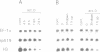Abstract
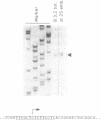
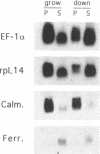
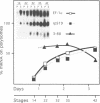
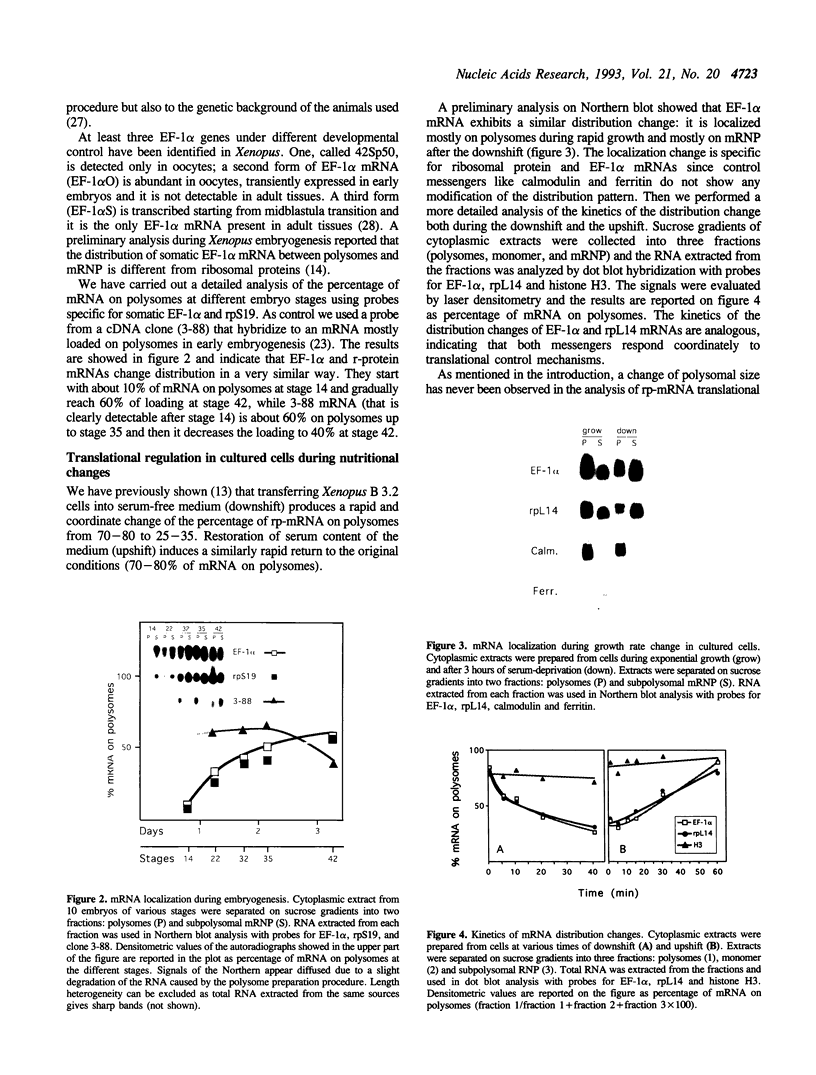
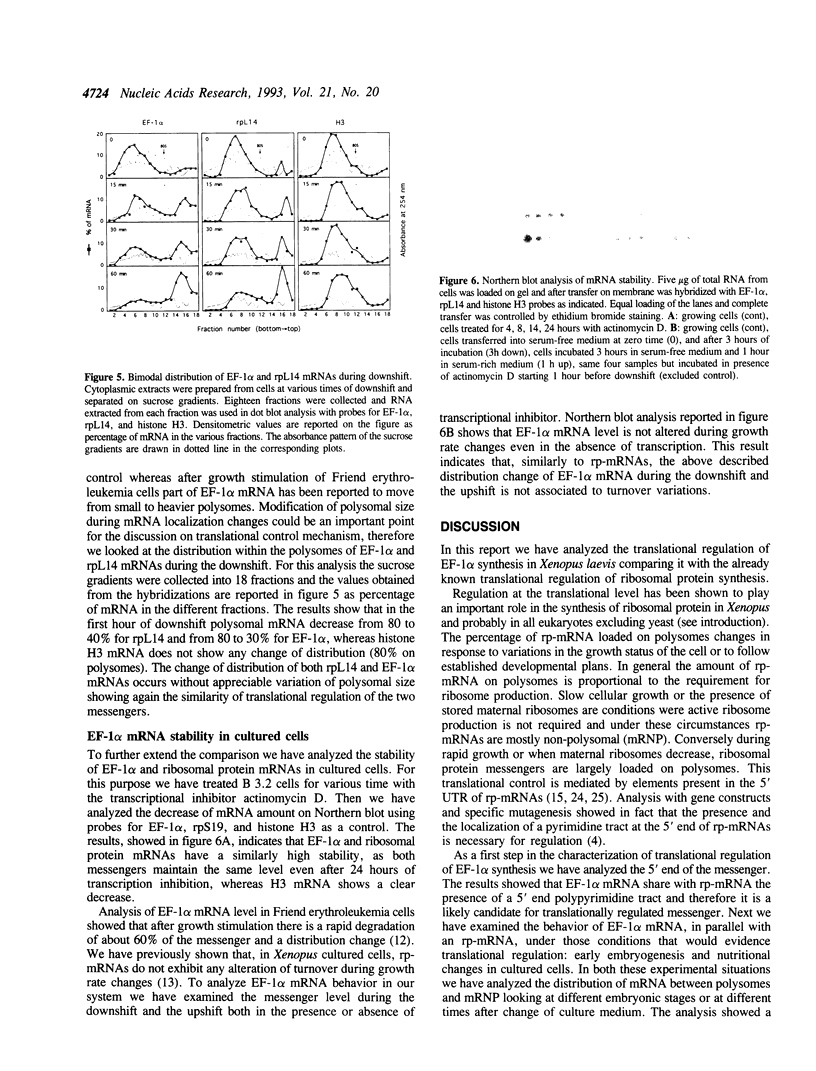
The regulation of the synthesis of elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) in Xenopus laevis has been analyzed from the point of view of translational control. The 5' end of EF-1 alpha mRNA, examined by primer extension, revealed the presence of a terminal pyrimidine tract that is characteristic of ribosomal protein mRNAs (rp-mRNAs). We have then compared the translation pattern of EF-1 alpha and rp-mRNAs during Xenopus embryogenesis and in Xenopus cultured cells during growth rate changes. In Xenopus embryos EF-1 alpha transcripts, that appear after midblastula transition, are initially mostly localized on mRNP and translationally inactive. Only later in embryogenesis, together with rp-mRNAs, they are gradually recruited on polysomes. Also in Xenopus cells B 3.2, EF-1 alpha mRNA shows a distribution change similar to an rp-mRNA: part of it moves from polysomes to mRNP during serum deprivation and goes back on polysomes after restitution of serum to the culture. Moreover EF-1 alpha mRNA, similarly to rp-mRNAs, is always localized on mRNP or fully loaded on polysomes but never on small polysomes. Therefore EF-1 alpha mRNA for structural features and translation behavior can be included in the 'regulatory' group of rp-mRNAs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal M. G., Bowman L. H. Transcriptional and translational regulation of ribosomal protein formation during mouse myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4868–4875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloni R., Peleg D., Meyuhas O. Selective translational control and nonspecific posttranscriptional regulation of ribosomal protein gene expression during development and regeneration of rat liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2203–2212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amaldi F., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Luo Z. X., Pierandrei-Amaldi P. Nucleotide sequences of cloned cDNA fragments specific for six Xenopus laevis ribosomal proteins. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amaldi F., Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Pierandrei-Amaldi P. Expression of ribosomal protein genes and regulation of ribosome biosynthesis in Xenopus development. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 May;14(5):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auth D., Brawerman G. A 33-kDa polypeptide with homology to the laminin receptor: component of translation machinery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4368–4372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagni C., Mariottini P., Terrenato L., Amaldi F. Individual variability in the translational regulation of ribosomal protein synthesis in Xenopus laevis. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jul;234(1):60–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00272345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum E. Z., Wormington W. M. Coordinate expression of ribosomal protein genes during Xenopus development. Dev Biol. 1985 Oct;111(2):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90500-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y. H., Dawid I. B. Isolation and characterization of calmodulin genes from Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):507–513. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djé M. K., Mazabraud A., Viel A., le Maire M., Denis H., Crawford E., Brown D. D. Three genes under different developmental control encode elongation factor 1-alpha in Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3489–3493. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Meyuhas O., Perry R. P., Johnson L. F. Regulation of ribosomal protein mRNA content and translation in growth-stimulated mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):685–693. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond M. L., Merrick W., Bowman L. H. Sequences mediating the translation of mouse S16 ribosomal protein mRNA during myoblast differentiation and in vitro and possible control points for the in vitro translation. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1723–1736. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Hershey J. W. Translational initiation factor expression and ribosomal protein gene expression are repressed coordinately but by different mechanisms in murine lymphosarcoma cells treated with glucocorticoids. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3679–3684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. A., Jacobs-Lorena M. Selective translational regulation of ribosomal protein gene expression during early development of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3583–3592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Varnum S. M., Wormington W. M., Melton D. A. The mRNA encoding elongation factor 1-alpha (EF-1 alpha) is a major transcript at the midblastula transition in Xenopus. Dev Biol. 1989 May;133(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S., Avni D., Hariharan N., Perry R. P., Meyuhas O. Oligopyrimidine tract at the 5' end of mammalian ribosomal protein mRNAs is required for their translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loreni F., Amaldi F. Translational regulation of ribosomal protein synthesis in Xenopus cultured cells: mRNA relocation between polysomes and RNP during nutritional shifts. Eur J Biochem. 1992 May 1;205(3):1027–1032. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loreni F., Francesconi A., Jappelli R., Amaldi F. Analysis of mRNAs under translational control during Xenopus embryogenesis: isolation of new ribosomal protein clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 25;20(8):1859–1863. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.8.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariottini P., Amaldi F. The 5' untranslated region of mRNA for ribosomal protein S19 is involved in its translational regulation during Xenopus development. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):816–822. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Thompson E. A., Jr, Perry R. P. Glucocorticoids selectively inhibit translation of ribosomal protein mRNAs in P1798 lymphosarcoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2691–2699. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaitis J. E., Pastori R. L., Schoenberg D. R. Sequence of Xenopus laevis ferritin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2184–2184. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Campioni N., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Amaldi F. Expression of ribosomal-protein genes in Xenopus laevis development. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao T. R., Slobin L. I. Regulation of the utilization of mRNA for eucaryotic elongation factor Tu in Friend erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):687–697. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberti I., Fragapane P., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Beccari E., Amaldi F., Bozzoni I. Characterization of histone genes isolated from Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis genomic libraries. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7543–7559. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel L. F., Jacobson A. Translational control of ribosomal protein synthesis during early Dictyostelium discoideum development. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):965–972. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Thomas G. Translational control of mRNA expression during the early mitogenic response in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells: identification of specific proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2137–2144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viel A., Armand M. J., Callen J. C., Gomez De Gracia A., Denis H., le Maire M. Elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) is concentrated in the Balbiani body and accumulates coordinately with the ribosomes during oogenesis of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1990 Oct;141(2):270–278. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90383-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]