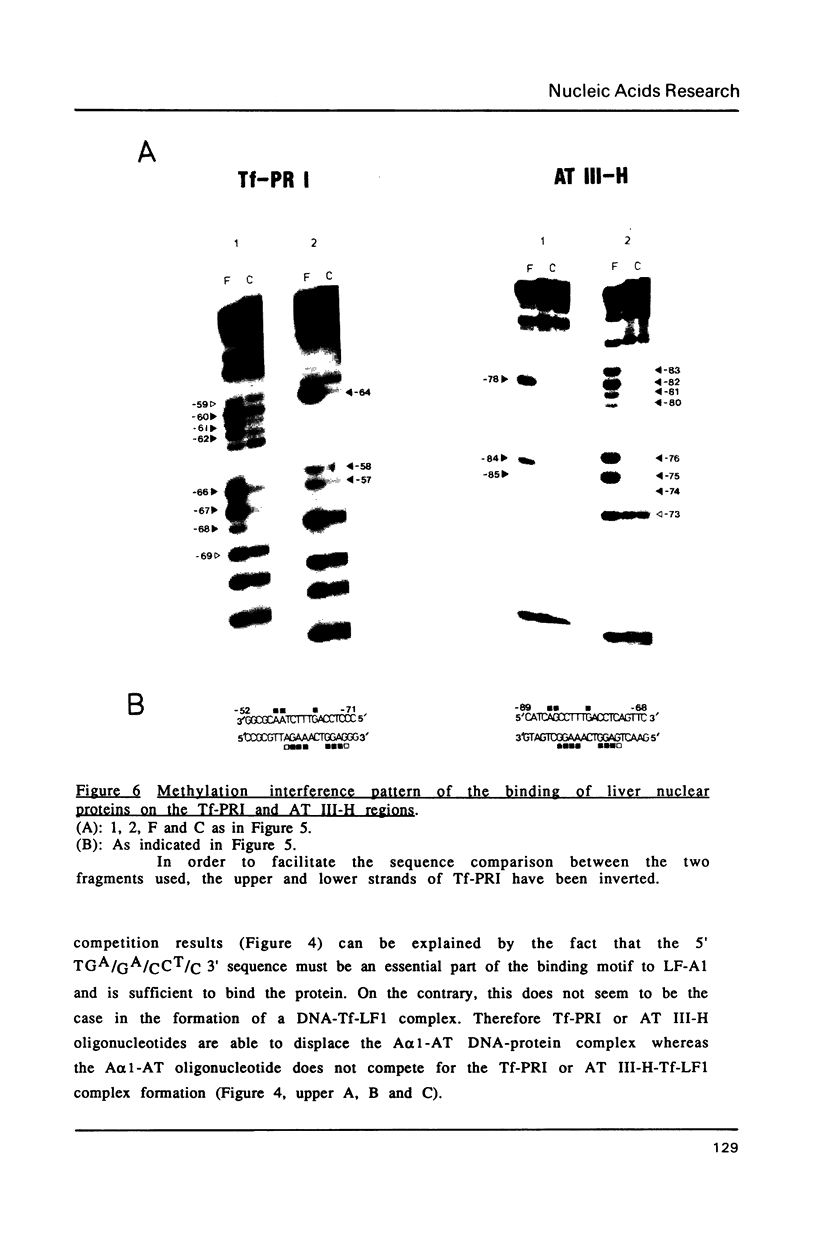
Abstract
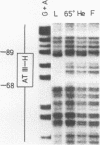
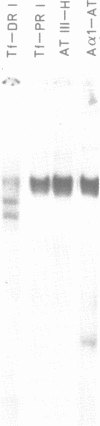
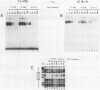
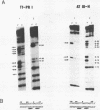
The proximal promoter region of the human transferrin gene contains an hepatocyte-specific cis-element (PRI, nucleotides -76 to -51) whose DNA sequence is homologous to a sequence (nucleotides -89 to -68) present in the transcriptionally essential 5' region of the human antithrombin III gene and to another hepatocyte-specific sequence (A domain) of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene promoter. The results reported here lead to the conclusion that the liver trans-acting factor Tf-LF1, binding to the transferrin PRI cis-element interacts with the homologous antithrombin III region, but is different from the transcription factor LF-A1 interacting with the A domain of the alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. The distal region DRI (nucleotides -480 to -454) of the human transferrin gene promoter presents in its core the same 10 nucleotide-long sequence as the PRI cis-element. We have previously shown that the liver protein Tf-LF2, binding to the DRI element is different from the Tf-LF1 trans-acting factor. In this paper we also show that Tf-LF2 is different from the transcription factor LF-A1 interacting with the alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. The results allow us to conclude that at least three distinct liver nuclear proteins bind to different subsets of 5' DNA regions containing similar sequences. These sequences are present in genes expressed essentially in liver.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi M. K., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Purification and characterization of chicken ovalbumin gene upstream promoter transcription factor from homologous oviduct cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4151–4158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunel F., Ochoa A., Schaeffer E., Boissier F., Guillou Y., Cereghini S., Cohen G. N., Zakin M. M. Interactions of DNA-binding proteins with the 5' region of the human transferrin gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10180–10185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Xanthopoulos K. G., Darnell J. E., Jr A liver-specific DNA-binding protein recognizes multiple nucleotide sites in regulatory regions of transthyretin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, albumin, and simian virus 40 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Morgan J. G., Campbell L. A., Fourel G., Crabtree G. R. Interaction of a liver-specific nuclear factor with the fibrinogen and alpha 1-antitrypsin promoters. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):688–692. doi: 10.1126/science.3499668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., Ciliberto G., Hardon E., Paonessa G., Palla F., Lundberg L., Cortese R. Cis- and trans-acting elements responsible for the cell-specific expression of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2759–2766. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardon E. M., Frain M., Paonessa G., Cortese R. Two distinct factors interact with the promoter regions of several liver-specific genes. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1711–1719. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugler W., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. Tissue-specificity of liver gene expression: a common liver-specific promoter element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3165–3174. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V. Relationship between an enhancer element in the human antithrombin III gene and an immunoglobulin light-chain gene enhancer. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):845–848. doi: 10.1038/316845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Sagami I., Wang H., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Interactions between a DNA-binding transcription factor (COUP) and a non-DNA binding factor (S300-II). Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]