Abstract
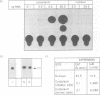
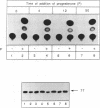
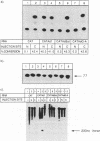
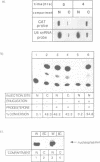
The translation of a capped, polyadenylated RNA after injection into the nucleus of Xenopus oocytes occurs only if the RNA contains an intron. A single point mutation in the splice donor site prevents translation. Intron-less RNA is exported efficiently to the cytoplasm and is held, undegraded, in a translationally inert state for several days. Translation can be activated by treating the oocytes with progesterone or by injecting antibodies that bind the FRGY2 class of messenger RNA binding proteins, p56 and p60, but these antibodies are only effective if delivered to the nucleus. Inhibitors of casein kinase II also activate translation whereas phosphatase inhibitors block progesterone-mediated activation of translation. These data suggest the presence of an RNA handling pathway in the nucleus of Xenopus oocytes which is regulated by casein kinase type II phosphorylation and which directs transcripts to be sequestered by p56/p60 or by closely related proteins. This pathway can be bypassed if the RNA contains an intron and it can be reversed by progesterone treatment. These data may have implications for understanding translational control during early development.
Full text
PDF


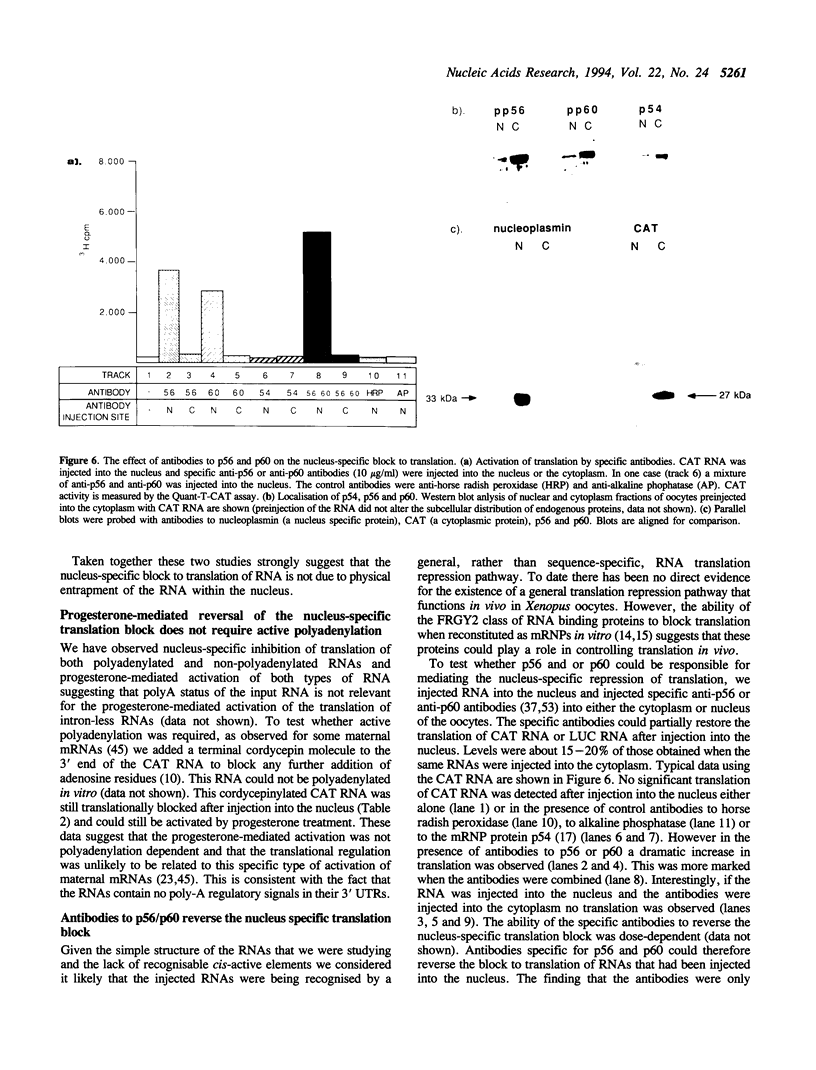
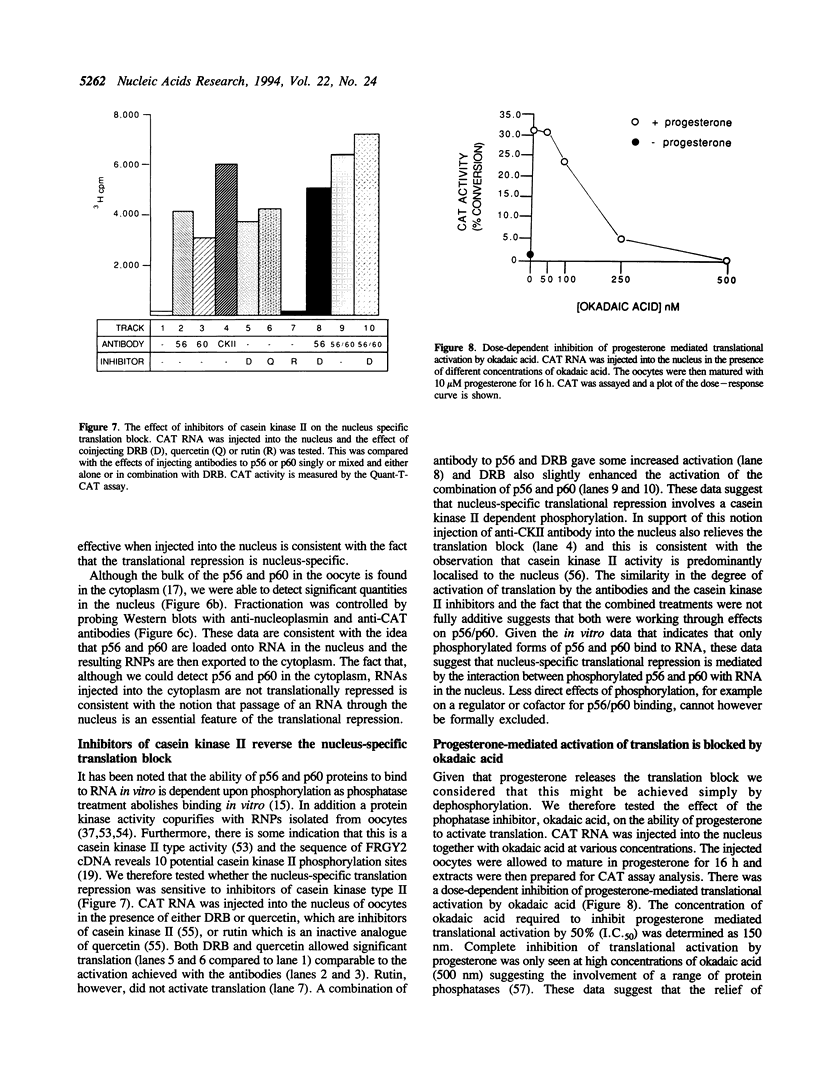


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo S. J., Chen I. S. Rev is necessary for translation but not cytoplasmic accumulation of HIV-1 vif, vpr, and env/vpu 2 RNAs. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):808–819. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baulieu E. E., Godeau F., Schorderet M., Schorderet-Slatkine S. Steroid-induced meiotic division in Xenopus laevis oocytes: surface and calcium. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):593–598. doi: 10.1038/275593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendig M. M., Williams J. G. Fidelity of transcription of Xenopus laevis globin genes injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes and unfertilized eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2109–2119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braddock M., Chambers A., Wilson W., Esnouf M. P., Adams S. E., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. HIV-1 TAT "activates" presynthesized RNA in the nucleus. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90841-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braddock M., Thorburn A. M., Chambers A., Elliott G. D., Anderson G. J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. A nuclear translational block imposed by the HIV-1 U3 region is relieved by the Tat-TAR interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1123–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90389-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capco D. G., Jäckle H. Localized protein synthesis during oogenesis of Xenopus laevis: analysis by in situ translation. Dev Biol. 1982 Nov;94(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Regulation by HIV Rev depends upon recognition of splice sites. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings A., Barrett P., Sommerville J. Multiple modifications in the phosphoproteins bound to stored messenger RNA in Xenopus oocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 14;1014(3):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings A., Sommerville J. Protein kinase activity associated with stored messenger ribonucleoprotein particles of Xenopus oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):45–56. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Agostino D. M., Felber B. K., Harrison J. E., Pavlakis G. N. The Rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promotes polysomal association and translation of gag/pol and vpu/env mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1375–1386. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargemont C., Kühn L. C. Export of mRNA from microinjected nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):1–9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnbrough C. H., Ford P. J. Identification in Xenopus laevis of a class of oocyte-specific proteins bound to messenger RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):415–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearsly A. L., Johnson R. M., Barrett P., Sommerville J. Identification of a 60-kDa phosphoprotein that binds stored messenger RNA of Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jul 1;150(1):95–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps S., Viel A., Denis H., le Maire M. Purification of two thermostable components of messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mRNPs) from Xenopus laevis oocytes, belonging to a novel class of RNA-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 22;282(1):110–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80456-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps S., Viel A., Garrigos M., Denis H., le Maire M. mRNP4, a major mRNA-binding protein from Xenopus oocytes is identical to transcription factor FRG Y2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13799–13802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Vazeux R., Peden K. The rev gene product of the human immunodeficiency virus affects envelope-specific RNA localization. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1155–1165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford C. C., Gurdon J. B. A method for enucleating oocytes of Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1977 Feb;37(1):203–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guddat U., Bakken A. H., Pieler T. Protein-mediated nuclear export of RNA: 5S rRNA containing small RNPs in xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90665-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Melton D. A. Gene transfer in amphibian eggs and oocytes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:189–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Wickens M. P. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:370–386. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Felber B. K., Cladaras C., Athanassopoulos A., Tse A., Pavlakis G. N. The rev (trs/art) protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects viral mRNA and protein expression via a cis-acting sequence in the env region. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1265–1274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1265-1274.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Monomethylated cap structures facilitate RNA export from the nucleus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90292-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarskjöld M. L., Heimer J., Hammarskjöld B., Sangwan I., Albert L., Rekosh D. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus env expression by the rev gene product. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1959–1966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1959-1966.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Standart N. Do the poly(A) tail and 3' untranslated region control mRNA translation? Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90235-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. F., Pickett S. C., Barker D. L. Autoradiography using storage phosphor technology. Electrophoresis. 1990 May;11(5):355–360. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kick D., Barrett P., Cummings A., Sommerville J. Phosphorylation of a 60 kDa polypeptide from Xenopus oocytes blocks messenger RNA translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4099–4109. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Maridor G., Nigg E. A. Casein kinase II is a predominantly nuclear enzyme. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):43–55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon Y. K., Murray M. T., Hecht N. B. Proteins homologous to the Xenopus germ cell-specific RNA-binding proteins p54/p56 are temporally expressed in mouse male germ cells. Dev Biol. 1993 Jul;158(1):99–100. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Cochrane A. W., Johnson C. V., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. The HIV-1 Rev protein: a model system for coupled RNA transport and translation. New Biol. 1991 Dec;3(12):1220–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrain P., Rosbash M. Some cis- and trans-acting mutants for splicing target pre-mRNA to the cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marello K., LaRovere J., Sommerville J. Binding of Xenopus oocyte masking proteins to mRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5593–5600. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrew L. L., Dworkin-Rastl E., Dworkin M. B., Richter J. D. Poly(A) elongation during Xenopus oocyte maturation is required for translational recruitment and is mediated by a short sequence element. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):803–815. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrew L. L., Richter J. D. Translational control by cytoplasmic polyadenylation during Xenopus oocyte maturation: characterization of cis and trans elements and regulation by cyclin/MPF. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3743–3751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., De Robertis E. M., Cortese R. Order and intracellular location of the events involved in the maturation of a spliced tRNA. Nature. 1980 Mar 13;284(5752):143–148. doi: 10.1038/284143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merriam R. W. Progesterone-induced maturational events in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. I. Continuous necessity for diffusible calcium and magnesium. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Sep;68(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90588-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. T., Krohne G., Franke W. W. Different forms of soluble cytoplasmic mRNA binding proteins and particles in Xenopus laevis oocytes and embryos. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):1–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. T., Schiller D. L., Franke W. W. Sequence analysis of cytoplasmic mRNA-binding proteins of Xenopus oocytes identifies a family of RNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris J., Richter J. D. Maturation-specific polyadenylation and translational control: diversity of cytoplasmic polyadenylation elements, influence of poly(A) tail size, and formation of stable polyadenylation complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5634–5645. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris J., Swenson K., Piwnica-Worms H., Richter J. D. Maturation-specific polyadenylation: in vitro activation by p34cdc2 and phosphorylation of a 58-kD CPE-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1697–1708. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan M., Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. Masking mRNA from translation in somatic cells. Genes Dev. 1993 Sep;7(9):1725–1736. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.9.1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Smith L. D. Reversible inhibition of translation by Xenopus oocyte-specific proteins. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):378–380. doi: 10.1038/309378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D. Translational control during early development. Bioessays. 1991 Apr;13(4):179–183. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Woodland H. R., Sturgess E. A. Modulations of histone messenger RNA during the early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1979 Jul;71(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Sommerville J., Bustin M. Injected histone antibodies interfere with transcription of lampbrush chromosome loops in oocytes of Pleurodeles. J Cell Sci. 1979 Dec;40:1–20. doi: 10.1242/jcs.40.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Fox C. A., Hunt T., Vande Woude G., Wickens M. The 3'-untranslated regions of c-mos and cyclin mRNAs stimulate translation by regulating cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 15;8(8):926–938. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.8.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerville J. RNA-binding phosphoproteins and the regulation of maternal mRNA in Xenopus. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1990;42:225–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerville J. RNA-binding proteins: masking proteins revealed. Bioessays. 1992 May;14(5):337–339. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowden M., Harrison S., Ashfield R., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Multiple cooperative interactions constrain BPV-1 E2 dependent activation of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):2959–2972. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. DNA binding, multimerization, and transcription stimulation by the Xenopus Y box proteins in vitro. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):349–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. Dual roles for transcription and translation factors in the RNA storage particles of Xenopus oocytes. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;3(3):94–98. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90080-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. Selective recruitment of masked maternal mRNA from messenger ribonucleoprotein particles containing FRGY2 (mRNP4). J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24255–24261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Wolffe A. P. Xenopus Y-box transcription factors: molecular cloning, functional analysis and developmental regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9028–9032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobian J. A., Drinkard L., Zasloff M. tRNA nuclear transport: defining the critical regions of human tRNAimet by point mutagenesis. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vankan P., McGuigan C., Mattaj I. W. Domains of U4 and U6 snRNAs required for snRNP assembly and splicing complementation in Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3397–3404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Vande Woude G. F., Ikawa Y., Sagata N. Specific proteolysis of the c-mos proto-oncogene product by calpain on fertilization of Xenopus eggs. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):505–511. doi: 10.1038/342505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Tafuri S., Ranjan M., Familari M. The Y-box factors: a family of nucleic acid binding proteins conserved from Escherichia coli to man. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):290–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland H. R., Flynn J. M., Wyllie A. J. Utilization of stored mRNA in Xenopus embryos and its replacement by newly synthesized transcripts: histone H1 synthesis using interspecies hybrids. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zandomeni R., Weinmann R. Inhibitory effect of 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole on a protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14804–14811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M. tRNA transport from the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell: carrier-mediated translocation process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6436–6440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Peña P., Zasloff M. Enhancement of mRNA nuclear transport by promoter elements. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):613–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]