Abstract
In our previous analysis of the information at binding sites on nucleic acids, we found that most of the sites examined contain the amount of information expected from their frequency in the genome. The sequences at bacteriophage T7 promoters are an exception, because they are far more conserved (35 bits of information content) than should be necessary to distinguish them from the background of the Escherichia coli genome (17 bits). To determine the information actually used by the T7 RNA polymerase, promoters were chemically synthesized with many variations and those that function well in an in vivo assay were sequenced. Our analysis shows that the polymerase uses 18 bits of information, so the sequences at phage genomic promoters have significantly more information than the polymerase needs. The excess may represent the binding site of another protein.
Full text
PDF
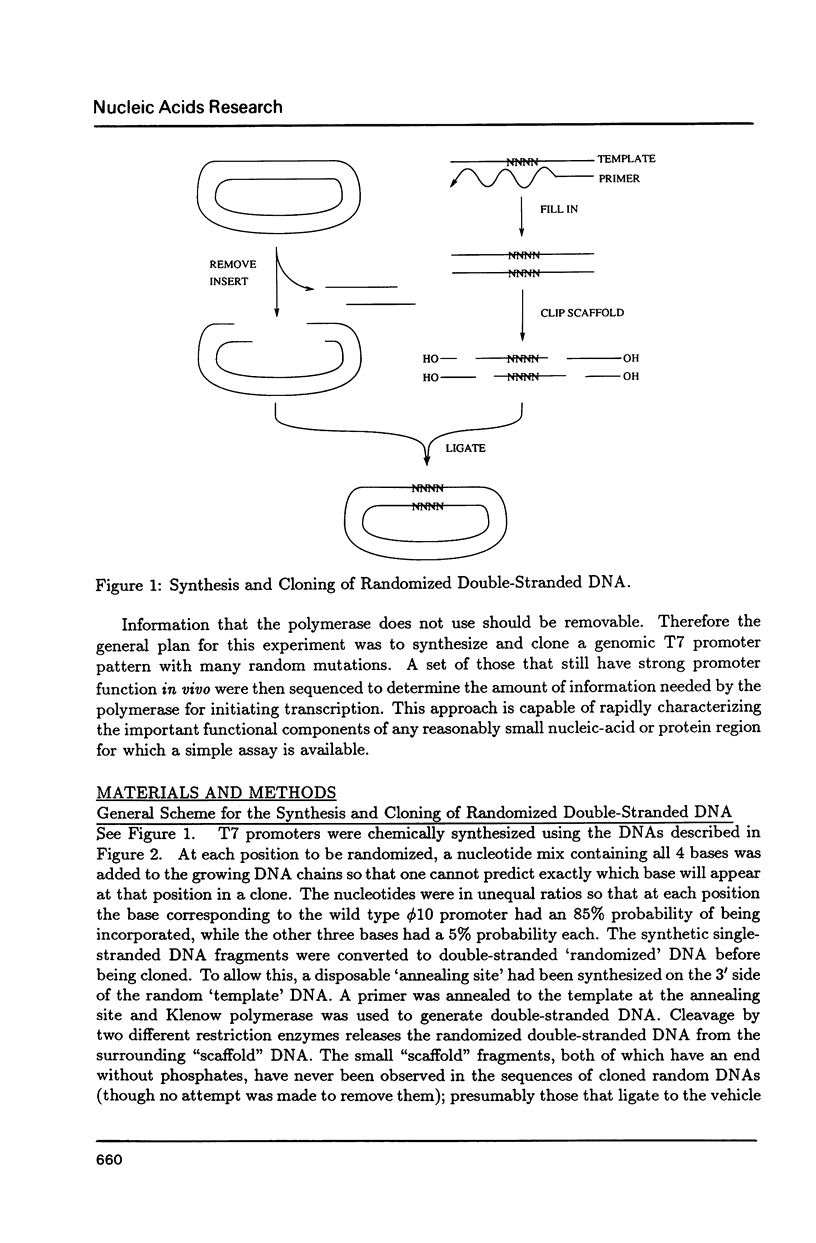







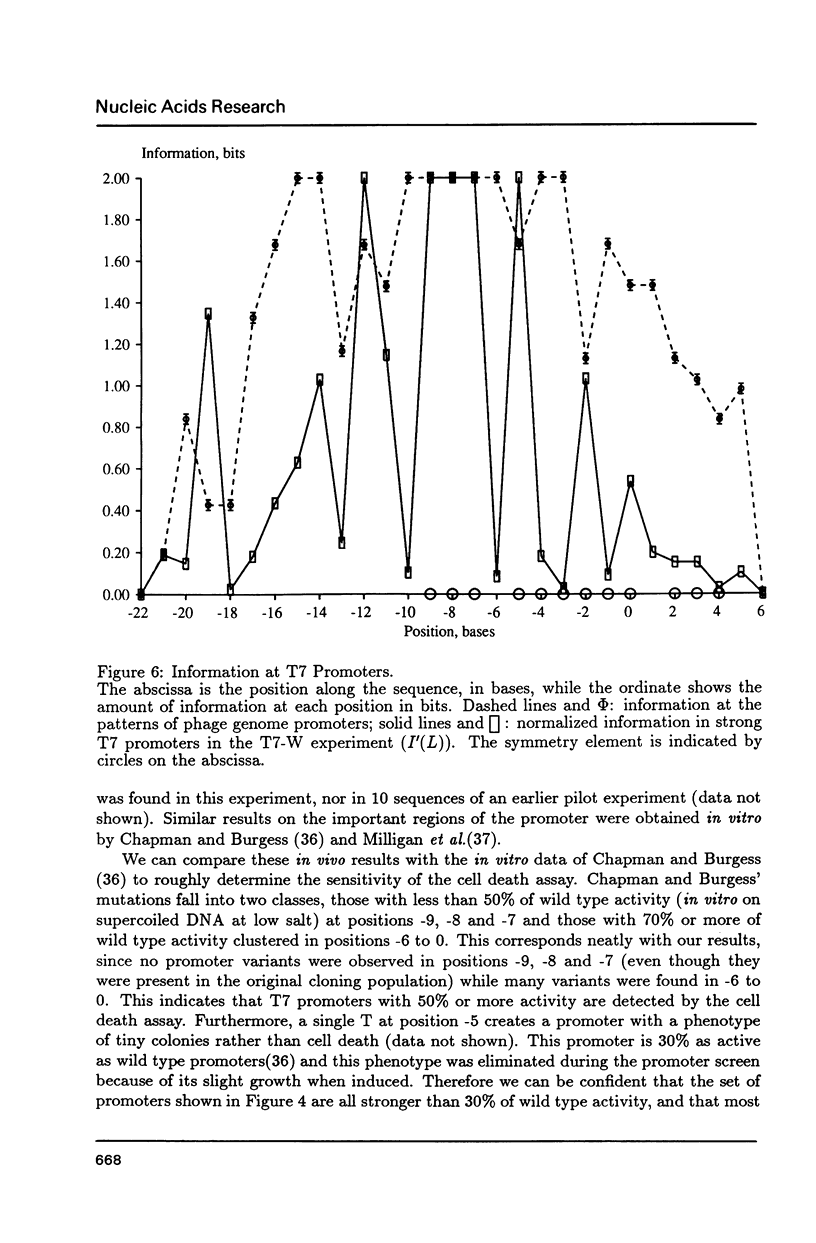






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., McGrath J., Waskell L. New RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T7. Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):227–231. doi: 10.1038/228227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman K. A., Burgess R. R. Construction of bacteriophage T7 late promoters with point mutations and characterization by in vitro transcription properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5413–5432. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman K. A., Gunderson S. I., Anello M., Wells R. D., Burgess R. R. Bacteriophage T7 late promoters with point mutations: quantitative footprinting and in vivo expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4511–4524. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clift B., Haussler D., McConnell R., Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D. Sequence landscapes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):141–158. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. E., Oliphant A. R., Struhl K. Mutagenesis with degenerate oligonucleotides: an efficient method for saturating a defined DNA region with base pair substitutions. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:558–568. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. S., Loeb L. A. Promoters selected from random DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7405–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A., Hayflick J., Dinkelspiel K., de Boer H. A. Mutagenesis of the three bases preceding the start codon of the beta-galactosidase mRNA and its effect on translation in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):623–629. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe L. K., Carter A. D., McAllister W. T. Identification of a potential control region in bacteriophage T7 late promoters. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):653–656. doi: 10.1038/299653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., Morris C., Rosenberg A. H., Studier F. W. Utilization of bacteriophage T7 late promoters in recombinant plasmids during infection. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):527–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley J. L., Strothkamp R. E., Sarris A. H., Coleman J. E. T7 RNA polymerase: promoter structure and polymerase binding. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):528–537. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Struhl K. The use of random-sequence oligonucleotides for determining consensus sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:568–582. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterman H. L., Coleman J. E. T7 ribonucleic acid polymerase-promotor interactions. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4884–4892. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao R. N., Rogers S. G. Plasmid pKC7: a vector containing ten restriction endonuclease sites suitable for cloning DNA segments. Gene. 1979 Sep;7(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa M. D. Four T7 RNA polymerase promoters contain an identical 23 bp sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG C. M., EDGAR R. S. A critical test of a current theory of genetic recombination in bacteriophage. Genetics. 1962 Feb;47:187–208. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Information content of binding sites on nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D. Computer methods for analyzing sequence recognition of nucleic acids. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:241–263. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. Quantitative analysis of the relationship between nucleotide sequence and functional activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6661–6679. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


