Abstract
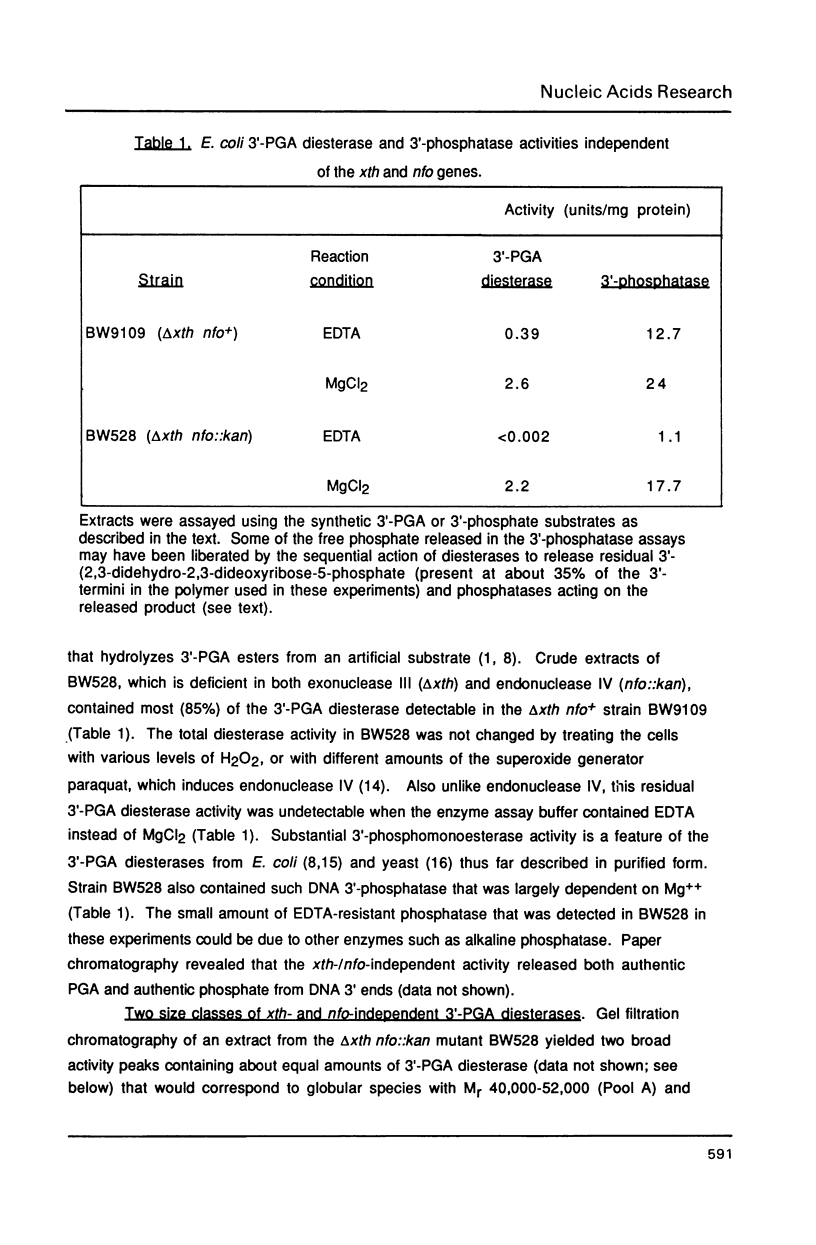
Escherichia coli contains multiple enzymes that hydrolyze deoxyribose fragments (phosphoglycolaldehyde, PGA) from the 3' termini of a synthetic DNA substrate. The major such activities are the main bacterial apurinic endonucleases, exonuclease III and endonuclease IV. In a double mutant deficient in both of these oxidation repair enzymes, Mg++-dependent 3'-PGA diesterase was detected at 3% the level found in wild-type bacteria. Gel filtration fractionated this residual diesterase activity into two peaks of Mr 40,000-52,000 (Pool A) and Mr 22,000-30,000 (Pool B) with differing abilities to remove 3'-phosphates from DNA. These multiple repair activities were resolved in 3'-PGA diesterase activity gels. The exonuclease III and endonuclease IV bands were identified using the purified proteins and by their specific absence from strains defective for the respective structural genes. Gel filtration Pool B yielded two activity bands of apparent Mr 25,000 and 28,000, but Pool A did not form a new band in the activity gels. Incubation of activity gels in different transition metals or boiling of the samples before electrophoresis also served to distinguish the various activities. The possible identities of the novel E. coli 3'-PGA diesterases and the importance of multiple repair enzymes for 3' damages are discussed.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E., Weiss B. Endonuclease IV of Escherichia coli is induced by paraquat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3189–3193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Saporito S. M., Spitzer S. G., Weiss B. Endonuclease IV (nfo) mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1120–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1120-1127.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Gates F. T., 3rd, Linn S. Purification and properties of Escherichia coli endodeoxyribonuclease V. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):224–231. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Halbrook J. Inducible repair of oxidative DNA damage in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):466–468. doi: 10.1038/304466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Johnson A., Fung D. Exonuclease III and endonuclease IV remove 3' blocks from DNA synthesis primers in H2O2-damaged Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7731–7735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Linn S. On the recognition and cleavage mechanism of Escherichia coli endodeoxyribonuclease V, a possible DNA repair enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2848–2855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr S. B., D'Ari R., Touati D. Oxygen-dependent mutagenesis in Escherichia coli lacking superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8268–8272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. The biology of oxygen radicals. Science. 1978 Sep 8;201(4359):875–880. doi: 10.1126/science.210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giloni L., Takeshita M., Johnson F., Iden C., Grollman A. P. Bleomycin-induced strand-scission of DNA. Mechanism of deoxyribose cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8608–8615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Demple B. Overproduction of peroxide-scavenging enzymes in Escherichia coli suppresses spontaneous mutagenesis and sensitivity to redox-cycling agents in oxyR-mutants. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2611–2617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03111.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner W. D., Rodriguez L. O., Hecht S. M., Haseltine W. A. gamma Ray induced deoxyribonucleic acid strand breaks. 3' Glycolate termini. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):711–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson F. Chemical changes induced in DNA by ionizing radiation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:115–154. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. D., Johnson A. W., Demple B. Homogeneous Escherichia coli endonuclease IV. Characterization of an enzyme that recognizes oxidative damage in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8066–8071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. G., Weiss B. Exonuclease III of Escherichia coli K-12, an AP endonuclease. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):201–211. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanos A., Hübscher U. Recovery of functional proteins in sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:263–277. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]