Fig. 2.
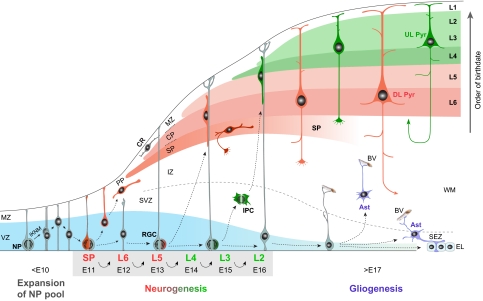
Schematic of projection neuron generation and migration in the mouse neocortex. Prior to the onset of neurogenesis, neural progenitors (NPs) in the ventricular zone (VZ; blue) of the developing neocortex divide symmetrically to expand the progenitor pool, undergoing interkinetic nuclear migration (IKNM) as they progress through the cell cycle. Starting at ∼E11.5, NPs assume radial glial morphology and begin dividing asymmetrically to generate neurons, which migrate from the germinal zones guided by radial glia cells (RGC) to reach the mantle layers. The first projection neurons settle within the preplate (PP) to form the nascent cortical plate (CP), which will subsequently become layers (L) 2 to 6 of the neocortex. Additional incoming CP neurons then split the PP into the marginal zone (MZ) and the subplate (SP). As neurogenesis progresses, diverse subtypes of projection neurons are generated sequentially through successive asymmetric divisions of NPs. Thus, neurons destined for the SP are generated first, followed by those destined for the deep layers (L6 and L5; red), and finally, those destined for the upper layers (L4, L3 and L2; green). The migration of newborn neurons into the CP occurs in an inside-first, outside-last manner; early-born neurons form the deep layers, whereas later-born neurons migrate past older neurons to form more superficial layers. Therefore, the cortical layers are sequentially generated in an ‘inside-out’ fashion. Some daughter cells of NPs become intermediate progenitor cells (IPCs), migrating away from the VZ and undergoing symmetric neurogenic divisions in the SVZ. This mode of neurogenesis contributes significantly to upper layer neurons. At the end of neurogenesis at ∼E17.5, the radial scaffold is dismantled and NPs become gliogeneic, generating cortical and subependymal zone (SEZ) astrocytes (Ast) and giving rise to a layer of ependymal cells (EL). The tangential migration and laminar positioning of interneurons are not illustrated. BV, blood vessel; CR, Cajal-Retzius neuron; DL Pyr, deep-layer pyramidal neuron; IZ, intermediate zone; UL Pyr, upper-layer pyramidal neuron, WM, white matter.