Abstract
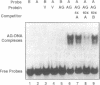
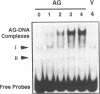
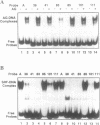
The Arabidopsis floral homeotic gene AGAMOUS (AG) is required for normal flower development. The deduced AG protein contains a region which shares substantial sequence similarity with the DNA-binding domains of known transcription factors, SRF (human) and MCM1 (yeast). Therefore, it is likely that AG is also a DNA-binding protein regulating transcription of floral genes. We describe here several experiments to characterize AG-DNA binding in vitro. We show that AG indeed binds a DNA sequence matching the consensus of SRF targets. Further, we have selected the AG-binding sequences from a pool of random oligonucleotides, and deduced an AG-binding consensus sequence of TT(A/T)CC(A/T)(A/t)2(T/A)NNGG(-G)(A/t)2. We have demonstrated that AG binds to the consensus region of three of the oligonucleotides by footprinting analysis. Finally, we have examined AG's relative binding affinity for different sequences, as compared to SRF, by gel mobility shift analysis. Our results indicate that AG is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein, and that the AG-binding consensus sequence is similar to those of MCM1 and SRF.
Full text
PDF



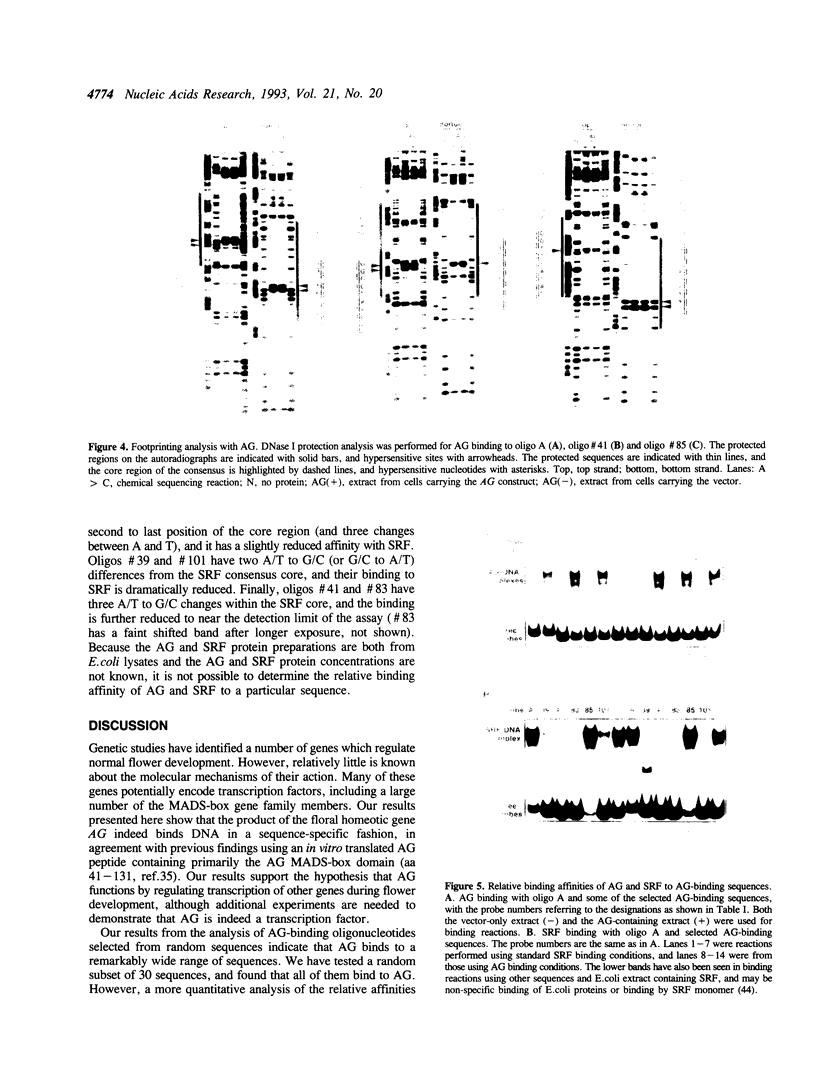


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr MAT alpha 1 protein, a yeast transcription activator, binds synergistically with a second protein to a set of cell-type-specific genes. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman J. L., Smyth D. R., Meyerowitz E. M. Genes directing flower development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):37–52. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman J. L., Smyth D. R., Meyerowitz E. M. Genetic interactions among floral homeotic genes of Arabidopsis. Development. 1991 May;112(1):1–20. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G., Kedes L. The sarcomeric actin CArG-binding factor is indistinguishable from the c-fos serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D., Carpenter R., Sommer H., Hartley N., Coen E. Complementary floral homeotic phenotypes result from opposite orientations of a transposon at the plena locus of Antirrhinum. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90052-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caelles C., Ferrer A., Balcells L., Hegardt F. G., Boronat A. Isolation and structural characterization of a cDNA encoding Arabidopsis thaliana 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Dec;13(6):627–638. doi: 10.1007/BF00016018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Meyerowitz E. M. The war of the whorls: genetic interactions controlling flower development. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):31–37. doi: 10.1038/353031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X., Mindrinos M., Davis K. R., Ausubel F. M. Induction of Arabidopsis defense genes by virulent and avirulent Pseudomonas syringae strains and by a cloned avirulence gene. Plant Cell. 1991 Jan;3(1):61–72. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E., Bercy J., Messenguy F. Characterization of two genes, ARGRI and ARGRIII required for specific regulation of arginine metabolism in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):142–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00331501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A., LaMontagne K., Reavis D., Stober-Grässer U., Lipsick J. S. Determinants of sequence-specific DNA-binding by p48v-myb. Oncogene. 1991 Feb;6(2):265–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grueneberg D. A., Natesan S., Alexandre C., Gilman M. Z. Human and Drosophila homeodomain proteins that enhance the DNA-binding activity of serum response factor. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1089–1095. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Sengupta P., Cochran B. H. The human c-fos serum response factor and the yeast factors GRM/PRTF have related DNA-binding specificities. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1713–1722. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. A regulatory hierarchy for cell specialization in yeast. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):749–757. doi: 10.1038/342749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huijser P., Klein J., Lönnig W. E., Meijer H., Saedler H., Sommer H. Bracteomania, an inflorescence anomaly, is caused by the loss of function of the MADS-box gene squamosa in Antirrhinum majus. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1239–1249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imajuku Y., Hirayama T., Endoh H., Oka A. Exon-intron organization of the Arabidopsis thaliana protein kinase genes CDC2a and CDC2b. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 8;304(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80592-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack T., Brockman L. L., Meyerowitz E. M. The homeotic gene APETALA3 of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a MADS box and is expressed in petals and stamens. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):683–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis E. E., Clark K. L., Sprague G. F., Jr The yeast transcription activator PRTF, a homolog of the mammalian serum response factor, is encoded by the MCM1 gene. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):936–945. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X., Abel S., Keller J. A., Shen N. F., Theologis A. The 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):11046–11050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.11046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma H., Yanofsky M. F., Meyerowitz E. M. AGL1-AGL6, an Arabidopsis gene family with similarity to floral homeotic and transcription factor genes. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):484–495. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M. A., Bowman J. L., Kempin S. A., Ma H., Meyerowitz E. M., Yanofsky M. F. Manipulation of flower structure in transgenic tobacco. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90272-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M. A., Gustafson-Brown C., Savidge B., Yanofsky M. F. Molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis floral homeotic gene APETALA1. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):273–277. doi: 10.1038/360273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson J., Söderman E., Svenson M., Borkird C., Engström P. A new homeobox-leucine zipper gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;18(5):1019–1022. doi: 10.1007/BF00019223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medford J. I., Elmer J. S., Klee H. J. Molecular cloning and characterization of genes expressed in shoot apical meristems. Plant Cell. 1991 Apr;3(4):359–370. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.4.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerowitz E. M., Bowman J. L., Brockman L. L., Drews G. N., Jack T., Sieburth L. E., Weigel D. A genetic and molecular model for flower development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Dev Suppl. 1991;1:157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami Y., Ma H. Ectopic expression of the floral homeotic gene AGAMOUS in transgenic Arabidopsis plants alters floral organ identity. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90271-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. G., Nordheim A. A protein domain conserved between yeast MCM1 and human SRF directs ternary complex formation. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4219–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Elble R., Tye B. K. A protein involved in minichromosome maintenance in yeast binds a transcriptional enhancer conserved in eukaryotes. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):921–935. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Maine G. T., Elble R., Christ C., Tye B. K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein involved in plasmid maintenance is necessary for mating of MAT alpha cells. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. A sensitive method for the determination of protein-DNA binding specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6197–6204. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards E. J., Goodman H. M., Ausubel F. M. The centromere region of Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 1 contains telomere-similar sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3351–3357. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan W. A., Jr, Franza B. R., Jr, Gilman M. Z. Two distinct cellular phosphoproteins bind to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Huijser P., Nacken W., Saedler H., Sommer H. Genetic Control of Flower Development by Homeotic Genes in Antirrhinum majus. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):931–936. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer H., Beltrán J. P., Huijser P., Pape H., Lönnig W. E., Saedler H., Schwarz-Sommer Z. Deficiens, a homeotic gene involved in the control of flower morphogenesis in Antirrhinum majus: the protein shows homology to transcription factors. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):605–613. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification and purification of a polypeptide that binds to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2711–2717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tröbner W., Ramirez L., Motte P., Hue I., Huijser P., Lönnig W. E., Saedler H., Sommer H., Schwarz-Sommer Z. GLOBOSA: a homeotic gene which interacts with DEFICIENS in the control of Antirrhinum floral organogenesis. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4693–4704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsay Y. F., Schroeder J. I., Feldmann K. A., Crawford N. M. The herbicide sensitivity gene CHL1 of Arabidopsis encodes a nitrate-inducible nitrate transporter. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90399-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne J., Treisman R. SRF and MCM1 have related but distinct DNA binding specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3297–3303. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky M. F., Ma H., Bowman J. L., Drews G. N., Feldmann K. A., Meyerowitz E. M. The protein encoded by the Arabidopsis homeotic gene agamous resembles transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):35–39. doi: 10.1038/346035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]