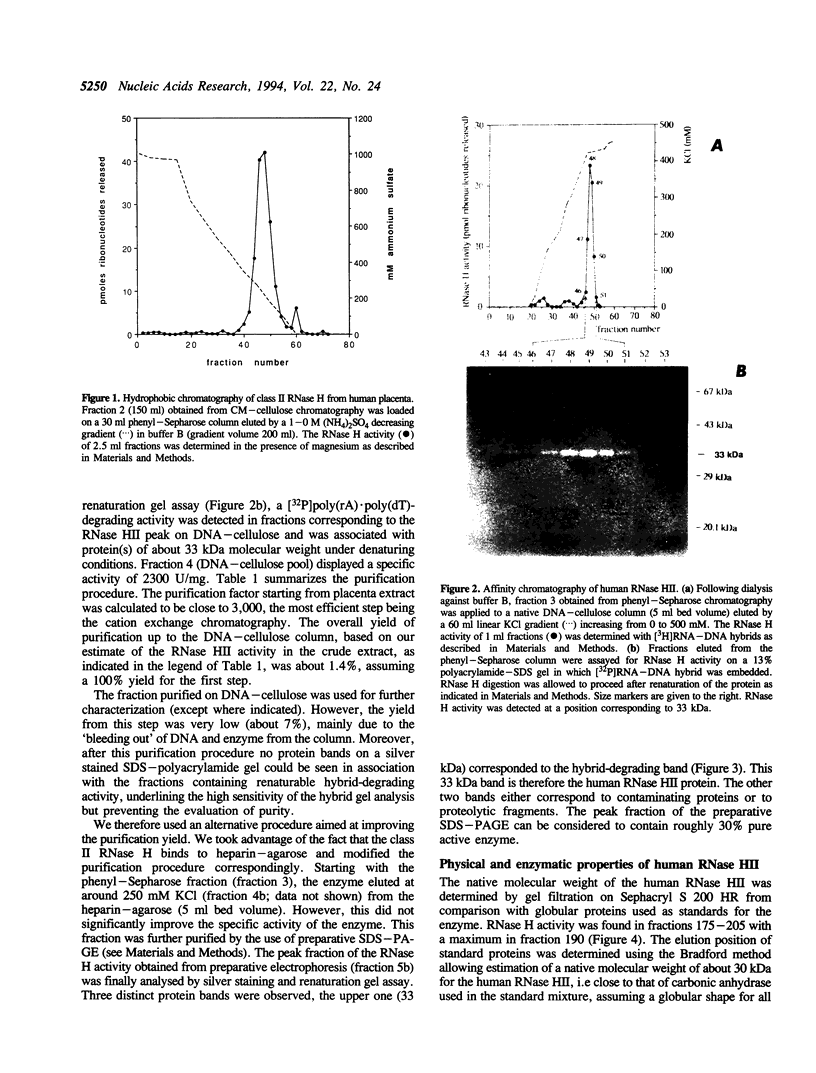
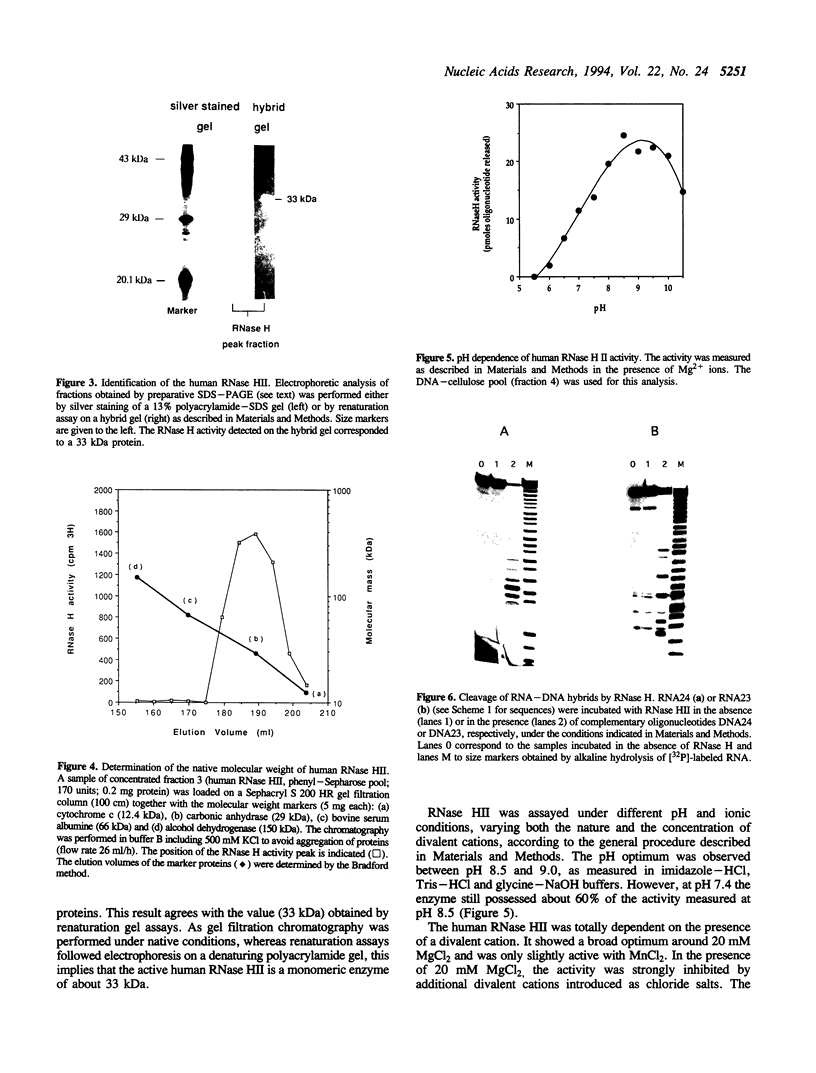
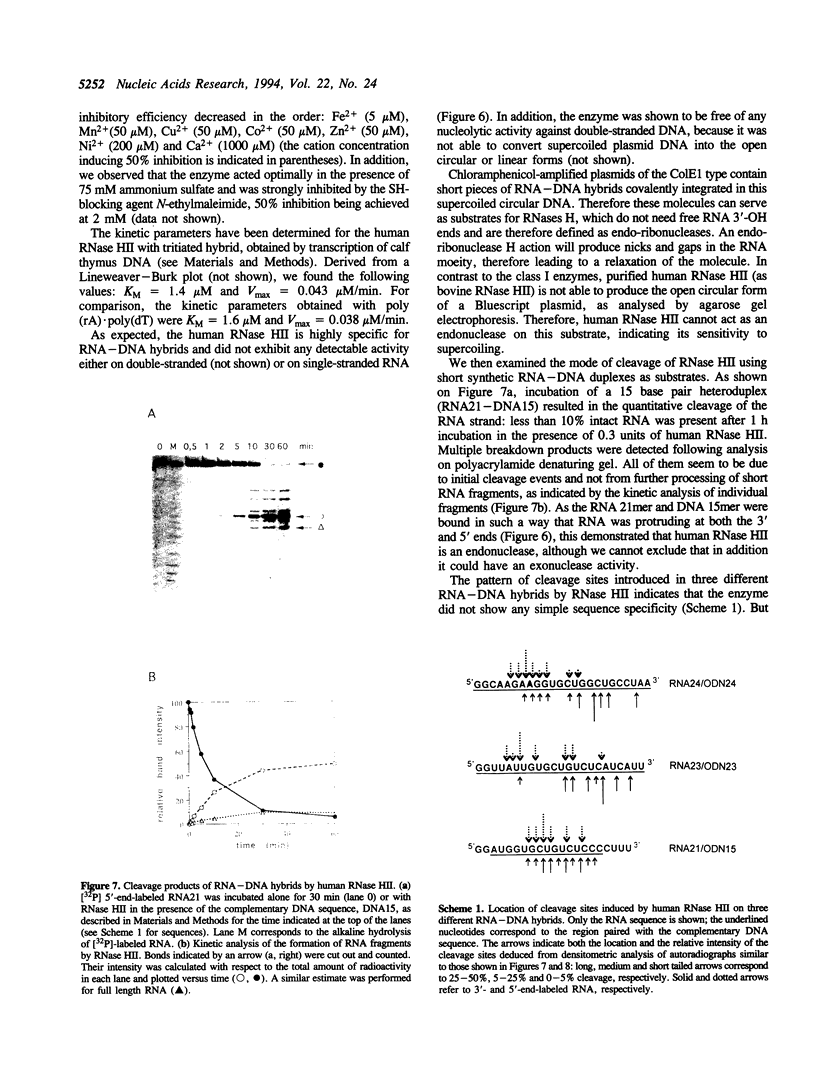
Abstract
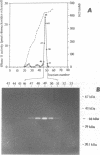
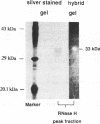
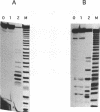
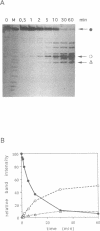
A ribonuclease H activity from human placenta has been separated by ion exchange chromatography from the major RNase HI enzyme. Additional chromatographic steps allowed further purification, more than 3,000 fold compared to the crude extract in which it represents about 15% of the total RNase H activity. The enzyme requires Mg2+ ions for its activity, is strongly inhibited by the addition of Mn2+ ions or other divalent transition metal ions, and exhibits a pH optimum between 8.5 and 9. It shows a strong sensitivity to the SH-blocking agent N-ethylmaleimide. It has a strict specificity for double-stranded RNA-DNA duplexes and exhibits neither single-stranded nor double-stranded RNase (or DNase) activities. Therefore, this enzyme displays the characteristics of class II RNase H and is now termed RNase HII. Renaturation gel assays and gel filtration experiments proved a monomeric structure for the active enzyme with a native molecular weight of about 33 kDa. The human RNase HII acts as an endonuclease and releases oligoribonucleotides with 3'-OH and 5'-phosphate ends. It is therefore a candidate for the RNase H-mediated effect of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Büsen Purification, subunit structure, and serologicai analysis of calf thymus ribonuclease H I. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9434–9443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büsen W., Hausen P. Distinct ribonuclease H activities in calf thymus. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 3;52(1):179–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büsen W., Peters J. H., Hausen P. Ribonuclease H levels during the response of bovine lymphocytes to concanavalin A. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 15;74(1):203–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büsen W. The subunit structure of calf thymus ribonuclease H i as revealed by immunological analysis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7106–7108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Rech J., Huet J., Jeanteur P. Isolation and characterization of two types of ribonucleases H in Krebs II ascites cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7353–7361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Frank P., Büsen W. Characterization of ribonuclease H activities present in two cell-free protein synthesizing systems, the wheat germ extract and the rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Biochimie. 1993;75(1-2):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90032-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Loreau N., Thuong N. T., Toulmé J. J., Hélène C. Enzymatic amplification of translation inhibition of rabbit beta-globin mRNA mediated by anti-messenger oligodeoxynucleotides covalently linked to intercalating agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4717–4736. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash P., Lotan I., Knapp M., Kandel E. R., Goelet P. Selective elimination of mRNAs in vivo: complementary oligodeoxynucleotides promote RNA degradation by an RNase H-like activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7896–7900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen M. L., Crouch R. J. Selective inhibition of RNase H by dextran. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11569–11573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Site specific enzymatic cleavage of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):179–192. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank P., Cazenave C., Albert S., Toulmé J. J. Sensitive detection of low levels of ribonuclease H activity by an improved renaturation gel assay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Nov 15;196(3):1552–1557. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberkern R. C., Cantoni G. L. Studies on a calf thymus ribonuclease specific for ribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybrids. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 19;12(13):2389–2395. doi: 10.1021/bi00737a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausen P., Stein H. Ribonuclease H. An enzyme degrading the RNA moiety of DNA-RNA hybrids. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):278–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogrefe H. H., Hogrefe R. I., Walder R. Y., Walder J. A. Kinetic analysis of Escherichia coli RNase H using DNA-RNA-DNA/DNA substrates. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5561–5566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Toulmé J. J. Specific regulation of gene expression by antisense, sense and antigene nucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 21;1049(2):99–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90031-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Hayase Y., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E. Sequence-dependent hydrolysis of RNA using modified oligonucleotide splints and RNase H. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 11;215(2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. M. Renaturase and ribonuclease H: a novel mechanism that influences transcript displacement by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3187–3196. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara N., Sawai Y., Tsukada K. Purification and properties of magnesium- and manganese-dependent ribonucleases H from chick embryo. J Biochem. 1982 Sep;92(3):855–864. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Van Keuren M. L. Gel protein stains: silver stain. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:441–447. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Hunt T. The use of single-stranded DNA and RNase H to promote quantitative 'hybrid arrest of translation' of mRNA/DNA hybrids in reticulocyte lysate cell-free translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6433–6451. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monia B. P., Lesnik E. A., Gonzalez C., Lima W. F., McGee D., Guinosso C. J., Kawasaki A. M., Cook P. D., Freier S. M. Evaluation of 2'-modified oligonucleotides containing 2'-deoxy gaps as antisense inhibitors of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14514–14522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong Y. W., Carl P. L. On the molecular weight and subunit composition of calf thymus ribonuclease H1. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):383–389. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarngadharan M. G., Leis J. P., Gallo R. C. Isolation and characterization of a ribonuclease from human leukemic blood cells specific for ribonucleic acid of ribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybrid molecules. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):365–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Hausen P. Enzyme from calf thymus degrading the RNA moiety of DNA-RNA Hybrids: effect on DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Science. 1969 Oct 17;166(3903):393–395. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3903.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro F., Ueno Y. Ribonuclease H from rat liver. I. Partial purification and characterization of nuclear ribonuclease H1. J Biochem. 1978 Aug;84(2):385–393. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro F., Ueno Y. Ribonuclease H from rat liver. II. Partial purification and characterization of cytosol ribonuclease H1. J Biochem. 1978 Aug;84(2):395–402. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichman-Weinberg A., Littauer U. Z., Ginzburg I. The inhibition of neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells by tubulin antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonwirth H., Frank P., Büsen W. Serological analysis and characterization of calf thymus ribonuclease H IIb. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Sep 15;184(2):321–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger U. Ribonucleases H of retroviral and cellular origin. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;48(2):259–280. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90083-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]