Abstract
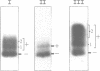
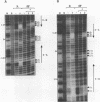
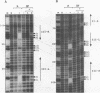
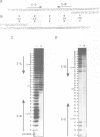
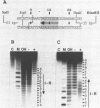
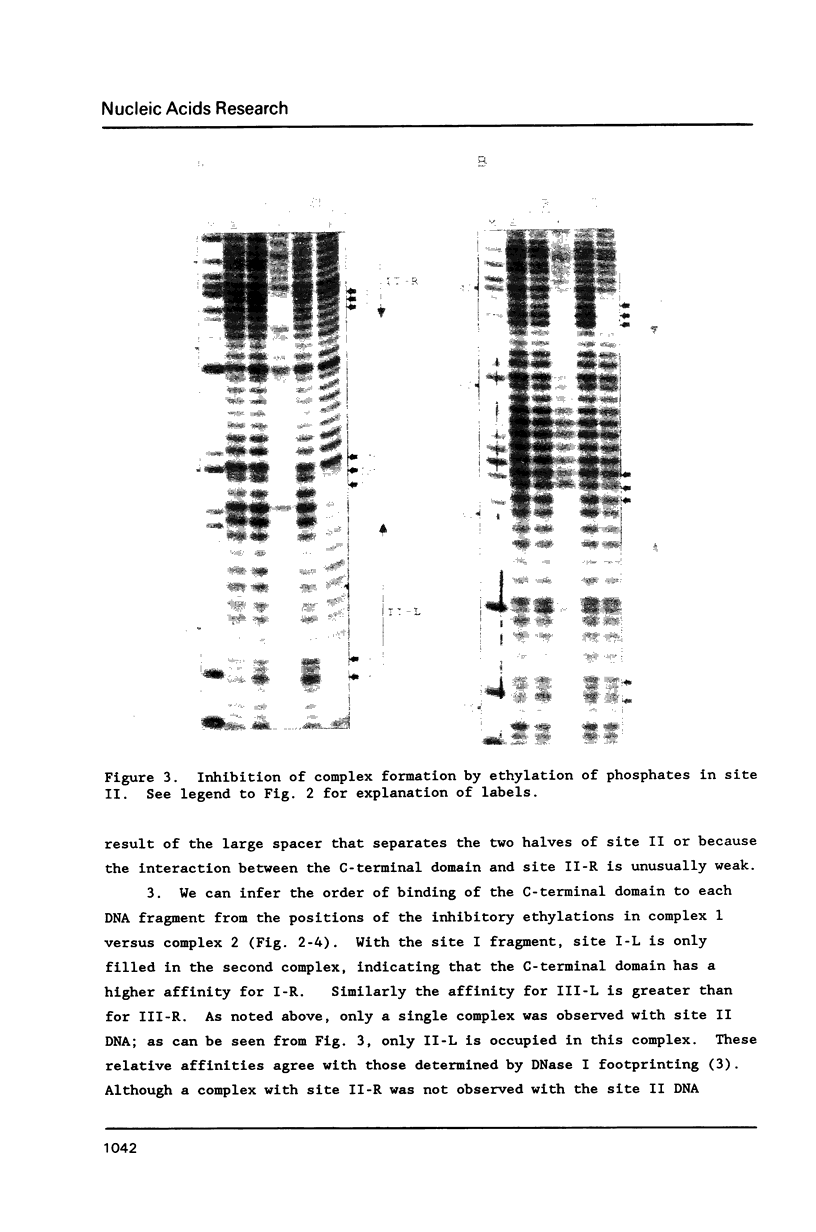
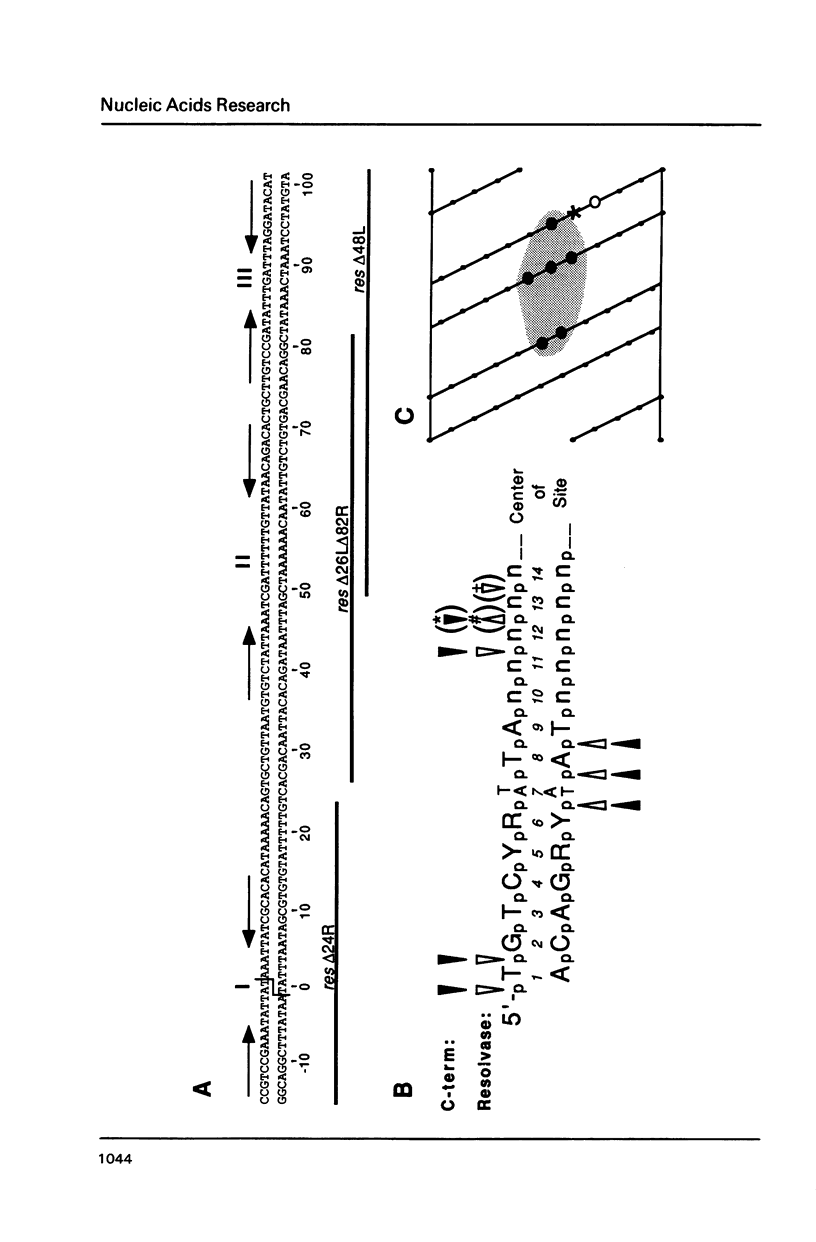
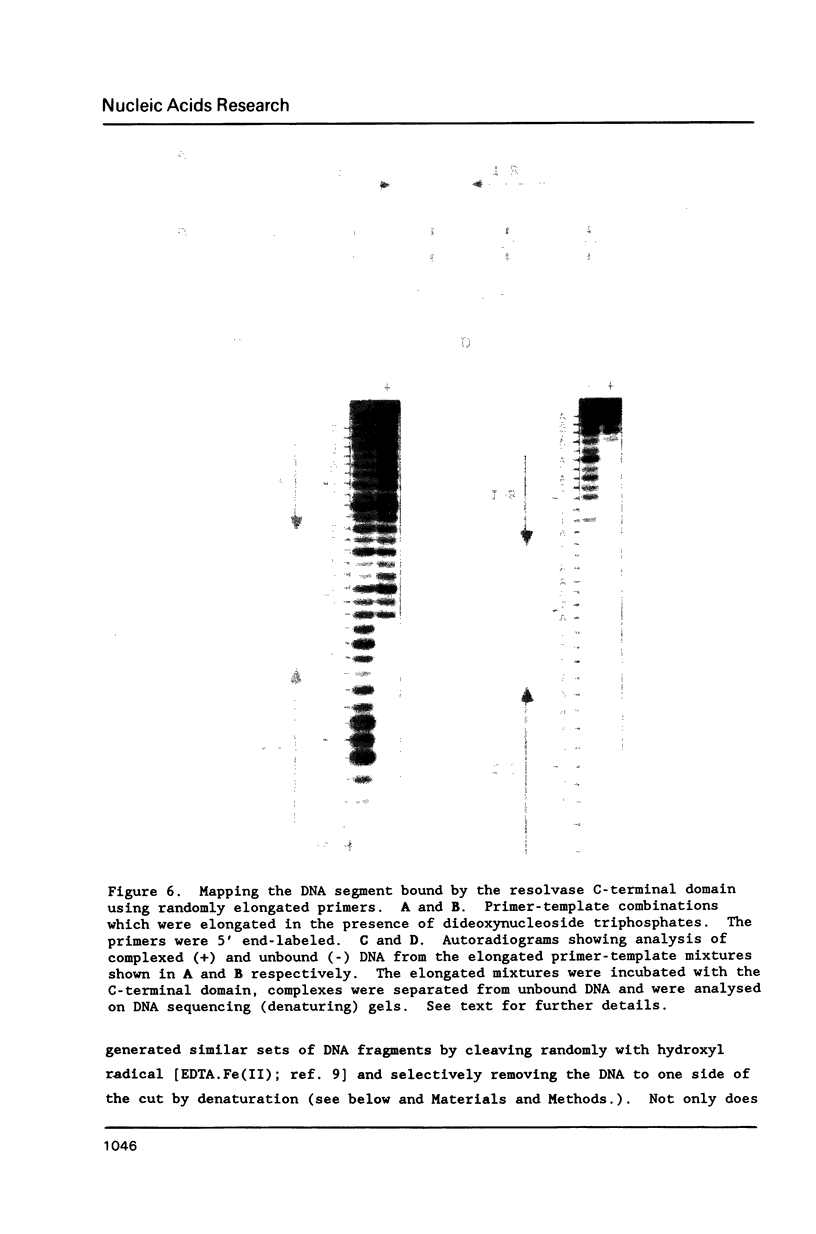
The carboxyl-terminal domain of gamma delta resolvase binds to each half of the three resolvase binding sites that constitute the recombination site, res. Ethylation inhibition experiments show that the phosphate contacts made by the C-terminal DNA binding domain are similar to those made by intact resolvase, with the exception of a single phosphate at the inside end of each contact region which is contacted solely by the intact resolvase. The DNA binding domain makes essentially identical contacts to all 6 half sites, whereas the intact resolvase makes slightly different contacts to each binding site. Despite its small size, only 43 amino acid residues, the resolvase C-terminal domain interacts with an unusually large segment of DNA. Phosphate contacts extend across an adjacent major and minor groove of DNA and about one third of the circumference around the helix. The minimal binding segment, determined experimentally, is a 12 bp sequence that includes the 9 base pair inverted repeat (common to all half sites), the adjacent 3 base pairs (towards the center of the intact resolvase binding site), and phosphates at both ends.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Grindley N. D., Templeton N. S., Steitz T. A. Cleavage of the site-specific recombination protein gamma delta resolvase: the smaller of two fragments binds DNA specifically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2001–2005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. E., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. A phage repressor-operator complex at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):596–601. doi: 10.1038/316596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliason J. L., Weiss M. A., Ptashne M. NH2-terminal arm of phage lambda repressor contributes energy and specificity to repressor binding and determines the effects of operator mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2339–2343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falvey E., Grindley N. D. Contacts between gamma delta resolvase and the gamma delta res site. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):815–821. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04824.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Reed R. R. Transpositional recombination in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:863–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Adhya S., Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Site-specific DNA binding of nuclear factor I: analyses of cellular binding sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):964–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F., Grindley N. D. Analysis of gamma delta resolvase mutants in vitro: evidence for an interaction between serine-10 of resolvase and site I of res. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5429–5433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht M. H., Nelson H. C., Sauer R. T. Mutations in lambda repressor's amino-terminal domain: implications for protein stability and DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2676–2680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W., Schleif R. A dimer of AraC protein contacts three adjacent major groove regions of the araI DNA site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Cleavage of DNA with methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II): reaction conditions and product analyses. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3934–3945. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otwinowski Z., Schevitz R. W., Zhang R. G., Lawson C. L., Joachimiak A., Marmorstein R. Q., Luisi B. F., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of trp repressor/operator complex at atomic resolution. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):321–329. doi: 10.1038/335321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Krovatin W., Jeffrey A., Sauer R. T. The N-terminal arms of lambda repressor wrap around the operator DNA. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):441–443. doi: 10.1038/298441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluka J. P., Horvath S. J., Bruist M. F., Simon M. I., Dervan P. B. Synthesis of a sequence-specific DNA-cleaving peptide. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1129–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.3120311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A. Hydroxyl radical "footprinting": high-resolution information about DNA-protein contacts and application to lambda repressor and Cro protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warwicker J., Engelman B. P., Steitz T. A. Electrostatic calculations and model-building suggest that DNA bound to CAP is sharply bent. Proteins. 1987;2(4):283–289. doi: 10.1002/prot.340020404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Grindley N. D. Analysis of the gamma delta res site. Sites required for site-specific recombination and gene expression. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 15;179(4):667–687. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton R. P., Brown E. L., Ptashne M. Substituting an alpha-helix switches the sequence-specific DNA interactions of a repressor. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90491-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton R. P., Ptashne M. Changing the binding specificity of a repressor by redesigning an alpha-helix. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):601–605. doi: 10.1038/316601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]