Abstract
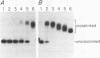
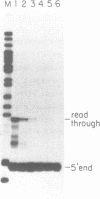
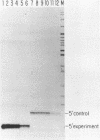
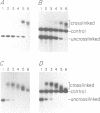
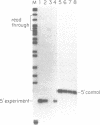
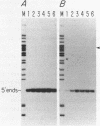
On the tandemly linked ribosomal genes of Xenopus laevis, the RNA polymerase transcribes past the 3' end of the 40S coding region and terminates at T3 just upstream of the gene promoter. The close proximity of T3 to the gene promoter, and the functional interdependence of these two elements, has led to the suggestion that polymerase terminating at T3 might be passed directly to the gene promoter. Such a mechanism might be necessary to maintain the characteristic high rate of transcription initiation seen on the ribosomal genes. We have performed a direct test of this model by introducing chain-terminating psoralen adducts into a circular plasmid containing a single gene promoter with its attendant T3 region upstream. We find that the psoralen adducts can completely prevent polymerase from traveling around the template circle (and thus prevent polymerase from approaching the promoter from upstream) without affecting the rate of transcription initiation at the gene promoter. This result suggests that recycling of polymerase from T3 to the promoter is not a significant mechanism in maintaining high initiation rates.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. M., Platt T. Pol I transcription: which comes first, the end or the beginning? Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):839–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakken A., Morgan G., Sollner-Webb B., Roan J., Busby S., Reeder R. H. Mapping of transcription initiation and termination signals on Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):56–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman E., Paule M. R. Promoter occlusion during ribosomal RNA transcription. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):985–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Alkaline gel electrophoresis of deoxyribonucleic acid photoreacted with trimethylpsoralen: rapid and sensitive detection of interstrand cross-links. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1431–1437. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimino G. D., Gamper H. B., Isaacs S. T., Hearst J. E. Psoralens as photoactive probes of nucleic acid structure and function: organic chemistry, photochemistry, and biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1151–1193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. A complex array of sequences enhances ribosomal transcription in Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):813–827. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90407-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. The ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis is transcribed as part of the primary ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6041–6051. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Maier U., Ohrlein A., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Transcription of mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3' spacer. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Ribosomal precursor 3' end formation requires a conserved element upstream of the promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90661-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchelson K., Moss T. The enhancement of ribosomal transcription by the recycling of RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9577–9596. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan G. T., Roan J. G., Bakken A. H., Reeder R. H. Variations in transcriptional activity of rDNA spacer promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6043–6052. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt S. C., Reeder R. H. Effect of intercalating agents on RNA polymerase I promoter selection in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2851–2857. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Gamper H., Hearst J. E. Interaction of T7 RNA polymerase with DNA in an elongation complex arrested at a specific psoralen adduct site. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):527–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Gamper H., Hearst J. E. The effects of covalent additions of a psoralen on transcription by E. coli RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6843–6854. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]