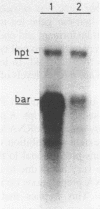
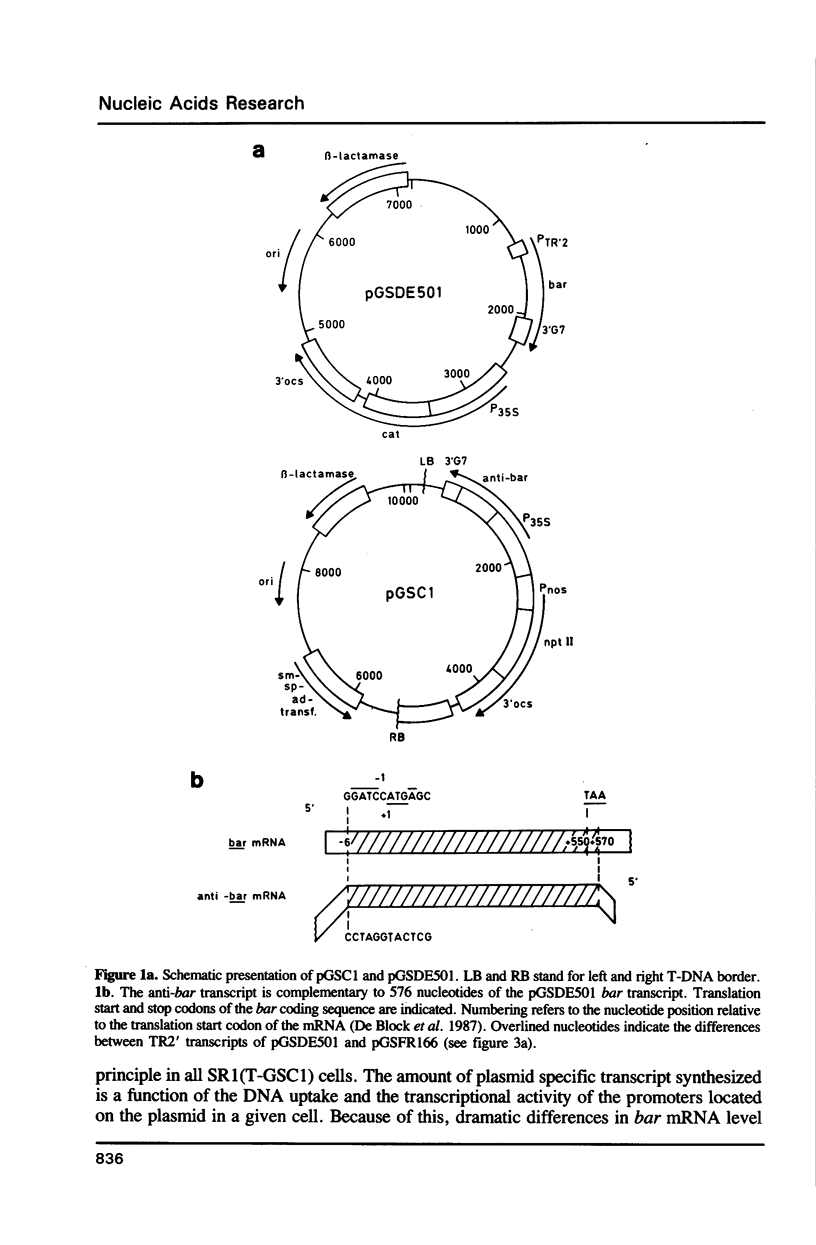
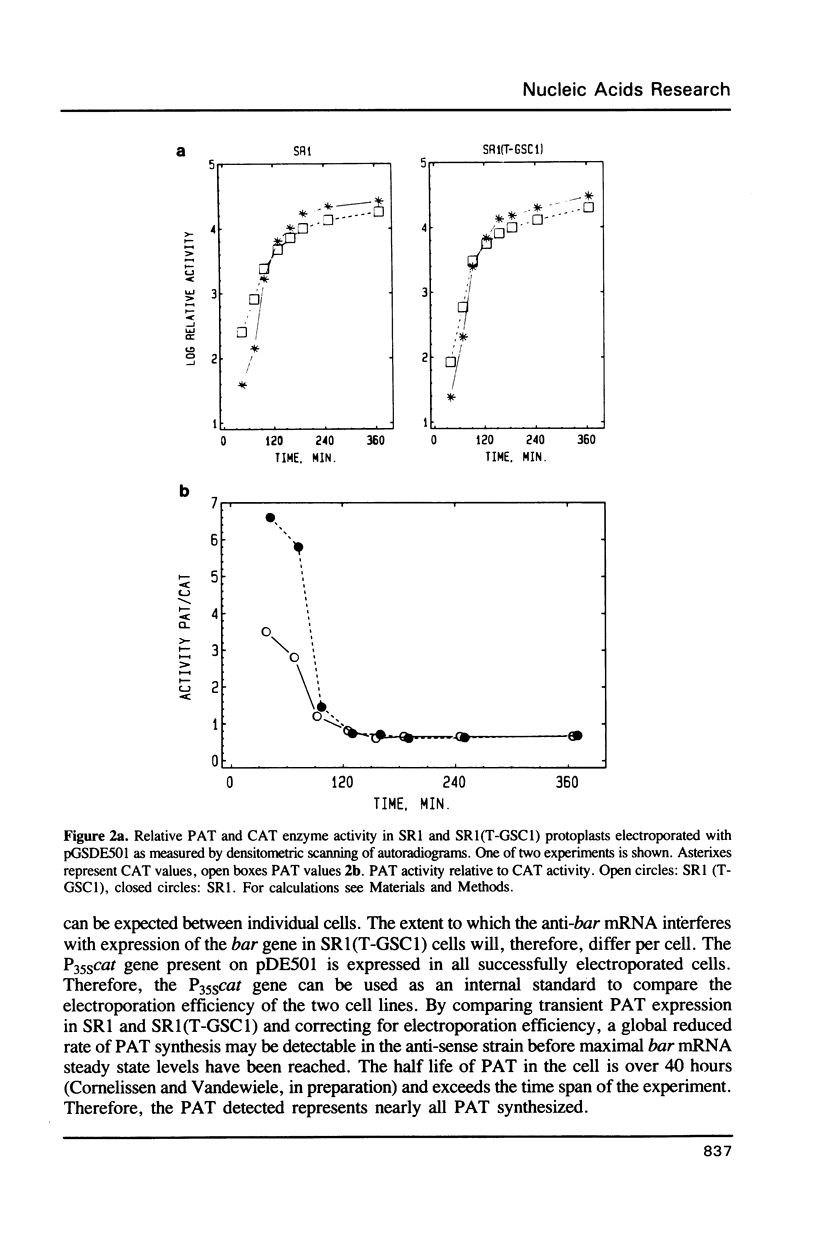
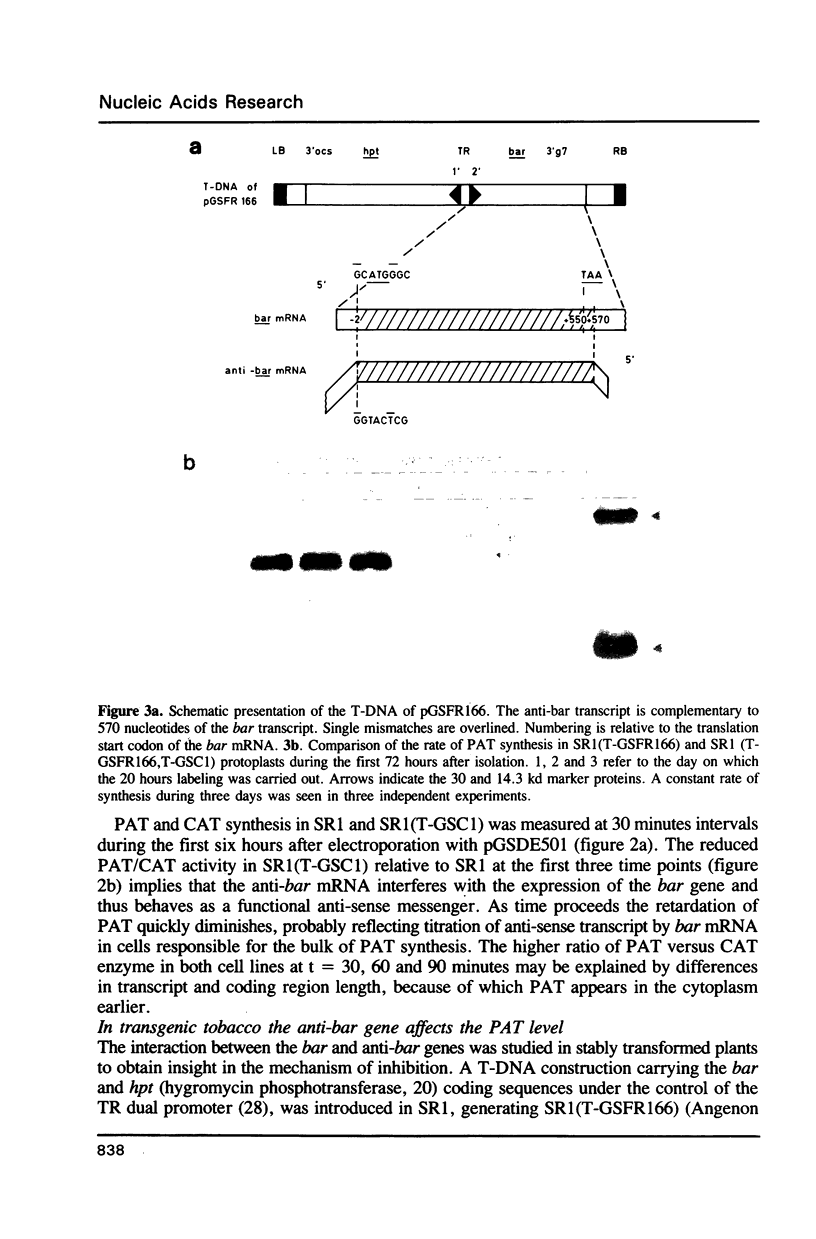
Abstract
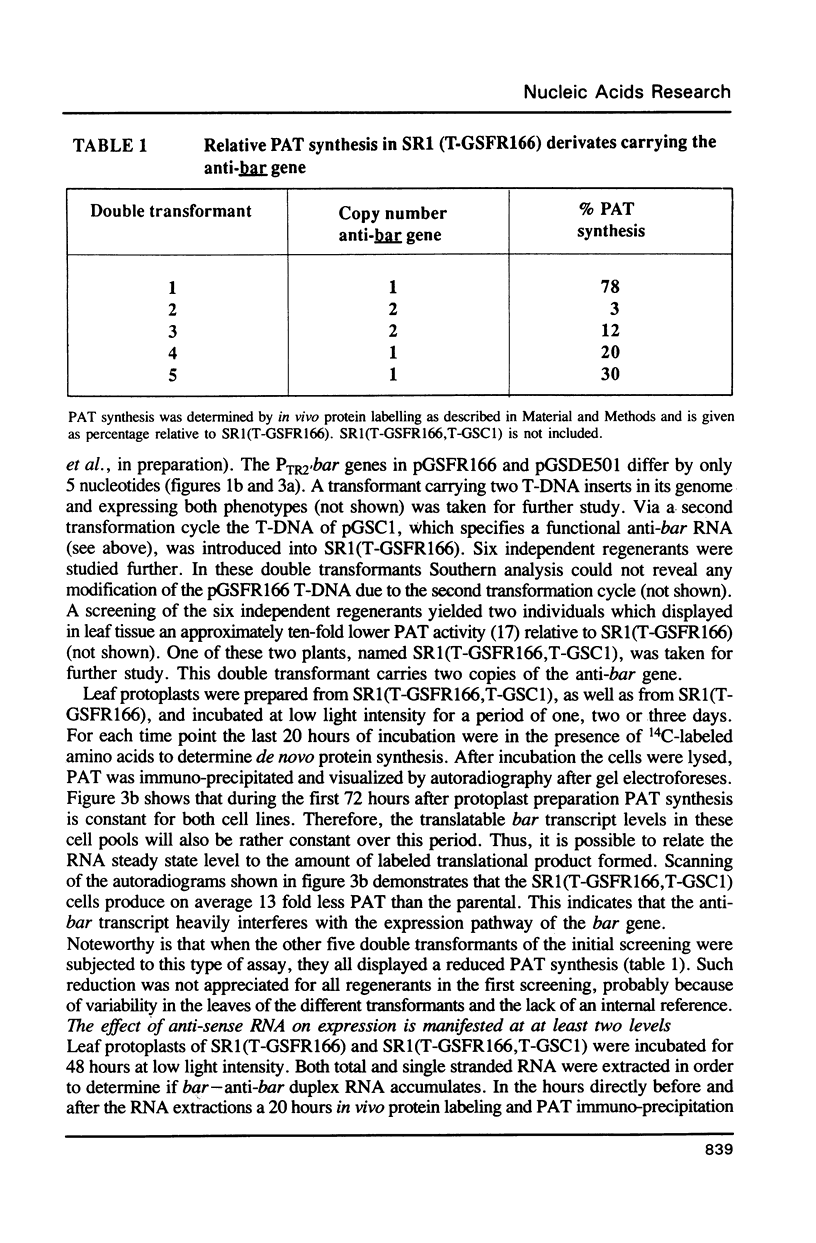
The effect of anti-sense RNA on the expression of the bialaphos resistance (bar) gene which encodes phosphinothricin acetyl transferase (PAT), was analysed in tobacco. Transient expression studies revealed that an anti-bar RNA with sequence complementarity to the complete bar coding region, inhibits PAT synthesis. To quantify the phenomenon, SR1 tobacco cells were transformed twice to introduce first a hybrid bar gene with a reporter gene and in a second instance an anti-bar gene. A first cycle transformant and a double transformant derived herefrom in which PAT synthesis was reduced to only 8%, were studied in detail. The interference of the anti-sense gene with the expression of the bar gene is manifested at least two levels. First, the bar mRNA steady state level is significantly reduced relative to the parental whereas the transcript level of the reporter gene is unchanged. Comparison of bar mRNA levels in total and single stranded (ss) RNA preparations demonstrated that little if any stably base-pairing bar and anti-bar RNA accumulates. Secondly, a three fold reduction of PAT synthesis per bar mRNA is observed. This supposes that because of unstable interactions with the complementary anti-bar RNA either a substantial part of the bar mRNA detected does not enter the cytoplasm and/or that in the cytoplasm the bar mRNA is less efficiently translated. It is not clear if or how the reduced bar mRNA level is related to such unstable interactions.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton N. K., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):864–869. doi: 10.1038/282864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E., Gugel K. H., Hägele K., Hagenmaier H., Jessipow S., König W. A., Zähner H. Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 98. Phosphinothricin und Phosphinothricyl-Alanyl-Alanin. Helv Chim Acta. 1972 Jan 31;55(1):224–239. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19720550126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. D., Botterman J., Vandewiele M., Dockx J., Thoen C., Gosselé V., Movva N. R., Thompson C., Montagu M. V., Leemans J. Engineering herbicide resistance in plants by expression of a detoxifying enzyme. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2513–2518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley T. E., Nellen W., Gomer R. H., Firtel R. A. Phenocopy of discoidin I-minus mutants by antisense transformation in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):633–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delauney A. J., Tabaeizadeh Z., Verma D. P. A stable bifunctional antisense transcript inhibiting gene expression in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4300–4304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Ruiz J. R., Kaper J. M. Isolation of viral double-stranded RNAs using a LiCl fractionation procedure. Prep Biochem. 1978;8(1):1–17. doi: 10.1080/00327487808068215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Weintraub H. Inhibition of thymidine kinase gene expression by anti-sense RNA: a molecular approach to genetic analysis. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. D., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. High level expression of introduced chimaeric genes in regenerated transformed plants. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2411–2418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03949.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Wold B. J. Stable reduction of thymidine kinase activity in cells expressing high levels of anti-sense RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacatena R. M., Cesareni G. Base pairing of RNA I with its complementary sequence in the primer precursor inhibits ColE1 replication. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):623–626. doi: 10.1038/294623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliga P., Sz-Breznovits A., Márton L. Streptomycin-resistant plants from callus culture of haploid tobacco. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 4;244(131):29–30. doi: 10.1038/newbio244029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A. Injected anti-sense RNAs specifically block messenger RNA translation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):144–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A unique mechanism regulating gene expression: translational inhibition by a complementary RNA transcript (micRNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1966–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Melton D. A. Antisense RNA injections in fertilized frog eggs reveal an RNA duplex unwinding activity. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):599–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg U. B., Preiss A., Seifert E., Jäckle H., Knipple D. C. Production of phenocopies by Krüppel antisense RNA injection into Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):703–706. doi: 10.1038/313703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein S. J., Dimaio J., Strand M., Rice D. Stable and heritable inhibition of the expression of nopaline synthase in tobacco expressing antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8439–8443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Translational control of IS10 transposition. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Gietz R. D., Hodgetts R. B. Overlapping transcription units in the dopa decarboxylase region of Drosophila. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):279–281. doi: 10.1038/322279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli A., Rickles R. J., Vassalli J. D. Antisense RNA directed against the 3' noncoding region prevents dormant mRNA activation in mouse oocytes. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):680–684. doi: 10.1126/science.2456615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J. Control of ColE1 plasmid replication: the process of binding of RNA I to the primer transcript. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velten J., Velten L., Hain R., Schell J. Isolation of a dual plant promoter fragment from the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2723–2730. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]