Abstract
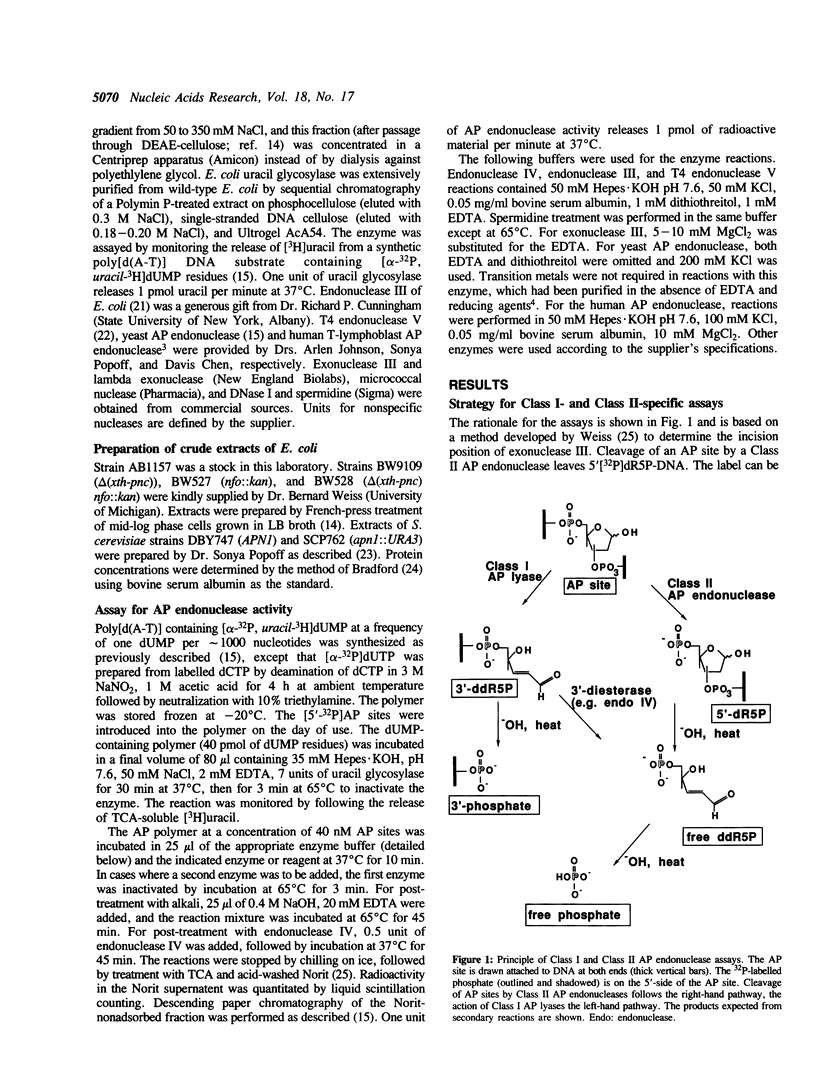
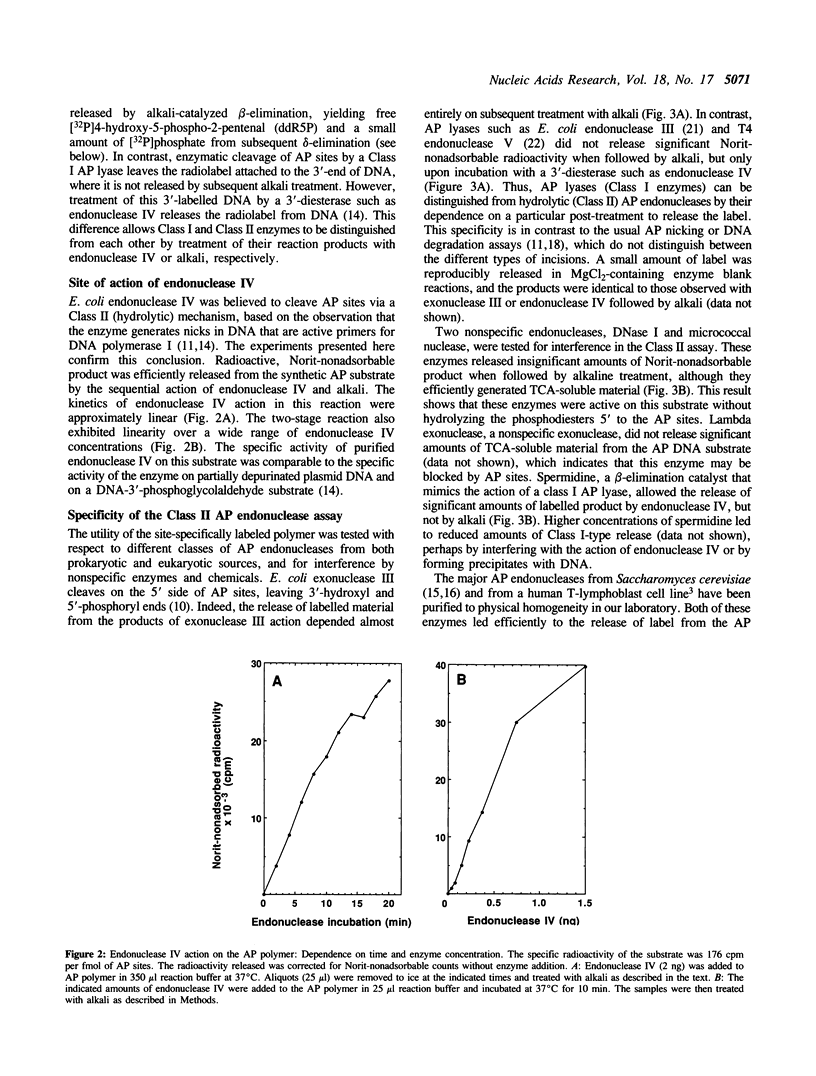
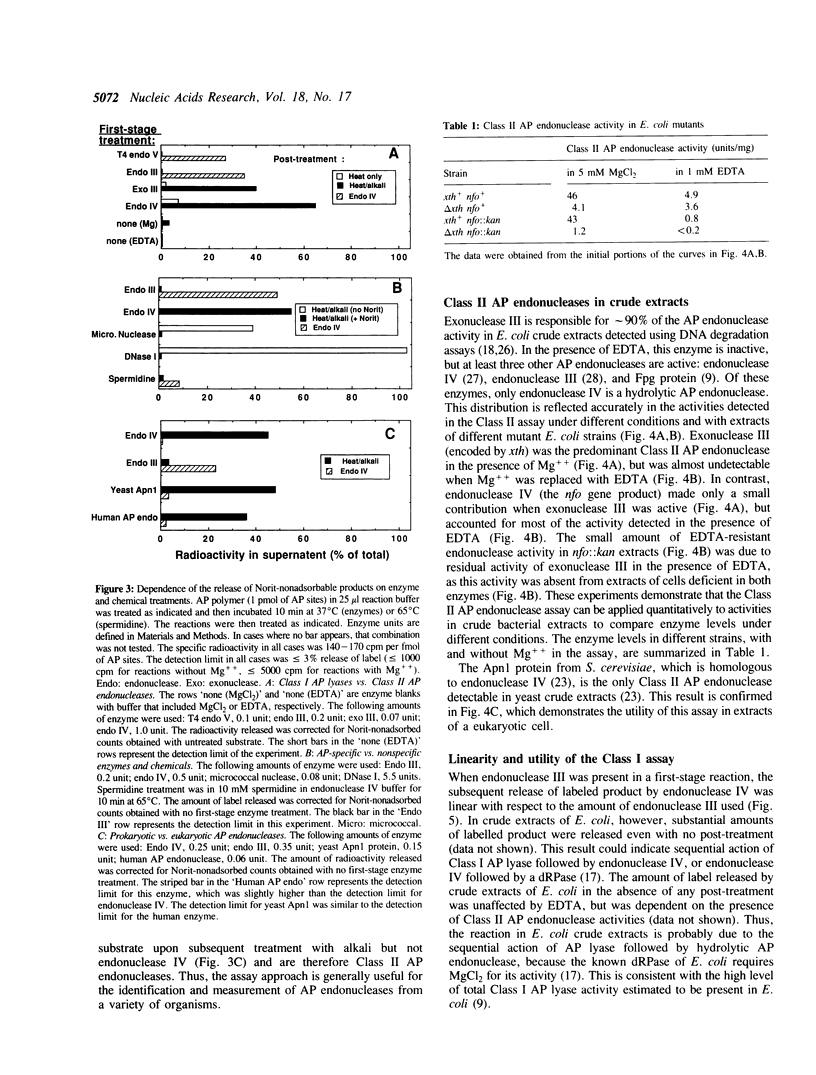
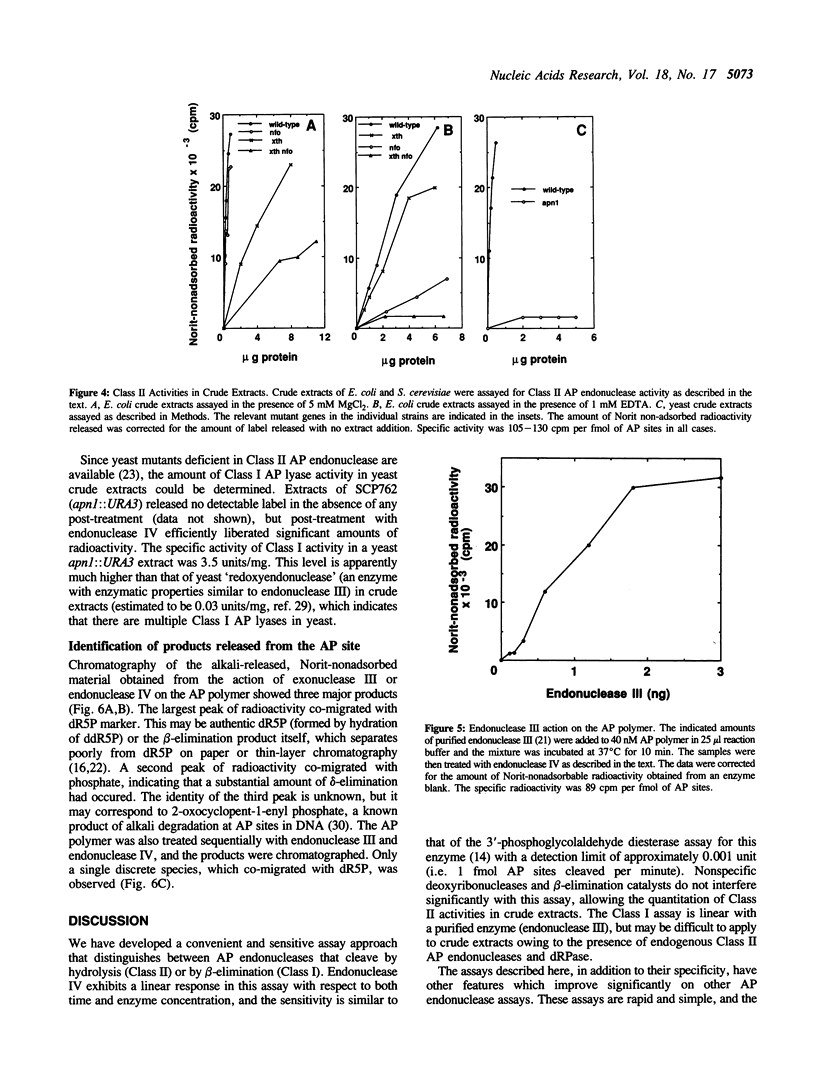
We have developed simple and sensitive assays that distinguish the main classes of apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) endonucleases: Class I enzymes that cleave on the 3' side of AP sites by beta-elimination, and Class II enzymes that cleave by hydrolysis on the 5' side. The distinction of the two types depends on the use of a synthetic DNA polymer that contains AP sites with 5'-[32P]phosphate residues. Using this approach, we now show directly that Escherichia coli endonuclease IV and human AP endonuclease are Class II enzymes, as inferred previously on the basis of indirect assays. The assay method does not exhibit significant interference by nonspecific nucleases or primary amines, which allows the ready determination of different AP endonuclease activities in crude cell extracts. In this way, we show that virtually all of the Class II AP endonuclease activity in E. coli can be accounted for by two enzymes: exonuclease III and endonuclease IV. In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the Class II AP endonuclease activity is totally dependent on a single enzyme, the Apn1 protein, but there are probably multiple Class I enzymes. The versatility and ease of our approach should be useful for characterizing this important class of DNA repair enzymes in diverse systems.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asahara H., Wistort P. M., Bank J. F., Bakerian R. H., Cunningham R. P. Purification and characterization of Escherichia coli endonuclease III from the cloned nth gene. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4444–4449. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly V., Verly W. G. Escherichia coli endonuclease III is not an endonuclease but a beta-elimination catalyst. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):565–572. doi: 10.1042/bj2420565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly V., Verly W. G. Importance of thiols in the repair mechanisms of DNA containing AP (apurinic or apyrimidinic) sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9489–9496. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., Huisman O. Isolation of a formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylase (fpg) mutant of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):300–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00339732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiteux S., O'Connor T. R., Lederer F., Gouyette A., Laval J. Homogeneous Escherichia coli FPG protein. A DNA glycosylase which excises imidazole ring-opened purines and nicks DNA at apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3916–3922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breimer L. H., Lindahl T. DNA glycosylase activities for thymine residues damaged by ring saturation, fragmentation, or ring contraction are functions of endonuclease III in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5543–5548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. E., Rogers S. G., Weiss B. A DNase for apurinic/apyrimidinic sites associated with exonuclease III of Hemophilus influenzae. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):2990–2999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Saporito S. M., Spitzer S. G., Weiss B. Endonuclease IV (nfo) mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1120–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1120-1127.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Weiss B. Endonuclease III (nth) mutants of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):474–478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Johnson A., Fung D. Exonuclease III and endonuclease IV remove 3' blocks from DNA synthesis primers in H2O2-damaged Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7731–7735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin W. A., Lindahl T. DNA deoxyribophosphodiesterase. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3617–3622. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett J., Lee K., Cunningham R. P., Doetsch P. W. Yeast redoxyendonuclease, a DNA repair enzyme similar to Escherichia coli endonuclease III. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2629–2634. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafstrom R. H., Shaper N. L., Grossman L. Human placental apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease. Mechanism of action. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13459–13464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson F. Chemical changes induced in DNA by ionizing radiation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:115–154. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. W., Demple B. Yeast DNA 3'-repair diesterase is the major cellular apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease: substrate specificity and kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18017–18022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. W., Demple B. Yeast DNA diesterase for 3'-fragments of deoxyribose: purification and physical properties of a repair enzyme for oxidative DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18009–18016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane C. M., Linn S. Purification and characterization of an apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3405–3414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Linn S. The mechanisms of action of E. coli endonuclease III and T4 UV endonuclease (endonuclease V) at AP sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1135–1141. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. D., Johnson A. W., Demple B. Homogeneous Escherichia coli endonuclease IV. Characterization of an enzyme that recognizes oxidative damage in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8066–8071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:61–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Ljungquist S., Siegert W., Nyberg B., Sperens B. DNA N-glycosidases: properties of uracil-DNA glycosidase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3286–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Rate of depurination of native deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3610–3618. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungquist S. A new endonuclease from Escherichia coli acting at apurinic sites in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2808–2814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungquist S., Lindahl T., Howard-Flanders P. Methyl methane sulfonate-sensitive mutant of Escherichia coli deficient in an endonuclease specific for apurinic sites in deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):646–653. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.646-653.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A., Preston B. D. Mutagenesis by apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:201–230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosbaugh D. W., Linn S. Further characterization of human fibroblast apurinic/apyrimidinic DNA endonucleases. The definition of two mechanistic classes of enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11743–11752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson B. J., Chang C. N., Grollman A. P., Henner W. D. Mechanism of DNA cleavage and substrate recognition by a bovine apurinic endonuclease. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3894–3901. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiering A. L., Deutsch W. A. Drosophila apurinic/apyrimidinic DNA endonucleases. Characterization of mechanism of action and demonstration of a novel type of enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3222–3228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita M., Chang C. N., Johnson F., Will S., Grollman A. P. Oligodeoxynucleotides containing synthetic abasic sites. Model substrates for DNA polymerases and apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10171–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace S. S. AP endonucleases and DNA glycosylases that recognize oxidative DNA damage. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1988;12(4):431–477. doi: 10.1002/em.2860120411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner H. R., Demple B. F., Deutsch W. A., Kane C. M., Linn S. Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases in repair of pyrimidine dimers and other lesions in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4602–4606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


