Abstract
In murine cells expressing the PaeR7 endonuclease and methylase genes, the recognition sites (CTCGAG) of these enzymes can be methylated at the adenine residue by the PaeR7 methylase and at the internal cytosine by the mouse DNA methyltransferase. Using nonadecameric duplex deoxyoligonucleotide substrates, the specificity of the PaeR7 endonuclease for unmethylated, hemi-methylated, and fully methylated N6-methyladenine (m6A) and C5-methylcytosine (m5C) versions of these substrates has been studied. The Km, Kcat, and Ki values for these model substrates have been measured and suggest that fully or hemi-m6A-methylated PaeR7 sites in the murine genome are completely protected. However, the reactivity of fully or hemi-m5C-methylated PaeR7 sites is depressed 2900- and 100-fold respectively, compared to unmodified PaeR7 sites. The implications of the kinetic constants of the PaeR7 endonuclease for these methylated recognition sites as they occur in murine cells expressing this endonuclease gene are discussed.
Full text
PDF


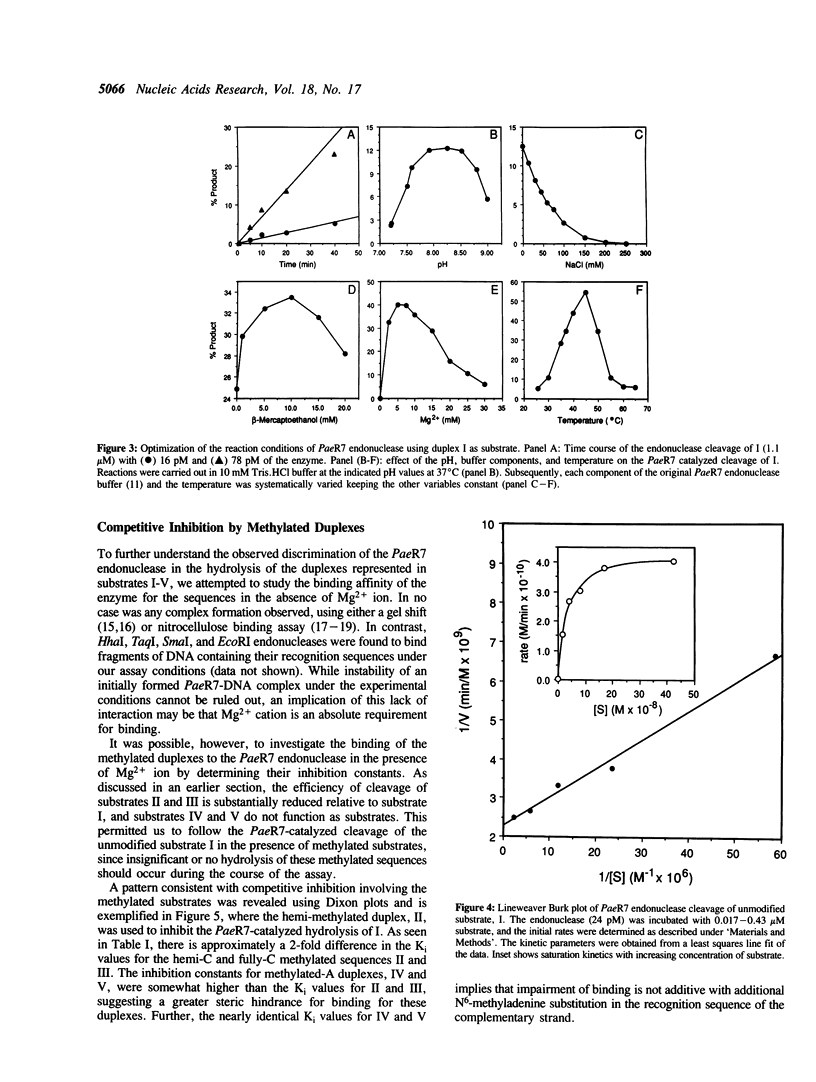
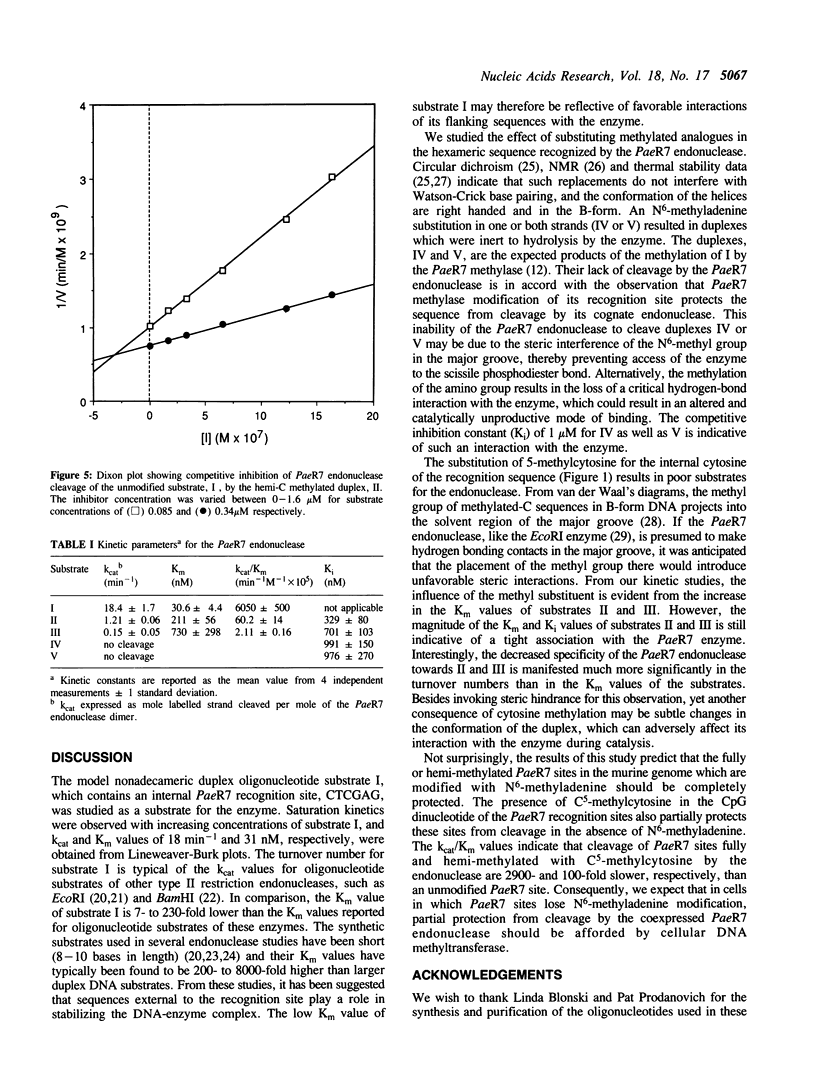

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bestor T., Laudano A., Mattaliano R., Ingram V. Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding DNA methyltransferase of mouse cells. The carboxyl-terminal domain of the mammalian enzymes is related to bacterial restriction methyltransferases. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):971–983. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan C. A., Gumport R. I. T4 RNA ligase catalyzed synthesis of base analogue-containing oligodeoxyribonucleotides and a characterization of their thermal stabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8665–8684. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan C. A., Van Cleve M. D., Gumport R. I. The effects of base analogue substitutions on the cleavage by the EcoRI restriction endonuclease of octadeoxyribonucleotides containing modified EcoRI recognition sequences. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7270–7278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer-Hallquist P., Kézdy F. J., Agarwal K. L. Interaction of the HpaI endonuclease with synthetic oligonucleotides. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4693–4700. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazakerley G. V., Téoule R., Guy A., Fritzsche H., Guschlbauer W. NMR studies on oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing the dam methylation site GATC. Comparison between d(GGATCC) and d(GGm6ATCC). Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4540–4548. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Wang A. H., van der Marel G., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of (m5 dC-dG)3: the role of the methyl group on 5-methyl cytosine in stabilizing Z-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7879–7892. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. S., Musso G. F. Covalent attachment of oligonucleotides to solid supports. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5353–5372. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingeras T. R., Brooks J. E. Cloned restriction/modification system from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):402–406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P. H., Poonian M. S., Nussbaum A. L., Tobias L., Garfin D. E., Boyer H. W., Goodman H. M. Restriction and modification of a self-complementary octanucleotide containing the EcoRI substrate. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 5;99(2):237–261. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Rossi J. J., Wallace R. B. Synthesis and use of synthetic oligonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:323–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita K., Hiraoka N., Kimizuka F., Obayashi A., Kojima H., Takahashi H., Saito H. Interaction of the restriction endonuclease ScaI with its substrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):7015–7024. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.7015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwoh T. J., Kwoh D. Y., McCue A. W., Davis G. R., Patrick D., Gingeras T. R. Introduction and expression of the bacterial PaeR7 methylase gene in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7713–7717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwoh T. J., Obermiller P. S., McCue A. W., Kwoh D. Y., Sullivan S. A., Gingeras T. R. Introduction and expression of the bacterial PaeR7 restriction endonuclease gene in mouse cells containing the PaeR7 methylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11489–11506. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClarin J. A., Frederick C. A., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Grable J., Rosenberg J. M. Structure of the DNA-Eco RI endonuclease recognition complex at 3 A resolution. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1526–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.3024321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono A., Ueda T. Synthesis of decadeoxyribonucleotides containing N6-methyladenine, N4-methylcytosine, and 5-methylcytosine: recognition and cleavage by restriction endonucleases (nucleosides and nucleotides part 74). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):219–232. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry B. J., Jack W. E., Rubin R. A., Modrich P. Thermodynamic parameters governing interaction of EcoRI endonuclease with specific and nonspecific DNA sequences. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9820–9825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriault G., Roy P. H., Howard K. A., Benner J. S., Brooks J. E., Waters A. F., Gingeras T. R. Nucleotide sequence of the PaeR7 restriction/modification system and partial characterization of its protein products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8441–8461. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]