Abstract
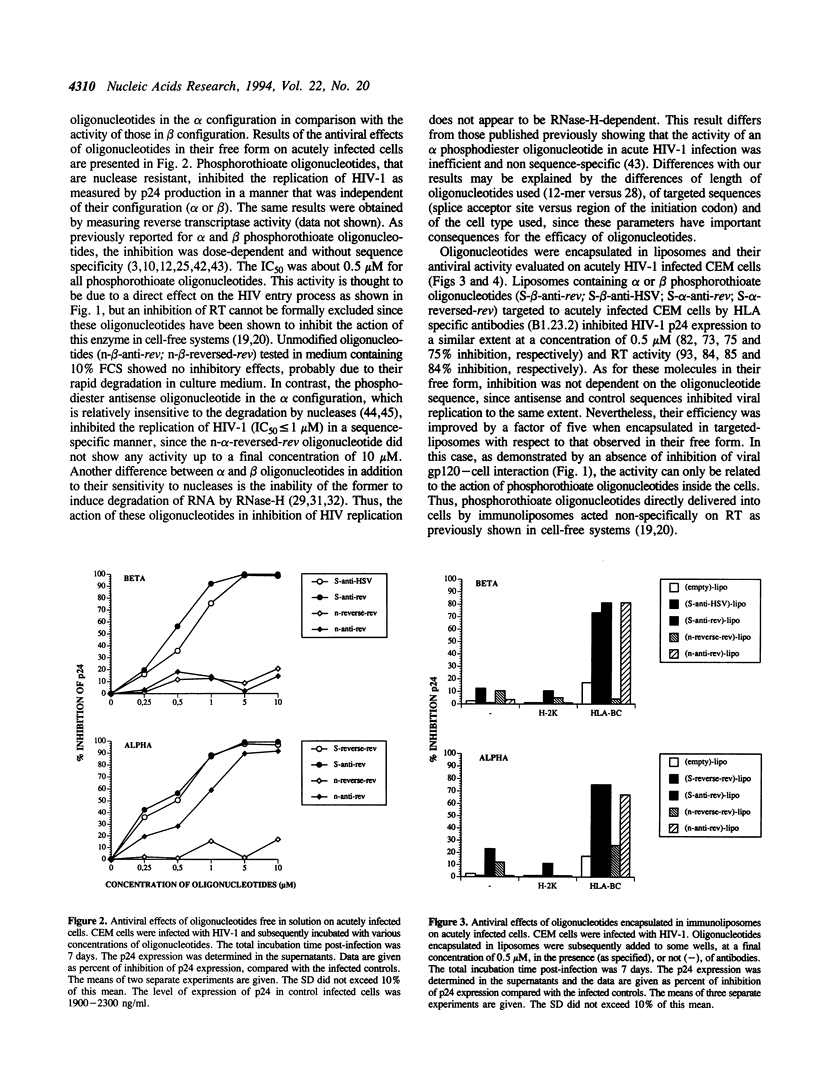
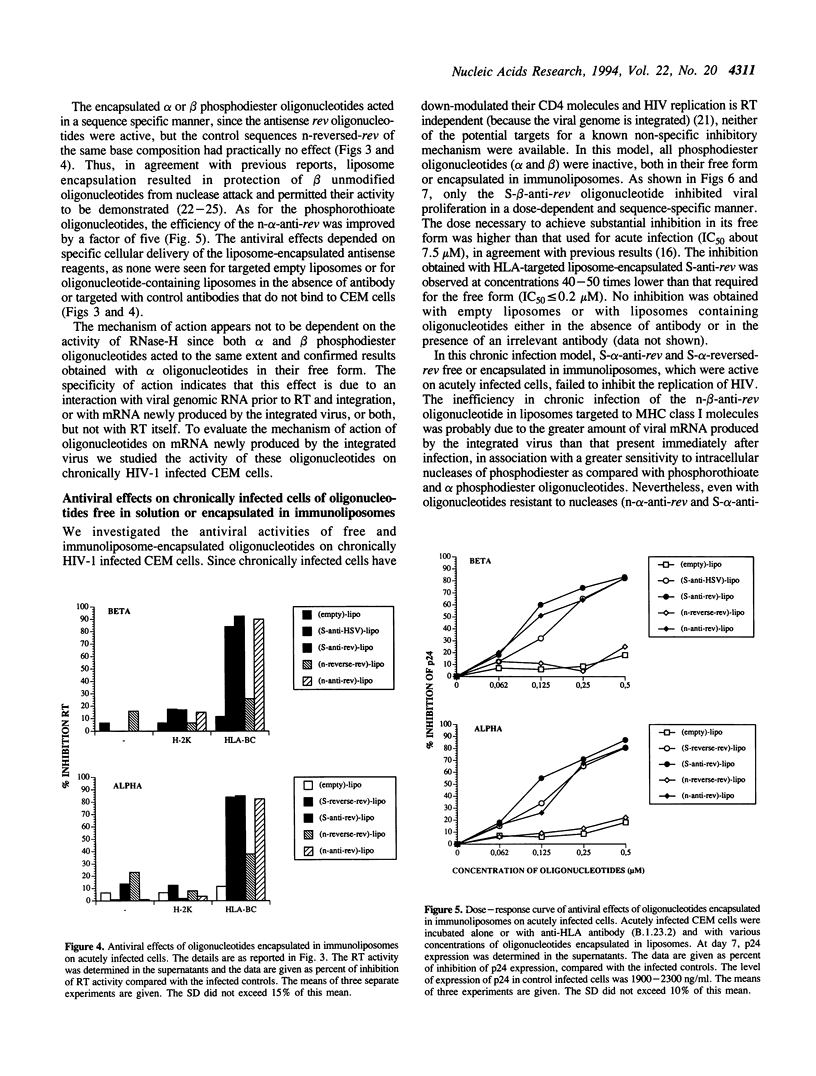
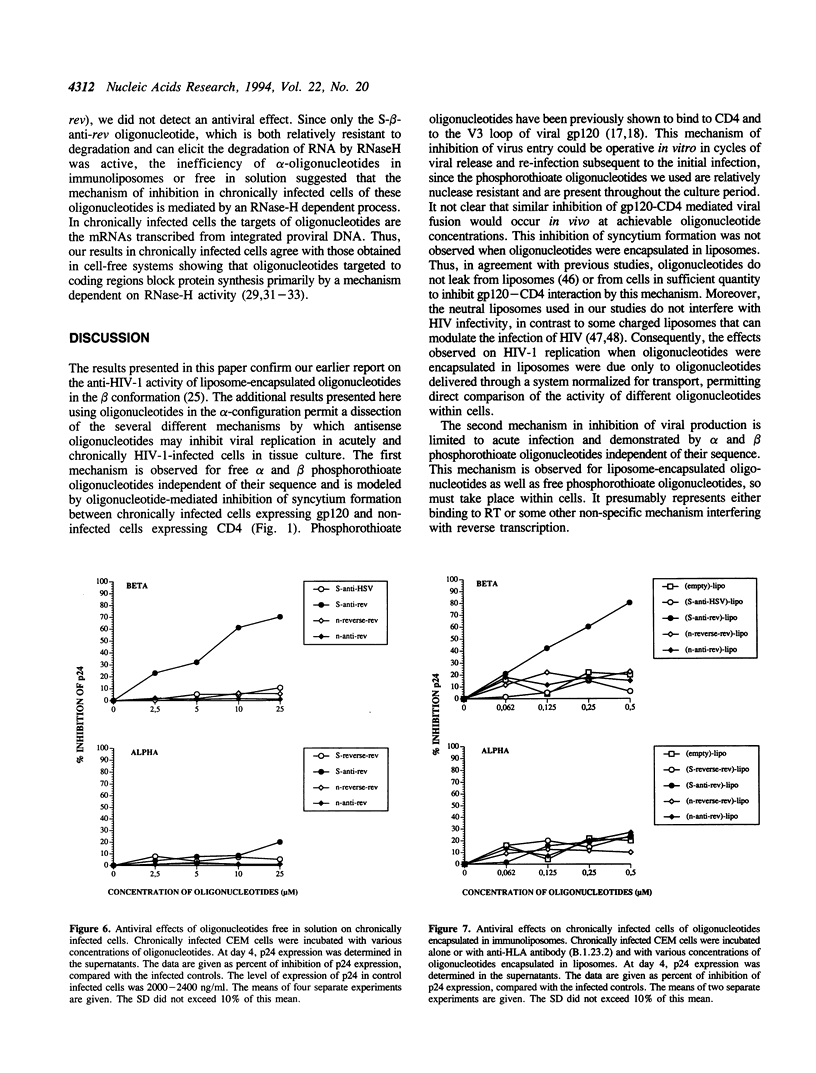
Phosphodiester and phosphorothioate oligonucleotides in alpha and beta configurations directed against the initiation codon region of the HIV-1 rev gene were evaluated for their ability to inhibit HIV-1 replication in acutely and chronically infected human CEM cells. Encapsulation in antibody-targeted liposomes (immunoliposomes) permitted intracellular delivery and distinction between oligonucleotide-mediated inhibition of viral entry and intracellular effects on viral RNA. Our results are consistent with four mechanisms of antiviral activity for these antisense oligonucleotides: (i) interference with virus-mediated cell fusion by free but not liposome-encapsulated phosphorothioate oligonucleotides of any sequence; (ii) interference with reverse transcription in a sequence non-specific manner by phosphorothioate oligonucleotides in alpha and beta configurations; (iii) interference with viral reverse transcription in a sequence-specific and RNase-H-independent manner by alpha and beta phosphodiester oligonucleotides; (iv) interference with viral mRNA in a sequence-specific and RNase-H-dependent manner by beta-phosphorothioate oligonucleotides.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal S., Ikeuchi T., Sun D., Sarin P. S., Konopka A., Maizel J., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus in early infected and chronically infected cells by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides and their phosphorothioate analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7790–7794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar S., Basu S., Wickstrom E., Juliano R. L. Interactions of antisense DNA oligonucleotide analogs with phospholipid membranes (liposomes). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5551–5559. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar S., Kole R., Juliano R. L. Stability of antisense DNA oligodeoxynucleotide analogs in cellular extracts and sera. Life Sci. 1991;49(24):1793–1801. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90480-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand J. R., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Paoletti C., Malvy C. Comparative activity of alpha- and beta-anomeric oligonucleotides on rabbit beta globin synthesis: inhibitory effect of cap targeted alpha-oligonucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91719-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiziau C., Kurfurst R., Cazenave C., Roig V., Thuong N. T., Toulmé J. J. Inhibition of translation initiation by antisense oligonucleotides via an RNase-H independent mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1113–1119. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiziau C., Moreau S., Toulmé J. J. A phosphorothioate oligonucleotide blocks reverse transcription via an antisense mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 7;340(3):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiziau C., Thuong N. T., Toulmé J. J. Mechanisms of the inhibition of reverse transcription by antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):768–772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier B., Hélène C., Barr P. J., Litvak S., Sarih-Cottin L. In vitro effect of antisense oligonucleotides on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 25;20(22):5999–6006. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.22.5999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Stein C. A., Loreau N., Thuong N. T., Neckers L. M., Subasinghe C., Hélène C., Cohen J. S., Toulmé J. J. Comparative inhibition of rabbit globin mRNA translation by modified antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4255–4273. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarenc J. P., Lebleu B., Léonetti J. P. Characterization of the nuclear binding sites of oligodeoxyribonucleotides and their analogs. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5600–5604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke S. T. Therapeutic applications of oligonucleotides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992;32:329–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.001553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degols G., Devaux C., Lebleu B. Oligonucleotide-poly(L-lysine)-heparin complexes: potent sequence-specific inhibitors of HIV-1 infection. Bioconjug Chem. 1994 Jan-Feb;5(1):8–13. doi: 10.1021/bc00025a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominski Z., Kole R. Restoration of correct splicing in thalassemic pre-mRNA by antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8673–8677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagnor C., Bertrand J. R., Thenet S., Lemaître M., Morvan F., Rayner B., Malvy C., Lebleu B., Imbach J. L., Paoletti C. alpha-DNA. VI: Comparative study of alpha- and beta-anomeric oligodeoxyribonucleotides in hybridization to mRNA and in cell free translation inhibition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10419–10436. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagnor C., Rayner B., Leonetti J. P., Imbach J. L., Lebleu B. Alpha-DNA.IX: Parallel annealing of alpha-anomeric oligodeoxyribonucleotides to natural mRNA is required for interference in RNase H mediated hydrolysis and reverse transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5107–5114. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Toulmé J. J. Specific regulation of gene expression by antisense, sense and antigene nucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 21;1049(2):99–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90031-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob A., Duval-Valentin G., Ingrand D., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Inhibition of viral growth by an alpha-oligonucleotide directed to the splice junction of herpes simplex virus type-1 immediate-early pre-mRNA species 22 and 47. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 15;216(1):19–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. G., Suzuki Y., Nakashima H., Yamamoto N., Takaku H. Phosphorothioate analogues of oligodeoxyribonucleotide: synthesis and activity as inhibitors of replication of human immunodeficiency virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1614–1619. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91759-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinchington D., Galpin S., Jaroszewski J. W., Ghosh K., Subasinghe C., Cohen J. S. A comparison of gag, pol and rev antisense oligodeoxynucleotides as inhibitors of HIV-1. Antiviral Res. 1992 Jan;17(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(92)90090-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotman M. E., Kim S., Buchbinder A., DeRossi A., Baltimore D., Wong-Staal F. Kinetics of expression of multiply spliced RNA in early human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of lymphocytes and monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5011–5015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka K., Davis B. R., Larsen C. E., Alford D. R., Debs R. J., Düzgüneş N. Liposomes modulate human immunodeficiency virus infectivity. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):2899–2907. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-2899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulka M., Smith C. C., Aurelian L., Fishelevich R., Meade K., Miller P., Ts'o P. O. Site specificity of the inhibitory effects of oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate)s complementary to the acceptor splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early mRNA 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6868–6872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti J. P., Machy P., Degols G., Lebleu B., Leserman L. Antibody-targeted liposomes containing oligodeoxyribonucleotides complementary to viral RNA selectively inhibit viral replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2448–2451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti J. P., Rayner B., Lemaitre M., Gagnor C., Milhaud P. G., Imbach J. L., Lebleu B. Antiviral activity of conjugates between poly(L-lysine) and synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leserman L. D., Barbet J., Kourilsky F., Weinstein J. N. Targeting to cells of fluorescent liposomes covalently coupled with monoclonal antibody or protein A. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):602–604. doi: 10.1038/288602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):183–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.183-289.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisziewicz J., Sun D., Klotman M., Agrawal S., Zamecnik P., Gallo R. Specific inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by antisense oligonucleotides: an in vitro model for treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11209–11213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisziewicz J., Sun D., Metelev V., Zamecnik P., Gallo R. C., Agrawal S. Long-term treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells with antisense oligonucleotide phosphorothioates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3860–3864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar C., Stein C. A., Cohen J. S., Broder S., Wilson S. H. Stepwise mechanism of HIV reverse transcriptase: primer function of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotide. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1340–1346. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura M., Shinozuka K., Zon G., Mitsuya H., Reitz M., Cohen J. S., Broder S. Phosphorothioate analogs of oligodeoxynucleotides: inhibitors of replication and cytopathic effects of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura M., Zon G., Shinozuka K., Robert-Guroff M., Shimada T., Stein C. A., Mitsuya H., Wong-Staal F., Cohen J. S., Broder S. Regulation of viral expression of human immunodeficiency virus in vitro by an antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotide against rev (art/trs) in chronically infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4244–4248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury G., el Alaoui A., Morvan F., Müller B., Imbach J. L., Goody R. S. Template. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides duplexes as inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 14;186(3):1249–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81540-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Porumb H., Degols G., Lefebvre I., Pompon A., Sproat B. S., Rayner B., Malvy C., Lebleu B., Imbach J. L. Comparative evaluation of seven oligonucleotide analogues as potential antisense agents. J Med Chem. 1993 Jan 22;36(2):280–287. doi: 10.1021/jm00054a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L. Alpha-oligonucleotides: a unique class of modified chimeric nucleic acids. Anticancer Drug Des. 1991 Dec;6(6):521–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L. alpha-Oligodeoxynucleotides. Methods Mol Biol. 1993;20:261–283. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-281-7:261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayner B., Matsukura M., Morvan F., Cohen J. S., Imbach J. L. Activité anti-VIH in vitro d'oligodésoxynucléotides phosphorothioates d'anomérie alpha. C R Acad Sci III. 1989;310(3):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Markham P. D., Wong-Staal F., Franchini G., Kalyanaraman V. S., Gallo R. C. Restricted expression of human T-cell leukemia--lymphoma virus (HTLV) in transformed human umbilical cord blood lymphocytes. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):51–64. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. P., Kent K., Bird J., Fishback J., Froehler B. Modified deoxyoligonucleotides stable to exonuclease degradation in serum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):747–750. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cleary A. M., Yakubov L., Lederman S. Phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides bind to the third variable loop domain (v3) of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120. Antisense Res Dev. 1993 Spring;3(1):19–31. doi: 10.1089/ard.1993.3.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Matsukura M., Subasinghe C., Broder S., Cohen J. S. Phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides are potent sequence nonspecific inhibitors of de novo infection by HIV. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Dec;5(6):639–646. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Neckers L. M., Nair B. C., Mumbauer S., Hoke G., Pal R. Phosphorothioate oligodeoxycytidine interferes with binding of HIV-1 gp120 to CD4. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(7):686–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. C. Colorimetric determination of phospholipids with ammonium ferrothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S. M., Gieseler R. K., Lenzner S., Ruppert J., Gabrysiak T. G., Peters J. H., Cox G., Richer L., Martin W. J., Scolaro M. J. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus-1 proliferation by liposome-encapsulated sense DNA to the 5' tat splice acceptor site. Antisense Res Dev. 1992 Fall;2(3):187–197. doi: 10.1089/ard.1992.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Zelphati O., Hildebrand G., Leserman L. CD4 and CD7 molecules as targets for drug delivery from antibody bearing liposomes. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Mar;193(1):112–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry A. R., Dritschilo A. Intracellular availability of unmodified, phosphorothioated and liposomally encapsulated oligodeoxynucleotides for antisense activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5691–5698. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. Oligodeoxynucleotide stability in subcellular extracts and culture media. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1986 Sep;13(2):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(86)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Goodchild J., Taguchi Y., Sarin P. S. Inhibition of replication and expression of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III in cultured cells by exogenous synthetic oligonucleotides complementary to viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4143–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelphati O., Zon G., Leserman L. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication in cultured cells with antisense oligonucleotides encapsulated in immunoliposomes. Antisense Res Dev. 1993 Winter;3(4):323–338. doi: 10.1089/ard.1993.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon G., Geiser T. G. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides: chemistry, purification, analysis, scale-up and future directions. Anticancer Drug Des. 1991 Dec;6(6):539–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




