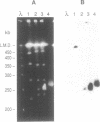
Abstract
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) represent the latest generation of vectors which have the great advantage of large insert size. The introduction of YACs into mammalian cells and organisms has become an important goal, since it offers the potential to study the control of large and complex transcription units and identify genes by complementation. Microinjection into the nucleus is the most direct and efficient way of delivering YAC DNA into cells, but requires the purification of the YAC from the remaining yeast chromosomes. Here we describe a detailed method for the isolation of pure, intact and highly concentrated YAC DNA. As a model system the murine tyrosinase gene was chosen and four YACs covering this locus were isolated. Introduction by homologous recombination in yeast of sequences permitting YAC amplification greatly facilitated the isolation of YAC DNA at high concentrations. YAC DNA stabilized in a salt and polyamine containing buffer did not compromise the survival of microinjected oocytes and was suitable for the generation of transgenic mice. Applications and benefits of this technique will be discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand R., Villasante A., Tyler-Smith C. Construction of yeast artificial chromosome libraries with large inserts using fractionation by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3425–3433. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beermann F., Ruppert S., Hummler E., Bosch F. X., Müller G., Rüther U., Schütz G. Rescue of the albino phenotype by introduction of a functional tyrosinase gene into mice. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2819–2826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgers P. M., Percival K. J. Transformation of yeast spheroplasts without cell fusion. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jun;163(2):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Gosule L. C., Schellman A. DNA condensation with polyamines. II. Electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi T. K., Hollenbach P. W., Pearson B. E., Ueda R. M., Weddell G. N., Kurahara C. G., Woodhouse C. S., Kay R. M., Loring J. F. Transgenic mice containing a human heavy chain immunoglobulin gene fragment cloned in a yeast artificial chromosome. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):117–123. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couto L. B., Spangler E. A., Rubin E. M. A method for the preparative isolation and concentration of intact yeast artificial chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):8010–8010. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.8010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliceiri B., Labella T., Hagino Y., Srivastava A., Schlessinger D., Pilia G., Palmieri G., D'Urso M. Stable integration and expression in mouse cells of yeast artificial chromosomes harboring human genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2179–2183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Luna J. L., Matthews R. J., Brownstein B. H., Schreiber R. D., Thomas M. L. Characterization and expression of the human leukocyte-common antigen (CD45) gene contained in yeast artificial chromosomes. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):756–764. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90460-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnirke A., Barnes T. S., Patterson D., Schild D., Featherstone T., Olson M. V. Cloning and in vivo expression of the human GART gene using yeast artificial chromosomes. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1629–1634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnirke A., Huxley C., Peterson K., Olson M. V. Microinjection of intact 200- to 500-kb fragments of YAC DNA into mammalian cells. Genomics. 1993 Mar;15(3):659–667. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosule L. C., Schellman J. A. DNA condensation with polyamines I. Spectroscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 25;121(3):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90366-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Bloom K. Genetic manipulation of centromere function. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2397–2405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdener-Kenny B., Sharan S. K., Magnuson T. Mouse albino-deletions: from genetics to genes in development. Bioessays. 1992 Dec;14(12):831–839. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley C., Hagino Y., Schlessinger D., Olson M. V. The human HPRT gene on a yeast artificial chromosome is functional when transferred to mouse cells by cell fusion. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):742–750. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90369-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Moore A. L., Green L. L., Vergara G. J., Maynard-Currie C. E., Austin H. A., Klapholz S. Germ-line transmission and expression of a human-derived yeast artificial chromosome. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):255–258. doi: 10.1038/362255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey G., Schedl A., Ruppert S., Niswander L., Magnuson T., Klebig M. L., Rinchik E. M., Schütz G. Physical mapping of the albino-deletion complex in the mouse to localize alf/hsdr-1, a locus required for neonatal survival. Genomics. 1992 Oct;14(2):275–287. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larin Z., Monaco A. P., Lehrach H. Yeast artificial chromosome libraries containing large inserts from mouse and human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachnis V., Pevny L., Rothstein R., Costantini F. Transfer of a yeast artificial chromosome carrying human DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5109–5113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavan W. J., Hieter P., Reeves R. H. Modification and transfer into an embryonal carcinoma cell line of a 360-kilobase human-derived yeast artificial chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4163–4169. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl A., Beermann F., Thies E., Montoliu L., Kelsey G., Schütz G. Transgenic mice generated by pronuclear injection of a yeast artificial chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3073–3077. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl A., Montoliu L., Kelsey G., Schütz G. A yeast artificial chromosome covering the tyrosinase gene confers copy number-dependent expression in transgenic mice. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):258–261. doi: 10.1038/362258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Smyth A. P., Moir D. T. Amplification of large artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8242–8246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Smyth A. P., Strauss W. M., Moir D. T. Incorporation of copy-number control elements into yeast artificial chromosomes by targeted homologous recombination. Mamm Genome. 1993;4(3):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00352229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss W. M., Dausman J., Beard C., Johnson C., Lawrence J. B., Jaenisch R. Germ line transmission of a yeast artificial chromosome spanning the murine alpha 1(I) collagen locus. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1904–1907. doi: 10.1126/science.8096090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss W. M., Jaenisch R. Molecular complementation of a collagen mutation in mammalian cells using yeast artificial chromosomes. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):417–422. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05070.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Yamamoto H., Takeuchi S., Takeuchi T. Melanization in albino mice transformed by introducing cloned mouse tyrosinase gene. Development. 1990 Feb;108(2):223–227. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama T., Silversides D. W., Waymire K. G., Kwon B. S., Takeuchi T., Overbeek P. A. Conserved cysteine to serine mutation in tyrosinase is responsible for the classical albino mutation in laboratory mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7293–7298. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]