Abstract
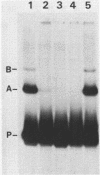
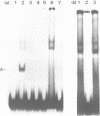
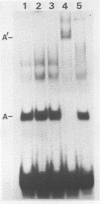
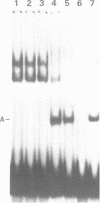
The binding of a herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) encoded polypeptide to a viral origin of DNA replication has been studied by using a gel retardation assay. Incubation of nuclear extract from HSV-1 infected cells with a labelled origin-containing fragment resulted in the formation of a specific retarded complex, the migration of which was further reduced in the presence of an antibody reactive with the UL9 gene product. Introduction of an additional copy of the UL9 gene, under the control of an immediate early (IE) promoter, conferred the ability to express origin binding activity at the non-permissive temperature upon an HSV-1 ts mutant blocked at the IE stage of infection. Endogenous or exogenous proteolytic activity revealed the presence of a relatively protease-resistant domain which retained sequence-specific DNA binding activity. The C-terminal 317 amino acids of the UL9 gene expressed as a fusion protein in Escherichia coli also bound to the origin. Our results demonstrate that the UL9 gene product binds to a viral origin and that sequence specific recognition and binding are specified by the C-terminal 37% of the polypeptide.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard H. U., Remaut E., Hershfield M. V., Das H. K., Helinski D. R., Yanofsky C., Franklin N. Construction of plasmid cloning vehicles that promote gene expression from the bacteriophage lambda pL promoter. Gene. 1979 Jan;5(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael E. P., Kosovsky M. J., Weller S. K. Isolation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 host range mutants defective in viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.91-99.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D. A method for identifying the viral genes required for herpesvirus DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9094–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Stow N. D., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of paar mutations of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 by intertypic marker rescue. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):265–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.265-276.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Knipe D. M., Jones P. C., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VII. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant produced by in vitro mutagenesis and defective in DNA synthesis and accumulation of gamma polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):191–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.191-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Doelberg M. A 67-base-pair segment from the Ori-S region of herpes simplex virus type 1 encodes origin function. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2516–2519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2516-2519.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., O'Donnell M. E., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA binding protein specific for an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Chiou H. C., Hall J. D., Mount D. W., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Coen D. M. Sequence and mapping analyses of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene predict a C-terminal substrate binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7969–7973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Weller S. K. An ICP6::lacZ insertional mutagen is used to demonstrate that the UL52 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 is required for virus growth and DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2970–2977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2970-2977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Johnson A. D. Homeo domain of the yeast repressor alpha 2 is a sequence-specific DNA-binding domain but is not sufficient for repression. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):1007–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2887035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. A., Bollekens J., Dorn A., Benoist C., Mathis D. Properties of a CCAAT box-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7265–7282. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Arsenakis M., Marchini A., Lee L., Roizman B., Kieff E. Herpes simplex virus expressing Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1. Virology. 1986 Jan 30;148(2):337–348. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Characterization of major recognition sequences for a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4096–4103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4096-4103.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Galloway D. A. Sequence and structural requirements of a herpes simplex viral DNA replication origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4018–4027. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti M. E., Smith C. A., Schaffer P. A. A temperature-sensitive mutation in a herpes simplex virus type 1 gene required for viral DNA synthesis maps to coordinates 0.609 through 0.614 in UL. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):715–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.715-721.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Campbell M. E., Haarr L., Frame M. C., Parris D. S., Murphy M., Hope R. G., Muller M. T., Preston C. M. The 65,000-Mr DNA-binding and virion trans-inducing proteins of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2428–2437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2428-2437.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz B., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Preston V. G. Physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutations of herpes simplex virus type 1 using cloned restriction endonuclease fragments. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2261–2270. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride A. A., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. The carboxy-terminal domain shared by the bovine papillomavirus E2 transactivator and repressor proteins contains a specific DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):533–539. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moitoso de Vargas L., Pargellis C. A., Hasan N. M., Bushman E. W., Landy A. Autonomous DNA binding domains of lambda integrase recognize two different sequence families. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):923–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M. Immobilization and purification of enzymes with staphylococcal protein A gene fusion vectors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris D. S., Cross A., Haarr L., Orr A., Frame M. C., Murphy M., McGeoch D. J., Marsden H. S. Identification of the gene encoding the 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):818–825. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.818-825.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Kryszke M. H., Yaniv M. Specific interaction of cellular factors with the B enhancer of polyoma virus. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2675–2685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. Temperature-sensitive mutants in two distinct complementation groups of herpes simplex virus type 1 specify thermolabile DNA polymerase. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):219–222. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence of the region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1 containing the genes for DNA polymerase and the major DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8143–8163. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Jackson I. J., Brown D. D. Domains of the positive transcription factor specific for the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Localization of an origin of DNA replication within the TRS/IRS repeated region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Carlstedt-Duke J., Weigel N. L., Dahlman K., Gustafsson J. A., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Carmichael E. P., Aschman D. P., Goldstein D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic and phenotypic characterization of mutants in four essential genes that map to the left half of HSV-1 UL DNA. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):198–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Lee K. J., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the gene for the major herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):354–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.354-366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]