Abstract
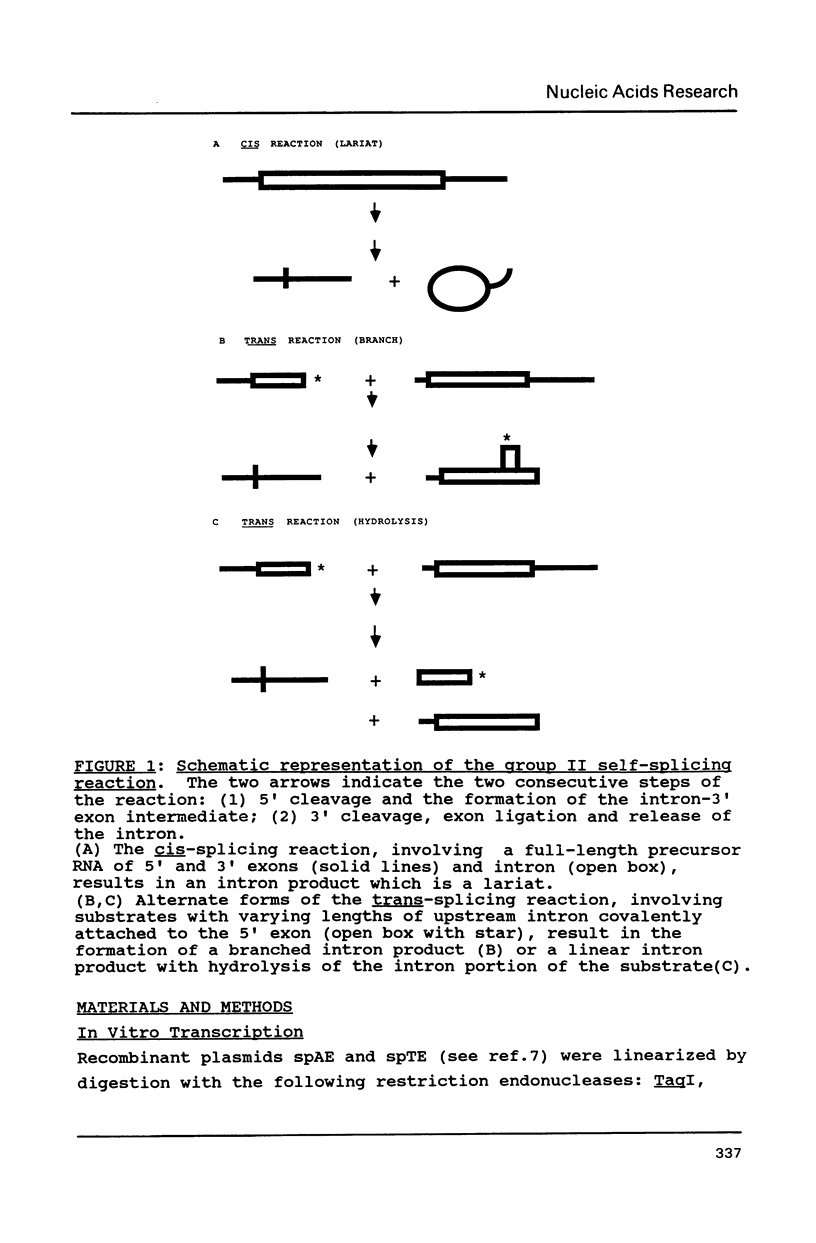
Evidence is presented for the existence of a specific intron-intron interaction, necessary for the formation of the branched product in the self-splicing reaction of a group II yeast mitochondrial intron. Trans-splicing reactions involving two RNA molecules (5' exon with covalently linked regions of intron and intron with covalently linked 3' exon) show that the presence of portions of intron domain I on the 5' molecule is necessary for the formation of branched products which are not seen with shorter 5' molecules. Modification/interference reactions show regions necesary for branch-formation and support a major role for specific regions of intron domain I. Further experiments, utilizing a truncated 3' molecule that is missing the conserved branchpoint nucleotide, indicate that domain VI may be required for a successful domain I interaction. A model for the formation of a proper branched structure includes implications for both cis and trans configurations.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cech T. R. The generality of self-splicing RNA: relationship to nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Zaug A. J., Grabowski P. J. In vitro splicing of the ribosomal RNA precursor of Tetrahymena: involvement of a guanosine nucleotide in the excision of the intervening sequence. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Michel F. Multiple exon-binding sites in class II self-splicing introns. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90658-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Rosbash M. Efficient trans-splicing of a yeast mitochondrial RNA group II intron implicates a strong 5' exon-intron interaction. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1099–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.2430332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. A., Dietrich R. C., Perlman P. S. Group II intron domain 5 facilitates a trans-splicing reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2361–2366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. A., Peebles C. L., Dietrich R. C., Romiti S. L., Perlman P. S. Group II intron self-splicing. Alternative reaction conditions yield novel products. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3432–3439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Perlman P. S., Mecklenburg K. L., Petrillo M. L., Tabor J. H., Jarrell K. A., Cheng H. L. A self-splicing RNA excises an intron lariat. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. Specific small nuclear RNAs are associated with yeast spliceosomes. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90561-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. An RNA processing activity that debranches RNA lariats. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):135–140. doi: 10.1126/science.2990042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Greene J. M., Green M. R. Cryptic branch point activation allows accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin intron mutants. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):833–844. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymond B. C., Rosbash M. A chemical modification/interference study of yeast pre-mRNA spliceosome assembly and splicing. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):428–439. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schweyen R. J. Self-splicing of group II introns in vitro: mapping of the branch point and mutational inhibition of lariat formation. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Grabowski P. J., Cech T. R. Autocatalytic cyclization of an excised intervening sequence RNA is a cleavage-ligation reaction. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):578–583. doi: 10.1038/301578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Arnberg A. C., van der Horst G., Bonen L., Tabak H. F., Grivell L. A. Excised group II introns in yeast mitochondria are lariats and can be formed by self-splicing in vitro. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Kwakman J. H., Grivell L. A. Mutations at the lariat acceptor site allow self-splicing of a group II intron without lariat formation. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3827–3831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]