Abstract
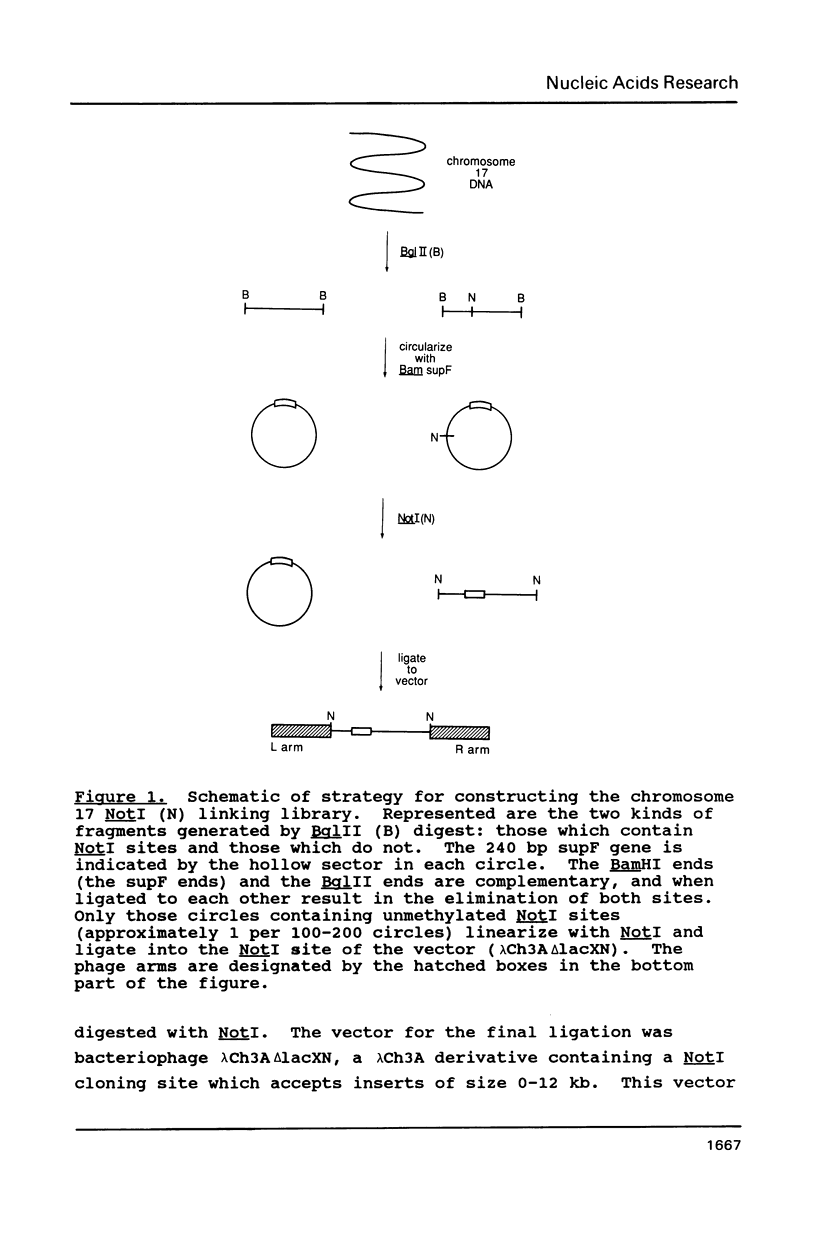
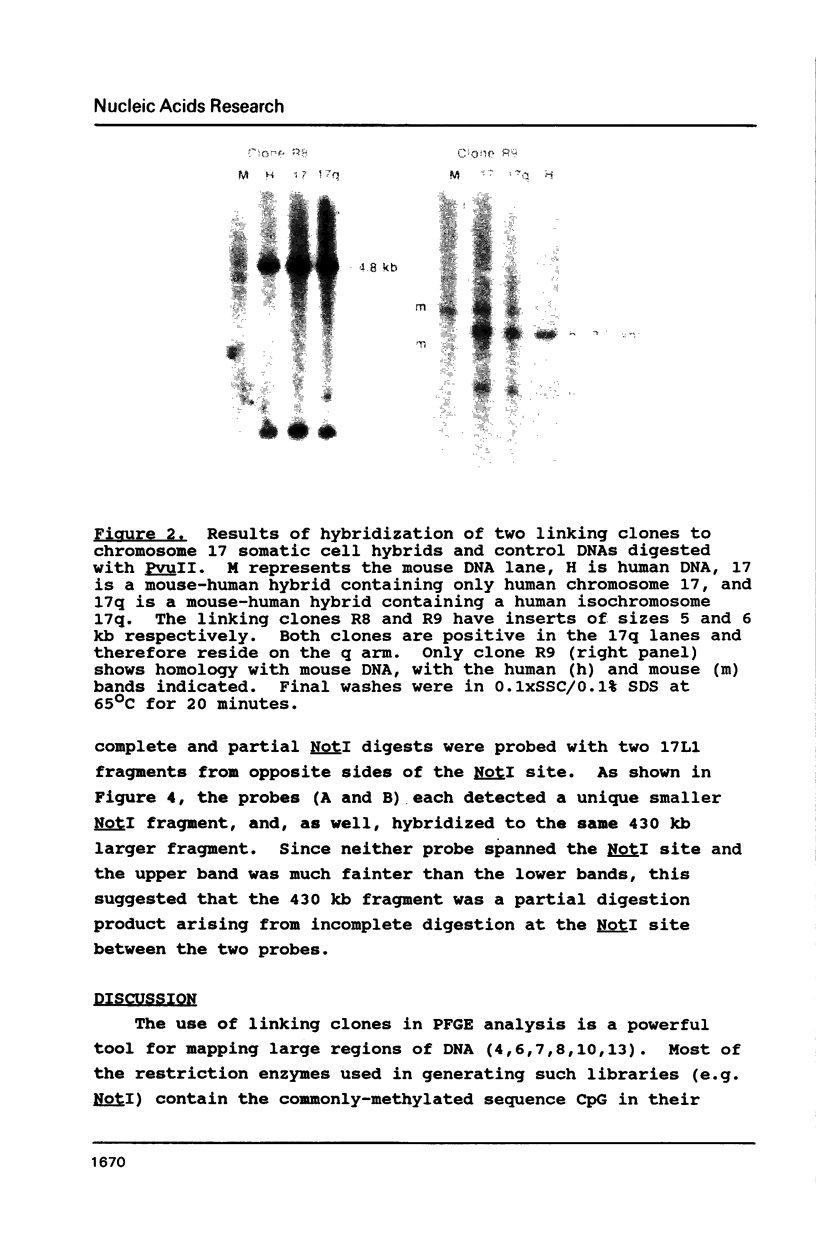
A linking library consists of genomic DNA fragments which contain a specific rare restriction enzyme site; such clones are very useful as probes in pulsed field gel electrophoresis and in mapping and cloning large regions of DNA. However, identifying those linking clones which map to a certain chromosomal region can be laborious. Therefore, we have developed a straightforward procedure for constructing a linking library directly from flow-sorted chromosomes. As a test of the approach, a NotI linking library was constructed from the chromosome 17 fraction of a flow-sort of human chromosomes, using only 70 ng of DNA. Thirteen of sixteen linking clones were mapped to chromosome 17, suggesting that the library is highly enriched for this chromosome. This method should be generally applicable to other chromosomes and enzymes as well.
Full text
PDF



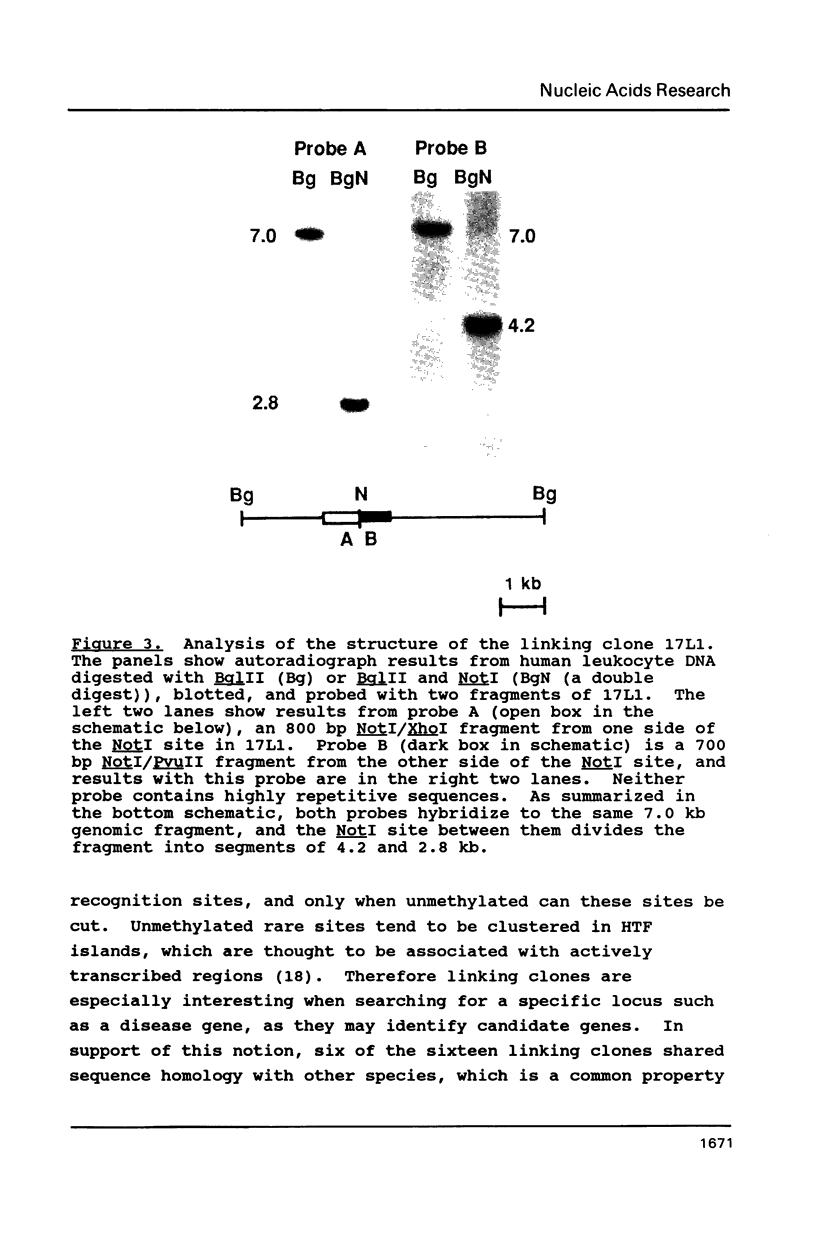






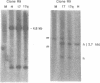
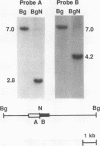
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield C. D., Trent J. M., van den Berghe H. Report of the committee on structural chromosome changes in neoplasia. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):344–366. doi: 10.1159/000132485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buiting K., Passarge E., Horsthemke B. Construction of a chromosome 15-specific linking library and identification of potential gene sequences. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fountain J. W., Wallace M. R., Brereton A. M., O'Connell P., White R. L., Rich D. C., Ledbetter D. H., Leach R. J., Fournier R. E., Menon A. G. Physical mapping of the von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis region on chromosome 17. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;44(1):58–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuscoe J. C., Clark L. M., Van Dilla M. A. Construction of fifteen human chromosome-specific DNA libraries from flow-purified chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(1-2):79–86. doi: 10.1159/000132301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. W., Dean P. N., Fuscoe J. C., Peters D. C., Trask B. J., van den Engh G. J., Van Dilla M. A. High-speed chromosome sorting. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):323–329. doi: 10.1126/science.2443974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Sakaki Y. A novel procedure for selective cloning of NotI linking fragments from mammalian genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9177–9184. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl T. M., Zimmer M., MacDonald M. E., Smith B., Bucan M., Poustka A., Volinia S., Searle S., Zehetner G., Wasmuth J. J. Construction of a NotI linking library and isolation of new markers close to the Huntington's disease gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9185–9198. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Pohl T. M., Barlow D. P., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Construction and use of human chromosome jumping libraries from NotI-digested DNA. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):353–355. doi: 10.1038/325353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Pohl T., Barlow D. P., Zehetner G., Craig A., Michiels F., Ehrich E., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Molecular approaches to mammalian genetics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):131–139. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Purification, specific fragmentation, and separation of large DNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:449–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Lawrance S. K., Gillespie G. A., Cantor C. R., Weissman S. M., Collins F. S. Strategies for mapping and cloning macroregions of mammalian genomes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;151:461–489. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)51038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton R. F., Dobyns W. B., Airhart S. D., Ledbetter D. H. New chromosomal syndrome: Miller-Dieker syndrome and monosomy 17p13. Hum Genet. 1984;67(2):193–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00273000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]