Abstract
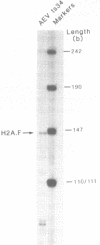
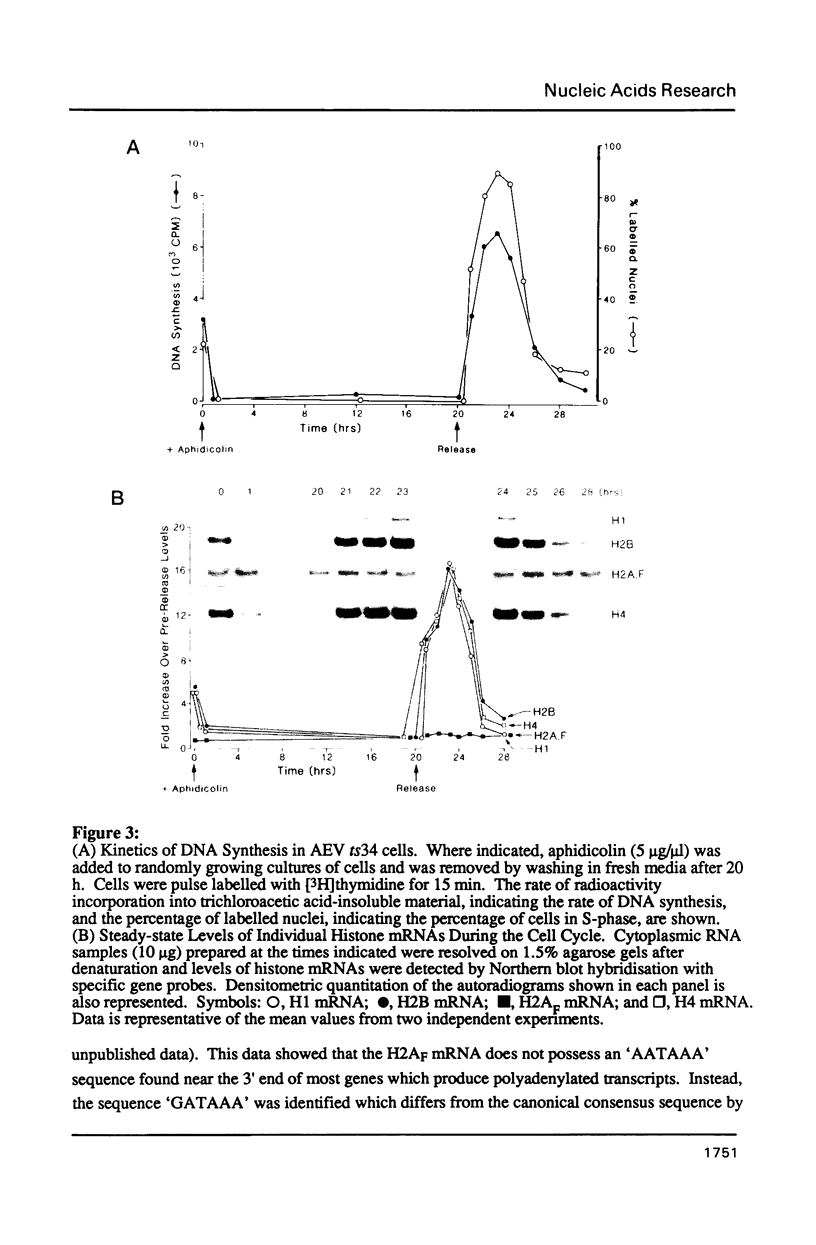
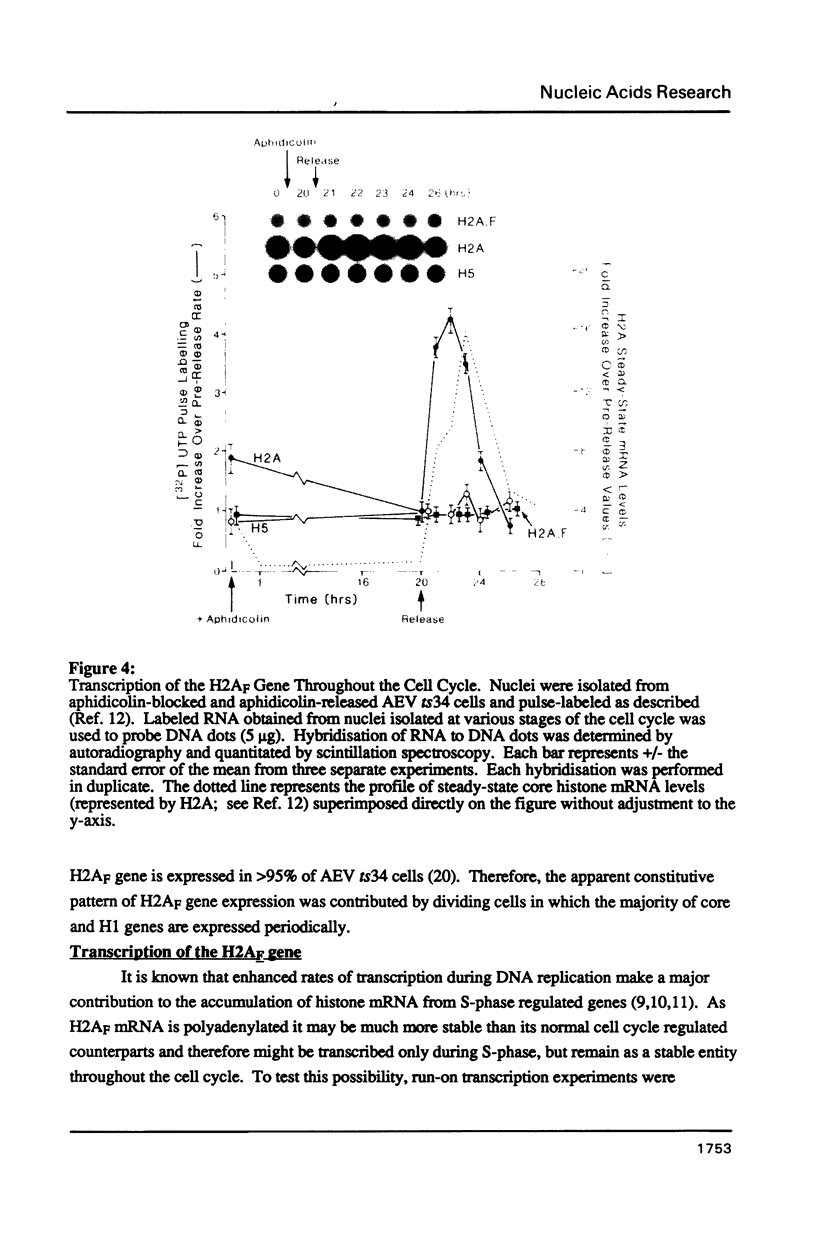
The nucleotide sequence of an 8.2 kb BamHI fragment containing the entire chicken histone H2AF gene has been determined. Unlike the majority of histone genes, the coding region is interrupted by four intervening sequences. While sequencing the 8.2 kb BamHI fragment it was found that the promoter and first exon of an unidentified non-histone gene lies immediately downstream of the H2AF gene. Studies of H2AF gene transcription show that, unlike the major core and H1 histone genes, it is not coupled to DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allis C. D., Glover C. V., Bowen J. K., Gorovsky M. A. Histone variants specific to the transcriptionally active, amitotically dividing macronucleus of the unicellular eucaryote, Tetrahymena thermophila. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):609–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allis C. D., Richman R., Gorovsky M. A., Ziegler Y. S., Touchstone B., Bradley W. A., Cook R. G. hv1 is an evolutionarily conserved H2A variant that is preferentially associated with active genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1941–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alterman R. B., Ganguly S., Schulze D. H., Marzluff W. F., Schildkraut C. L., Skoultchi A. I. Cell cycle regulation of mouse H3 histone mRNA metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):123–132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball D. J., Slaughter C. A., Hensley P., Garrard W. T. Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal domain of calf thymus histone H2A.Z. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 5;154(1):166–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80896-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea R. J., Coles L. S., Lesnikowski C., Tabe L., Wells J. R. Chromosomal organization of chicken histone genes: preferred associations and inverted duplications. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3108–3115. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Coleman J. R., Wells J. R. Transcription of the histone H5 gene is not S-phase regulated. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):601–606. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisle A. J., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F., Johnson L. F. Regulation of histone mRNA production and stability in serum-stimulated mouse 3T6 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):1920–1929. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.1920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Yamamoto M., Engel J. D. Chicken histone H3.3B cDNA sequence confirms unusual 3' UTR structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6294–6294. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., Sugarman B. J., Dodgson J. B. A chicken histone H3 gene contains intervening sequences. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):434–436. doi: 10.1038/297434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst S. G., Miller H., Brenner C. A., Nocente-McGrath C., Francis S., McIsaac R. Characterization of a cDNA clone coding for a sea urchin histone H2A variant related to the H2A.F/Z histone protein in vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4629–4644. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Rapid reversible changes in the rate of histone gene transcription and histone mRNA levels in mouse myeloma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):351–357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Whiting J. A., Coles L. S., Krieg P. A., Wells J. R. H2A.F: an extremely variant histone H2A sequence expressed in the chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2819–2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch C. L., Bonner W. M., Moudrianakis E. N. Minor histone 2A variants and ubiquinated forms in the native H2A:H2B dimer. Science. 1983 Jul 29;221(4609):468–470. doi: 10.1126/science.6306766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch C. L., Bonner W. M. Sequence of cDNAs for mammalian H2A.Z, an evolutionarily diverged but highly conserved basal histone H2A isoprotein species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1113–1124. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Robins A. J., Colman A., Wells J. R. Chicken histone H5 mRNA: the polyadenylated RNA lacks the conserved histone 3' terminator sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6777–6785. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G. S., Morris N. R. The unique histone H2A gene of Aspergillus nidulans contains three introns. Gene. 1987;58(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. C., Spence A., Smith M. The distal transcription signals of the herpesvirus tk gene share a common hexanucleotide control sequence. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossouw C. M., Vergeer W. P., du Plooy S. J., Bernard M. P., Ramirez F., de Wet W. J. DNA sequences in the first intron of the human pro-alpha 1(I) collagen gene enhance transcription. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15151–15157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Histone mRNA concentrations are regulated at the level of transcription and mRNA degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. H., Bonner W. M. Structural comparisons of mouse histones 2A.X and 2A.Z with 2A.1 and 2A.2. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1983;76(3):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(83)90275-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E. M., Shapiro D. L., Allis C. D., Gorovsky M. A. Sequence and properties of the message encoding Tetrahymena hv1, a highly evolutionarily conserved histone H2A variant that is associated with active genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):179–198. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Daal A., White E. M., Gorovsky M. A., Elgin S. C. Drosophila has a single copy of the gene encoding a highly conserved histone H2A variant of the H2A.F/Z type. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7487–7497. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]