Abstract
The integrity of blood vessels controls vascular permeability and extravasation of blood cells, across the endothelium. Thus, the impairment of endothelial integrity leads to hemorrhage, edema, and inflammatory infiltration. However, the molecular mechanism underlying vascular integrity has not been fully understood. Here, we demonstrate an essential role for A-kinase anchoring protein 12 (AKAP12) in the maintenance of endothelial integrity during vascular development. Zebrafish embryos depleted of akap12 (akap12 morphants) exhibited severe hemorrhages. In vivo time-lapse analyses suggested that disorganized interendothelial cell-cell adhesions in akap12 morphants might be the cause of hemorrhage. To clarify the molecular mechanism by which the cell-cell adhesions are impaired, we examined the cell-cell adhesion molecules and their regulators using cultured endothelial cells. The expression of PAK2, an actin cytoskeletal regulator, and AF6, a connector of intercellular adhesion molecules and actin cytoskeleton, was reduced in AKAP12-depleted cells. Depletion of either PAK2 or AF6 phenocopied AKAP12-depleted cells, suggesting the reduction of PAK2 and AF6 results in the loosening of intercellular junctions. Consistent with this, overexpression of PAK2 and AF6 rescued the abnormal hemorrhage in akap12 morphants. We conclude that AKAP12 is essential for integrity of endothelium by maintaining the expression of PAK2 and AF6 during vascular development.
Keywords: AKAP12 protein, human; disease models, animal; hemorrhage; hemostatic disorders; MLLT4 protein, human; PAK2 protein, human; zebrafish
Introduction
Endothelial cells line the interior surface of blood vessels and form barrier between lumen and tissues. Interendothelial cell-cell adhesion regulates vascular integrity, controlling the exchange of fluids, electrolytes, and proteins across the endothelial barrier (Taddei et al., 2008). Impairment of vascular integrity results in hemorrhage and edema in tissues and organs.
The structural integrity of endothelium is dependent upon tight and adherens junctions between endothelial cells. Adherens junctions are composed of vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin), as well as nectins and JAMs (A-C), all of which interact homophilically with each other. Tight junctions are zipper-like structures formed by homophilic interactions between occludins and claudins (Anderson and Van Itallie, 1995; Balda and Matter, 1998; Aijaz et al., 2006). VE-cadherin and nectin are linked to actin via β-catenin/α-catenin and AF6 (afadin), respectively. Similarly, tight junction molecules are anchored to actin via zona occludens-1/2 (ZO-1/2). Therefore, the adhesion between the endothelial cells depends on not only adhesion molecules but also the actin filaments that support the intercellular adhesions.
Formation of both cortical actin filaments at the cell-cell adhesion and stress fibers between focal adhesions is regulated by actin-myosin coupling that is dependent on the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of myosin light chain (MLC) by MLC kinase (MLCK) and MLC phosphatase (MLCP). The activation of Rho kinase, an effector of GTP-bound RhoA, results in contraction by inactivating MLCP. p21-activated kinase (PAK) family proteins (PAK1 and PAK2), effectors of GTP-bound Cdc42 or Rac, are reported to either increase or decrease MLC phosphorylation (Stockton et al., 2004). Interestingly, PAK1 and PAK2 appear to play opposite roles in regulating MLC phosphorylation. While depletion of PAK1 decreases phospho-MLC levels in cells, that of PAK2 enhances MLC phosphorylation (Coniglio et al., 2008).
We have previously shown that A-kinase anchoring protein 12 (AKAP12) (also called AKAP250, gravin, and SSeCKS) in astrocytes is important for vascular stability in the brain and retina by halting angiogenesis and inducing barriergenesis (Choi et al., 2007; Choi and Kim, 2008). AKAP12 is a multivalent scaffolding protein that mediates the precise spatiotemporal control of the activities of several protein kinases, such as protein kinase A (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC). It provides a dynamic and reversible platform for multiple signaling pathways (Wong and Scott, 2004). In addition, AKAP12 is expressed in various cell types, including neurons and astrocytes, and is implicated in the control of cell migration and morphogenesis during embryogenesis in mice and zebrafish (Weiser et al., 2007; Choi and Kim, 2008). However, the function of AKAP12 in endothelial cells has not been clarified.
In this study, we aimed at investigating the role for AKAP12 in the vascular integrity using zebrafish embryos and cultured endothelial cells. akap12 morphants exhibited severe hemorrhages. AKAP12 depletion in cultured endothelial cells resulted in the reduced expression of PAK2 and AF6 involved in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton. Hemorrhage in akap12-depleted zebrafish embryos was rescued by the overexpression of PAK2 and AF6. Our results reveal the importance of AKAP12-mediated maintenance of PAK2 and AF6 for vascular integrity.
Results
Depletion of akap12 leads to hemorrhage in zebrafish embryos
In zebrafish, two isoforms of akap12 (akap12α and akap12β), splicing variants from the same gene, have been identified, although the functional difference between these two isoforms has not yet been clarified. Thus, we knocked down each isoforms in zebrafish to examine the functional distinction between akap12α and akap12β by using 2 types of MOs for each isoforms (MO1, mRNA splicing-blocking and MO2, translation-blocking) (Supplemental Figure 1A) (Corey and Abrams, 2001). The knockdown efficiency by the MOs (MO1 and MO2) was confirmed by experimental procedures (Supplemental Figures 1B and 1C).
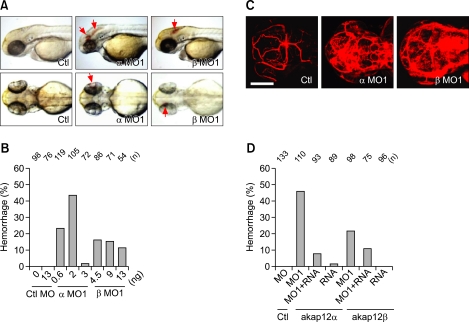
We found that reduction of akap12α and akap12β by the injection of α and β MOs led to hemorrhages in zebrafish embryos (red arrows) (Figure 1A and Supplemental Figures 1D and 1E). Hemorrhages started between 48 and 72 hpf and were found at multiple sites such as in the brains and eyes (red arrows) (Figure 1A). We observed hemorrhage in the brain mainly. Furthermore, the injection of αMO1 led to hemorrhages at lower MO dosages than βMO1 and resulted in a dose-dependent increase proportion of embryos showing hemorrhages (Figure 1B and Supplemental Table 1). However, at higher doses both MOs (αMO1, > 3 ng; βMO1, > 13 ng) induced heart failure, which led to a reduction in the hemorrhage rate.
Figure 1.
Loss of akap12 leads to hemorrhage. (A) Lateral views (top) and dorsal views (bottom) of akap12 morphants (α MO1, 2 ng; β MO1, 7.5 ng) at 48 hpf. Red arrows denote hemorrhage. (B) Incidence of hemorrhage by morpholino dose at 48-72 hpf. Note that at a higher MO dosage (αMO1, > 3 ng; βMO1, > 13 ng), the rate of hemorrhage was reduced because of circulation failure by failing heart in akap12 morphant. (C) Images of vasculature after by injection of fluorescent tracers (rhodamine-dextran, 2000 kDa) into the lumen of the blood vessels. Fluorescent tracers observed by a confocal microscope at 48 to 60 hpf. Scale bar, 200 µm. (D) akap12 mRNA rescue experiment. Coinjection of akap12 mRNA (akap12α, 50 pg; akap12β, 50 pg) with akap12 MOs (akap12α, 2 ng; akap12β, 7.5 ng) reduced the ratio of hemorrhage. Ctl, control; MO, morpholino; MO1, splicing blocking MO; n, number of the embryos observed.
We assumed that multiple hemorrhages might reflect the increase in the permeability of blood vessels in the akap12 morphants. We thus examined vascular permeability in the akap12 morphants by intravascular injection of a fluorescent tracer (rhodamine-dextran, 2000 kDa). The tracer did not clearly image the blood vessels in the akap12 morphants, while it generated a fine image of the brain blood vessels in the control (Figure 1C), suggesting the leakage of the tracer from the blood vessels in akap12 morphants. The hemorrhage (Figure 1A) and fluorescent dye leakage (Figure 1C) suggest a reduced vascular integrity in akap12 morphants.
To determine whether hemorrhage is due to the depletion of akap12, we performed rescue experiment using zebrafish akap12 mRNA that is resistant to akap12 MOs. When embryos were coinjected with akap12 MOs (akap12α, 2 ng; akap12β, 7.5 ng) and in vitro transcribed zebrafish akap12 mRNAs (akap12α, 50 pg; akap12β, 50 pg) at the 1-cell stage, the rate of hemorrhage was significantly reduced by the injection of akap12 mRNA (Figure 1D and Supplemental Table 2). These results indicate that the hemorrhages are caused by the reduction in akap12 expression. In a previous study by Weiser et al., akap12β morphants show trunk defects that are caused by inappropriate convertgence-extension movements during gastrulation (Weiser et al., 2007). Similarly, we observed trunk defects in akap12 morphants (Supplemental Figure 1E). However, hemorrhages (arrows) were found in the akap12 morphants with and without trunk defects (Supplemental Figures 1D and 1E and Supplemental Table 1). These findings demonstrate that hemorrhages are not caused by abnormal convergence-extension movements during gastrulation and suggest an essential role for akap12 in vascular integrity during blood vessel development.
akap12 is expressed in the vasculature
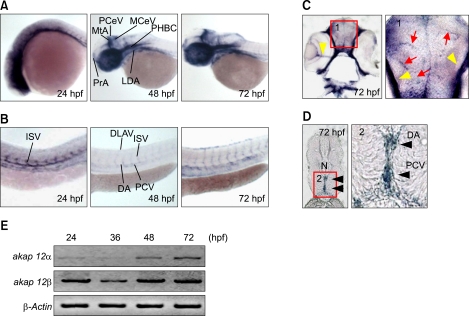
To investigate whether hemorrhage was caused by the depletion of akap12 in the vasculature, we examined the expression of akap12 by in situ hybridization (ISH). We could not obtain the specific ISH probes enabling us to distinguish the two akap12 isoforms, because isoform-specific sequences are too short. Therefore, we used a pan-akap12 mRNA probe (Supplemental Figure 1A) and found that akap12 mRNA was specifically expressed in the blood vessels of the trunk at 24 hpf (Figures 2A and 2B), although in the head it was expressed ubiquitously at a low level, akap12 was strongly expressed in the vasculature of both head and trunk. In addition, strong expression of akap12 was found in microvessels (Figure 2C, red arrows) in the brain and large vessels in the retina (Figure 2C, yellow arrowheads) and the trunk (Figure 2D, black arrowheads). Furthermore, RT-PCR analyses revealed that both akap12 isoforms were strongly expressed at some point during active angiogenesis in the brain and trunk (between 24 and 72 hpf) (Figure 2E). These results suggest that depletion of akap12 in the blood vessels is the primary cause of hemorrhage.
Figure 2.
akap12 is expressed in the blood vessels. (A, B) Whole mount ISH of zebrafish embryos using akap12 mRNA probe at 24, 48, and 72 hpf. C and D, Sections of the brain (C) and the trunk (D) obtained from whole mount ISH at 72 hpf. Positive signals were indicated by red arrows (pointing microvessels), yellow arrowheads (pointing the retinal vessels), and black arrowheads (pointing main trunk vessels). (E) RT-PCR analyses of akap12 isoforms during development at the time point indicated at the top. DA, dorsal aorta; DLAV, dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel; ISV, intersegmental vessel; LDA, lateral dorsal aorta; MCeV, middle cerebral vein; MtA, metencephalic artery; N, notochord; PCV, posterior cardinal vein; PCeV, posterior cerebral vein; PHBC, primordial hindbrain channel; PrA, prosencephalic artery.
akap12 depletion results in the abnormal structure of blood vessels
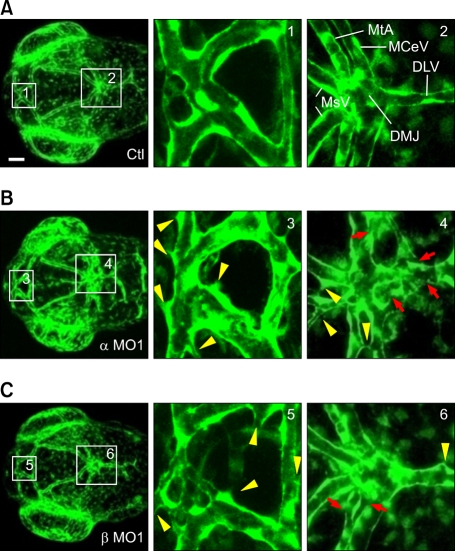
We considered the possibility that endothelial cell death might be induced by the depletion of akap12, causing blood vessel regression. To exclude this possibility, we performed TUNEL staining to elucidate whether endothelial cell death was induced in the akap12 morphants. There was no difference in TUNEL-positive staining between the akap12 morphants and the controls (Supplemental Figure 2), indicating that the death of endothelial cells was not the cause of hemorrhage in akap12 morphants. We further studied the vascular structure to examine whether structural alteration was induced in akap12 morphants. To visualize the blood vessels, we used a transgenic line, Tg(fli1:EGFP)y1, which expressed EGFP exclusively in vascular endothelial cells in which the Fli1 promoter is activated. There were more abnormal sproutings (yellow arrow heads) in the akap12α and -β morphants than the control morphants (Figure 3). Furthermore, akap12 morphants showed a discontinuous endothelial layer (red arrows). Collectively, these data suggest the loosening of interendothelial cell-cell junctions in akap12 morphants.
Figure 3.
akap12 morphants exhibit abnormalities in vascular structure. (A-C) (A, control; B, akap12 α morphant (α MO1, 2 ng); C, akap12 β morphant (β MO1, 7.5 ng)), confocal EGFP images of the brain blood vessels of akap12-depleted Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 embryos at 60 hpf. Boxed regions numbered in the left panel were enlarged in the center and right panels. Abnormal sproutings (yellow arrowheads) and disruption (red arrows) of endothelial cells. Scale bar, 50 µm. DLV, dorsal longitudinal vein; DMJ, dorsal midline junction; MCeV, middle cerebral vein; MsV, mesencephalic vein; MtA, metencephalic artery.
Hemorrhage is attributable to the loss of cell-cell adhesions in akap12 morphant vessels
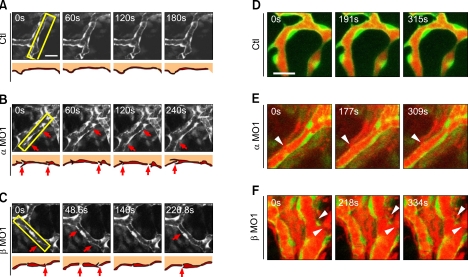
To further confirm these abnormalities of vascular structures in akap12 morphants, we examined vessel development by using in vivo confocal time-lapse imaging of the Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 fish embryos treated with MOs. We observed the vascular endothelial cells located on blood vessels around dorsal midline junction (DMJ), during the period between 48 and 60 hpf (Figure 4). The vessels of akap12 morphants exhibited unstable connections with their neighbors, due to frequent loss of cell-cell contacts (red arrows) (Figures 4B and 4C). In contrast, the blood vessels in the control embryos were in a quiescent state, as endothelial cells were stably connected (Figure 4A).
Figure 4.
akap12 knockdown causes the loss of endothelial cell-cell contacts and subsequent hemorrhage. (A-C) (A, control; B, akap12 α morphant (α MO1, 2 ng); C, akap12 β morphant (β MO1, 7.5 ng)), in vivo confocal time-lapse images of the endothelium of Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 embryos at 48-60hpf. Images were sequentially obtained after the time points (s, seconds) after starting observation (0 s). Boxed region was schematically illustrated at the bottom. akap12-silenced vascular endothelial cells had disconnections between endothelial cells (red arrows in the upper and lower panels). Scale bar, 20 µm. (D-F) (D, control; E, akap12 α morphant (α MO1, 2 ng); F, akap12 β morphant (β MO1, 7.5 ng)), in vivo confocal time-lapse images of Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 embryos in which red fluorescent dye (lysine-fixable rhodamine-dextran, 2000 kDa) was injected into the lumen of the blood vessel. Note the leakage of the tracers (white arrowheads) at the sites where cell-to-cell contacts were disrupted in the akap12 morphants. Scale bar, 20 µm.
We then examined whether the leakage of luminal fluorescence to the ablumen could be ascribed to the loss of cell-cell contacts in akap12 morphants by simultaneously imaging the blood vessels and the fluorescent tracer injected into blood vessels. Although the control vessels retained the tracers within the lumen, the tracers were frequently and massively leaked in various regions of the akap12 morphant vessels (Figures 4D-4F). Leakage of the tracers was found at the sites where the cell-cell contacts were disrupted (white arrowheads). These data strongly suggest that hemorrhage in akap12 morphants is due to the loss of integrity in interendothelial cell-cell adhesions.
AKAP12 depletion leads to the disruption of interendothelial junctions
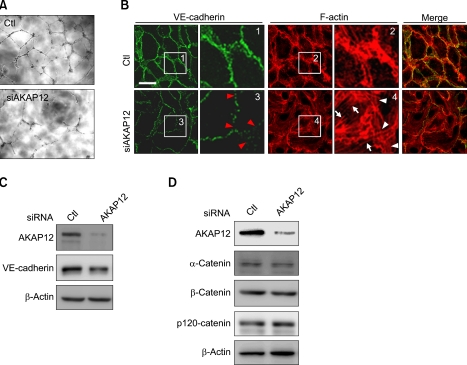
akap12 morphant embryos exhibited the disruption of interendothelial adhesions. To understand how AKAP12 depletion resulted in loosening of interendothelial adhesions, we first assessed the effect of AKAP12 depletion on tube formation in vitro by using cultured HUVECs. AKAP12 was knocked down by using AKAP12 siRNA duplex (Supplemental Figure 3A). AKAP12-depleted HUVECs exhibited discontinuous capillary structures (Figure 5A). To further find the primary changes causing the disruption of cell-cell adhesion in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs, we examined the expression of VE-cadherin and cortical actin by IF staining. AKAP12-depleted HUVECs exhibited marked increases in traversing actin stress fibers (white arrows) with a decrease of cortical actin filaments (white arrowheads) at the cell-cell contacts and the disruption of VE-cadherin junctions (red arrowheads) (Figure 5B).
Figure 5.
AKAP12-depleted endothelial cells exhibit the disruption of junctional integrity. (A) In vitro tube formation assay. Compared to the controls (top), HUVECs depleted of AKAP12 (bottom) showed poor development of capillary networks. (B) Fluorescence images of HUVECs (HUVECs treated with control siRNA, top; those treated with 10 nmol/L siRNA for AKAP12, bottom): immunostained with anti-VE-cadherin (Trepel et al.), rhodamine-phalloidine (center) and the merge (right). Boxed regions with number are enlarged. Note the disruption of VE-cadherin junctions (red arrowheads in box 3), and decreased cortical actin assembly (white arrowheads in box 4), and increased stress fiber formation (white arrows in box 4 in AKAP12 depleted endothelial cells). Scale bar, 20 µm. (C, D) Immunoblotting for VE-cadherin and α-, β-, and p120 catenin using the cell lysates from the HUVECs treated with siRNA as indicated at the top.
To clarify the molecular mechanism underlying the weakened cell-cell adhesion in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs, we examined the expression of VE-cadherin and its binding partners, α-catenin, β-catenin, and p120 catenin (Vestweber, 2008). Immunoblotting using specific antibodies for these molecules revealed subtle decreases in the amounts of VE-cadherin and α-catenin in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs, although those of β-catenin and p120-catenin were unchanged (Figures 5C and 5D). These results suggest that the disruption of interendothelial cell-cell adhesion is not caused by decreased expression of VE-cadherin and its binding partners in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs.
PAK2 is decreased in AKAP12-depleted endothelial cells
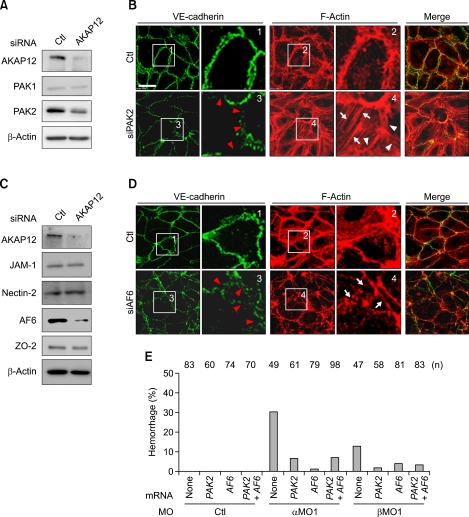
We tried to understand why the formation of cortical actin fibers was reduced, while that of stress fibers was enhanced in AKAP12-deficient HUVECs. PAKs, the effectors of GTP-bound Cdc42 or Rac, are well known to be involved in the reorganization of actin fibers by regulating actin-myosin coupling (Bokoch, 2003; Coniglio et al., 2008). We, thus, examined the expression of PAKs (PAK1 and PAK2) by western blotting. AKAP12-depleted HUVECs showed the reduction of the expression of PAK2, but not PAK1 (Figure 6A). To determine the effect of reduction in PAK2 expression, we performed IF staining to examine the actin cytoskeleton in PAK2-depleted HUVECs; expectedly, PAK2-depleted HUVECs exhibited enhanced stress fiber formation (white arrows) and reduced cortical actin bundles (white arrowheads) concomitant with disruption of cell-cell junctions (red arrowheads) (Figure 6B). Furthermore, PAK2-depleted HUVECs exhibited less capillary tube formation than control (Supplemental Figure 3B). These results suggest that the reduction in interendothelial cell-cell adhesions in AKAP12-depleted cells is partly due to decrease in PAK2 expression.
Figure 6.
AKAP12 depletion leads to decreases in PAK2 and AF6 expression. (A) Immunoblot analyses using antibodies indicated at the left using the cell lysates from HUVECs treated with siRNA indicated at the top. (B) Fluorescence images of immune-stained HUVECs treated with siRNA indicated at the left (anti-VE-cadherin, left; rhodamine phalloidine, center; and merged image, right). Boxed regions with number are enlarged. Note the increased stress fiber formation (white arrows in box4), decreased cortical actin assembly (white arrowheads in box 4), and the disruption of VE-cadherin junctions (red arrowheads in box 3 in PAK2-depleted endothelial cells). Scale bar, 20 µm. (C) Immunoblot analyses similar to A. (D) Fluorescence images similar to B. Note the similar changes found in AF6-depleted cells to those found in PAK2-depleted cells. (E) Rescue experiments using PAK2 and AF6 mRNAs. The percentage of embryos with hemorrhage at 48-72 hpf is indicated on the y-axis. Embryos were injected with a mixture of morpholino (akap12α, 2 ng; akap12β, 7.5 ng) and mRNA (in vitro transcribed mRNA; PAK2, 25 pg; AF6, 25 pg) as indicated on the x-axis.
AF6 is decreased in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs
PAK2 depletion potentially increases actin-myosin coupling by inducing MLC phosphorylation (Coniglio et al., 2008). Thus, PAK2 depletion may increase cortical actin assembly. However, AKAP12-depleted HUVECs exhibited reduced cortical actin assembly. We speculated that this was due to decrease in production of molecules involved in cortical actin assembly at the cell-cell adhesions. Immunoblotting using specific antibodies against JAM-1, nectin-2 and ZO-2, which anchors cell adhesion molecules to actin cytoskeleton, revealed that expression of these molecules was not changed in the AKAP12-depleted cells (Figure 6C). However, AF6 expression was clearly reduced. Therefore, we performed IF staining to determine whether knockdown of AF6 expression led to a decrease in cortical actin assembly. We found that AF6 depletion would lead to the cortical actin disassembly (white arrows) and the disruption of VE-cadherin junctions (red arrowheads) in HUVECs (Figure 6D). Moreover, AF6-depleted HUVECs had similar result in the capillary tube formation assay to that found in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs (Supplemental Figure 3C). These results suggest that the disassembly of cortical actin in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs is caused by decrease in AF6 expression.
Expression of PAK2 and AF6 rescues hemorrhages in akap12 morphants
To confirm the finding that the reduction of PAK2 and AF6 was the main cause of hemorrhage in akap12 morphants, we conducted rescue experiments. Synthetic mRNAs (PAK2, 25 pg; AF6, 25 pg) were injected with akap12 MOs (akap12α, 2 ng; akap12β, 7.5 ng) into the 1-cell stage embryos. We found that PAK2 and AF6 expression reduced the rate of hemorrhage in akap12 morphants (Figure 6E and Supplemental Table 3). These results indicate that hemorrhages in akap12 morphants are probably caused by a similar mechanism.
Discussion
Previous studies reported that a break in the connection between adjoining endothelial cells or a reduced interaction between endothelial cells and surrounding cells such as vascular smooth muscle cells, pericytes, and astrocytes leads to tissue edema, vessel rupture, and hemorrhage (Murakami and Simons, 2009). akap12 was strongly expressed in the blood vessels during vascular development in zebrafish embryos (Figures 2A-2D). We, therefore, tried to understand how akap12 expression in endothelial cells regulates the integrity of interendothelial cell-cell junctions.
Disconnection and loosening of interendothelial cell-cell junctions were confirmed by the direct visualization of blood vessels and by the leakage of fluorescent dyes, respectively, in the akap12 morphants (Figures 3 and 4). Endothelial junctions are made of adhesion molecules: VE-cadherins and nectins at adherens junctions, and claudins, occludins and JAMs at tight junctions. In addition, these adhesion molecules are linked to intracellular actin cytoskeletons to be stabilized at the cell-cell junction via adaptor proteins such as α-catenin, β-catenin and AF6 in adherens junctions and ZO-1/2 in tight junctions, respectively (Bazzoni and Dejana, 2004; Dejana, 2004; Taddei et al., 2008; Wallez and Huber, 2008). Therefore, examining the expression of adhesion molecules and the actin cytoskeleton that supports the cell-cell adhesions are critical to assess the integrity of interendothelial cell-cell junction. Our findings suggest that disruption of junctional integrity in akap12 morphant vessels might be caused by the changes in the expression of adhesion molecules or by the alteration of actin cytoskeleton.
Among interendothelial adhesion molecules, VE-cadherin plays a central role in the maintenance and development of blood vessels (Dejana et al., 2008; Vestweber, 2008). However, we did not observe a significant decrease in the expression of VE-cadherin or its binding molecules, although the integrity of VE-cadherin junctions was severely disrupted in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs (Figure 5). Strikingly, the actin cytoskeleton was rearranged in the AKAP12-depleted cells. The cortical actin fibers parallel to the cell-cell adhesion were reduced. The stabilization of VE-cadherin depends on the cortical actin. Homophilic engagement of VE-cadherin induces cortical actin assembly and vice versa. Without cortical actin assembly, VE-cadherin fails to be stabilized. Thus, our findings are consistent with the notion that the integrity of VE-cadherin dependent cell-cell adhesion is based on the assembly and disassembly of cortical actin (Fung et al., 1994).
AKAP12 depletion in endothelial cells induced the rearrangement of the actin cytoskeleton. AKAP12-depleted HUVECs exhibited increase in stress fiber formation and decrease in cortical actin assembly (Figure 5B). In addition, AKAP12 depletion decreased the expression of PAK2 (Figure 6A). Actin-myosin coupling-induced stress fiber formation is mainly regulated by MLC phosphorylation (Pellegrin and Mellor, 2007). PAK2 depletion is known to induce MLC phosphorylation (Coniglio et al., 2008). Recent studies report that pak2 mutant zebrafish exhibit hemorrhages (Buchner et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2007). Our findings from in vivo and in vitro studies are consistent with the phenotypes in PAK2 mutants. Furthermore, in the rescue experiments, the expression of PAK2 reduced the rate of hemorrhage in akap12 morphants (Figure 6E). These results suggest that the disruption of endothelial junctions in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs may be partly explained by the depletion of PAK2, further suggesting that hemorrhages are due to PAK2 depletion in akap12 morphants.
AKAP12-depleted endothelial cells also exhibit decreased cortical actin formation. Although PAK2 depletion could explain the induction of stress fiber formation in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs, it is not yet clear by which molecular mechanism the disassembly of cortical actin occurred. We found that AF6 expression was markedly decreased in AKAP12-depleted HUVECs (Figure 6C). Furthermore, AF6 depletion led to the disassembly of cortical actin in endothelial cells (Figure 6D). AF6 expression rescued the abnormal hemorrhage phenotype in akap12 morphants (Figure 6E). These results indicate that the disruption of junctional integrity, especially the disassembly of cortical actin, is caused by AF6 depletion in akap12 morphants.
AKAP12 in the astrocytes of the brain and the retina as well as that in endothelial cells also has a potential to maintain endothelial interaction via PAK2 and AF6 expression, because the stability of astrocytes supporting endothelial cells might indirectly affect the endothelial cell stability. However, we found that AKAP12 was strongly expressed in the vascular endothelial cells during development (Figures 2A-2D). These demonstrate the possibility that PAK2 and AF6 might function downstream of AKAP12 directly in endothelial cells. However, we cannot rule out the indirect effect of the overexpressed PAK2 and AF6 in astrocytes.
However, we still do not know how AKAP12 is involved in the regulation of PAK2 and AF6 expression. Since we did not find significant changes of PAK2 and AF6 mRNA levels in zebrafish embryos and in HUVEC (Supplemental Figures 3D, 3E), AKAP12 might regulate the protein stability of PAK2 and AF6. This problem remains to be solved by future studies.
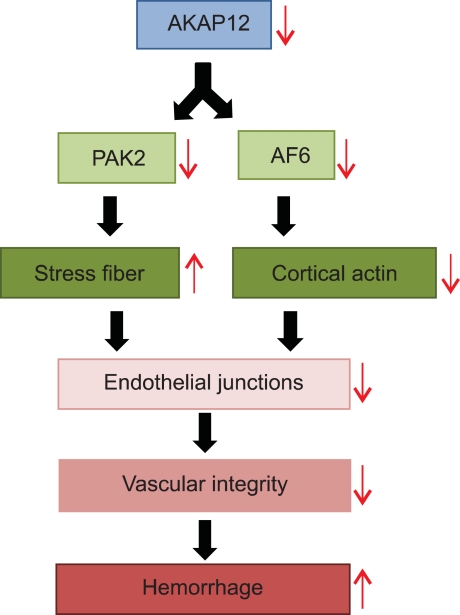
In summary, we revealed the role of AKAP12 in the maintenance of vascular integrity by regulating the actin cytoskeleton through PAK2 and AF6 (Figure 7). AKAP12 might become a target to reduce permeability or hemorrhage of vessel that is the main cause of the diseases such as stroke, retinopathy, and cerebellar hemorrhage in preterm infants.
Figure 7.
Model for the molecular processes underlying hemorrhage phenotype in AKAP12 morphant. AKAP12 depletion in endothelial cells decreases PAK2 and AF6 expression. PAK2 depletion induces stress fiber formation, while AF6 depletion decreases cortical actin assembly in AKAP12-depleted endothelial cells. These changes in AKAP12-depleted endothelial cells lead to the disruption of endothelial junctions and the loss of vascular integrity, thereby causing hemorrhages in akap12 morphants. This model conversely indicates the role for AKAP12 in the maintenance of both PAK2 and AF6 expression.
Methods
Zebrafish maintenance
Wild-type zebrafish (Danio rerio) were purchased from a local fish store, and the transgenic line Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 was obtained from the Zebrafish International Resource Center (University of Oregon, OR). Zebrafish were raised, and maintained under standard laboratory conditions (Westerfield, 1995).
Live imaging
For live imaging, Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 embryos were anesthetized in tricaine (Sigma, MO), mounted in a drop of 1.5% low melting agarose in 1 ×Danieau's solution in a glass-based dish, and imaged under a Zeiss LSM510 meta NLO confocal microscope (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with a video camera at 28℃. Time-lapse analysis of the leakage of a fluorescent dye was performed after intravascular injection of lysine-fixable tetramethylrhodamine-dextran (rhodamine-dextran, 2000 kDa, Molecular Probes Inc., OR) into the Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 zebrafish embryos (Lawson and Weinstein, 2002).
Cell culture and small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were purchased from Kurabo (Kurashiki, Japan), maintained as described previously, and used for the experiments before passage 9 (Fukuhara et al., 2008). HUVECs were transfected with 10 nmol/L siRNA duplexes by using Lipofectamine RNAi MAX reagent (Invitrogen, CA). After incubation for 48 h, the cells were used for the experiments. Stealth siRNAs targeted to human AKAP12 (CCCTCTGTCTGAGTATGATGCTGTA), human PAK2 (Cat. No. HSS107579), and human AF6 (Cat. No.HSS106591) were purchased from Invitrogen. As a control, stealth RNAi negative controls contained a comparable amount of GC, low GC (Cat. No.12935-200) and medium GC (Cat.No.12935-300) were used respectively.
Plasmids and morpholinos
akap12α and akap12β cDNA were isolated and sequenced from 48-h postfertilization (hpf) wild-type zebrafish embryos. Full-length akap12α and akap12β isoforms were introduced into the pcDNA3.1 vector (Invitrogen) and the pEGFP vector (Clontech, CA) for rescue experiments.
Zebrafish embryos were injected with 0.6-3 ng of akap12α morpholino oligomer (MO) (α MO1), 4.5-13 ng of akap12β MO (β MO1), 2 ng of akap12α MO (α MO2) and 7.5 ng of akap12β MO (β MO2), at the 1- to 4-cell stage. In rescue experiments, 50 pg of zebrafish akap12α and akap12β mRNAs were coinjected with splice-blocking MOs for akap12α and akap12β, respectively. The following MOs were used in the study: Standard control MO (Ctl MO, 5'-CCTCTTACCTCAGTTACAATTTATA-3') (Gene Tools, OR, akap12α splice-blocking MO (α MO1, 5'-TACCTTGCCATCTGCGGTTTCTCCA-3'), akap12β splice-blocking MO (β MO1, 5'-TCTTACCTGTTAGAGTTATTGTCCC-3'), akap12α translation-blocking MO (α MO2, 5'-CACGGATGGTGTCGCTCCCATGATC-3'), and akap12β translation-blocking MO (β MO2, 5'CTGTTAGAGTTATTGTCCCAAGCAT-3'). All MOs were purchased from Gene Tools, LLC.
Western blots
Cells were lysed in a lysis buffer containing 10 mmol/L HEPES (pH 7.9), 400 mmol/L NaCl, 0.1 mmol/L EDTA, 5% glycerol, 1 mmol/L DL-dithiothreitol (DTT), and a protease inhibitor cocktail. Whole cell lysates were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), followed by electrophoretic transfer onto a polyvinyl difluoride membrane (Millipore, Berlin, FRG). We used specific antibodies for immunoblots as follows: anti-VE-cadherin was obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA), BD Biosciences (San Jose, CA), and Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA); anti-α-catenin was obtained from Zymed Laboratories (San Francisco, CA), anti-β-catenin and anti-p120 catenin were obtained from BD Bioscience, anti-β-actin was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich; anti-PAK2 and anti-AF6 were obtained from Cell signaling Technology and BD Bioscience; anti-β-actin was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich; horseradish peroxidase-coupled goat anti-mouse and horseradish peroxidase-coupled goat anti-rabbit IgG were obtained from GE Healthcare (Piscataway, NJ); and horseradish peroxidase-coupled donkey anti-goat IgG was obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology.
Immunofluorescent (IF) staining
For IF staining in HUVECs, monolayer-cultured HUVECs grown on a collagen-coated glass-base dish were fixed 48 h after AKAP12 siRNA treatment in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 2% formaldehyde for 30 min at 4℃, permeabilized with 0.05% Triton X-100 for 30 min at 4℃, and blocked with PBS containing 4% BSA for 1 h at room temperature. The cells were then stained with rhodamine-phalloidin and with anti-VE-cadherin. Protein reacting with antibody was visualized with species-matched Alexa 488-labeled secondary antibodies. Fluorescence images of Alexa 488 and rhodamine were recorded with a FluoView FV1000 confocal microscope with a × 60 oil immersion objective lens.
Supplemental data
Supplemental data include three figures and three tables, and can be found with this article online at http://e-emm.or.kr/article/article_files/SP-44-3-05.pdf.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Y. G. Kwon (Yonsei University) and Dr. Y. A. Cho (The Catholic University of Korea) for their generous gift of HUVECs; to Dr. J. Y. Jeong (Seoul National University) for advice on embryo staining; to Dr. D. M. Kang (Ehwa Womans University) for his valuable feedback on the experiments; and to Dr. K. J. Kumar (Seoul National University) for critical reading of this manuscript. We also thank the Aging Tissue Bank (Pusan National University) for providing research information.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology through the Creative Research Initiative Program (R16-2004-001-01001-0), the World Class University Program (R31-2008-000-10103-0) and the Global Research Laboratory Program (2011-0021874) and the Global Core Research Center (GCRC) Program (2011-0030677).
Abbreviations
- AKAP12
a-kinase anchoring protein 12
- hpf
hour post fertilization
- ISH
in situ hybridization
- MLC
myosin light chain
- MLCK
MLC kinase
- MLCP
MLC phosphatase
- MO
morpholino
- PAK
p21-activated kinase
- VE-cadherin
vascular endothelial cadherin
- ZO-1/2
zona occludens-1/2
Supplementary Material
Supplemental Data
References
- 1.Aijaz S, Balda MS, Matter K. Tight junctions: molecular architecture and function. Int Rev Cytol. 2006;248:261–298. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(06)48005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Anderson JM, Van Itallie CM. Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:G467–G475. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.269.4.G467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Balda MS, Matter K. Tight junctions. J Cell Sci. 1998;111:541–547. doi: 10.1242/jcs.111.5.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bazzoni G, Dejana E. Endothelial cell-to-cell junctions: molecular organization and role in vascular homeostasis. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:869–901. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00035.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bokoch GM. Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:743–781. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Buchner DA, Su F, Yamaoka JS, Kamei M, Shavit JA, Barthel LK, McGee B, Amigo JD, Kim S, Hanosh AW, Jagadeeswaran P, Goldman D, Lawson ND, Raymond PA, Weinstein BM, Ginsburg D, Lyons SE. pak2a mutations cause cerebral hemorrhage in redhead zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:13996–14001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700947104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Choi YK, Kim JH, Kim WJ, Lee HY, Park JA, Lee SW, Yoon DK, Kim HH, Chung H, Yu YS, Kim KW. AKAP12 regulates human blood-retinal barrier formation by downregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. J Neurosci. 2007;27:4472–4481. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5368-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Choi YK, Kim KW. AKAP12 in astrocytes induces barrier functions in human endothelial cells through protein kinase Czeta. FEBS J. 2008;275:2338–2353. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Coniglio SJ, Zavarella S, Symons MH. Pak1 and Pak2 mediate tumor cell invasion through distinct signaling mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:4162–4172. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01532-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Corey DR, Abrams JM. Morpholino antisense oligonucleotides: tools for investigating vertebrate development. Genome Biol. 2001;2:REVIEWS1015. doi: 10.1186/gb-2001-2-5-reviews1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dejana E. Endothelial cell-cell junctions: happy together. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:261–270. doi: 10.1038/nrm1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dejana E, Orsenigo F, Lampugnani MG. The role of adherens junctions and VE-cadherin in the control of vascular permeability. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:2115–2122. doi: 10.1242/jcs.017897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fukuhara S, Sako K, Minami T, Noda K, Kim HZ, Kodama T, Shibuya M, Takakura N, Koh GY, Mochizuki N. Differential function of Tie2 at cell-cell contacts and cell-substratum contacts regulated by angiopoietin-1. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:513–526. doi: 10.1038/ncb1714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fung SI, Chan JY, Manzoni D, White SR, Lai YY, Strahlendorf HK, Zhuo H, Liu RH, Reddy VK, Barnes CD. Cotransmitter-mediated locus coeruleus action on motoneurons. Brain Res Bull. 1994;35:423–432. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(94)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lawson ND, Weinstein BM. In vivo imaging of embryonic vascular development using transgenic zebrafish. Dev Biol. 2002;248:307–318. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2002.0711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu J, Fraser SD, Faloon PW, Rollins EL, Vom Berg J, Starovic-Subota O, Laliberte AL, Chen JN, Serluca FC, Childs SJ. A betaPix Pak2a signaling pathway regulates cerebral vascular stability in zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:13990–13995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700825104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Murakami M, Simons M. Regulation of vascular integrity. J Mol Med. 2009;87:571–582. doi: 10.1007/s00109-009-0463-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pellegrin S, Mellor H. Actin stress fibres. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:3491–3499. doi: 10.1242/jcs.018473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stockton RA, Schaefer E, Schwartz MA. p21-activated kinase regulates endothelial permeability through modulation of contractility. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:46621–46630. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408877200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Taddei A, Giampietro C, Conti A, Orsenigo F, Breviario F, Pirazzoli V, Potente M, Daly C, Dimmeler S, Dejana E. Endothelial adherens junctions control tight junctions by VE-cadherin-mediated upregulation of claudin-5. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:923–934. doi: 10.1038/ncb1752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Trepel M, Stoneham CA, Eleftherohorinou H, Mazarakis ND, Pasqualini R, Arap W, Hajitou A. A heterotypic bystander effect for tumor cell killing after adeno-associated virus/phage-mediated, vascular-targeted suicide gene transfer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:2383–2391. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vestweber D. VE-cadherin: the major endothelial adhesion molecule controlling cellular junctions and blood vessel formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28:223–232. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.158014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wallez Y, Huber P. Endothelial adherens and tight junctions in vascular homeostasis, inflammation and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778:794–809. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Weiser DC, Pyati UJ, Kimelman D. Gravin regulates mesodermal cell behavior changes required for axis elongation during zebrafish gastrulation. Genes Dev. 2007;21:1559–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.1535007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Westerfield M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish. 3rd Ed. Eugene, USA: University of Oregon Press; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wong W, Scott JD. AKAP signalling complexes: focal points in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:959–970. doi: 10.1038/nrm1527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental Data