D. pokkuri, a Drosophila gene encoding an E-26-specific (Ets) domain protein, prevents overproduction of the R7 photoreceptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6856–6860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Wang C. Y., Ho I. C., Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Miesfeldt S., Zhang L., Nabel G. J., Karpinski B. cis-acting sequences required for inducible interleukin-2 enhancer function bind a novel Ets-related protein, Elf-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1043–1053. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. W., Boom J. D., Marsh A. G. First non-vertebrate member of the myc gene family is seasonally expressed in an invertebrate testis. Oncogene. 1992 Oct;7(10):2007–2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Petryniak B., Ho I. C., Thompson C. B., Leiden J. M. Evolutionarily conserved Ets family members display distinct DNA binding specificities. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1391–1399. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams-Smith M. J., Kozak C., Reeves R., Gearhart J., Nunn M. F., Nash W., Fowle J. R., 3rd, Duesberg P., Papas T. S. Conserved chromosomal positions of dual domains of the ets protooncogene in cats, mice, and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1792–1796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams M. J., Lapis P., Lautenberger J. A., Schweinfest C. W., Papas T. S. Mammalian ets-1 and ets-2 genes encode highly conserved proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7862–7866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster P. J., Mansour T. E. Conserved classes of homeodomains in Schistosoma mansoni, an early bilateral metazoan. Mech Dev. 1992 Jul;38(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90035-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff C. M., Stiegler P., Baltzinger M., Meyer D., Ghysdael J., Stéhelin D., Befort N., Remy P. Isolation of two different c-ets-2 proto-oncogenes in Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4603–4604. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin J. H., Cowie A., Lachance P., Hassell J. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of PEA3, a new member of the Ets oncogene family that is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):481–496. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


