Abstract
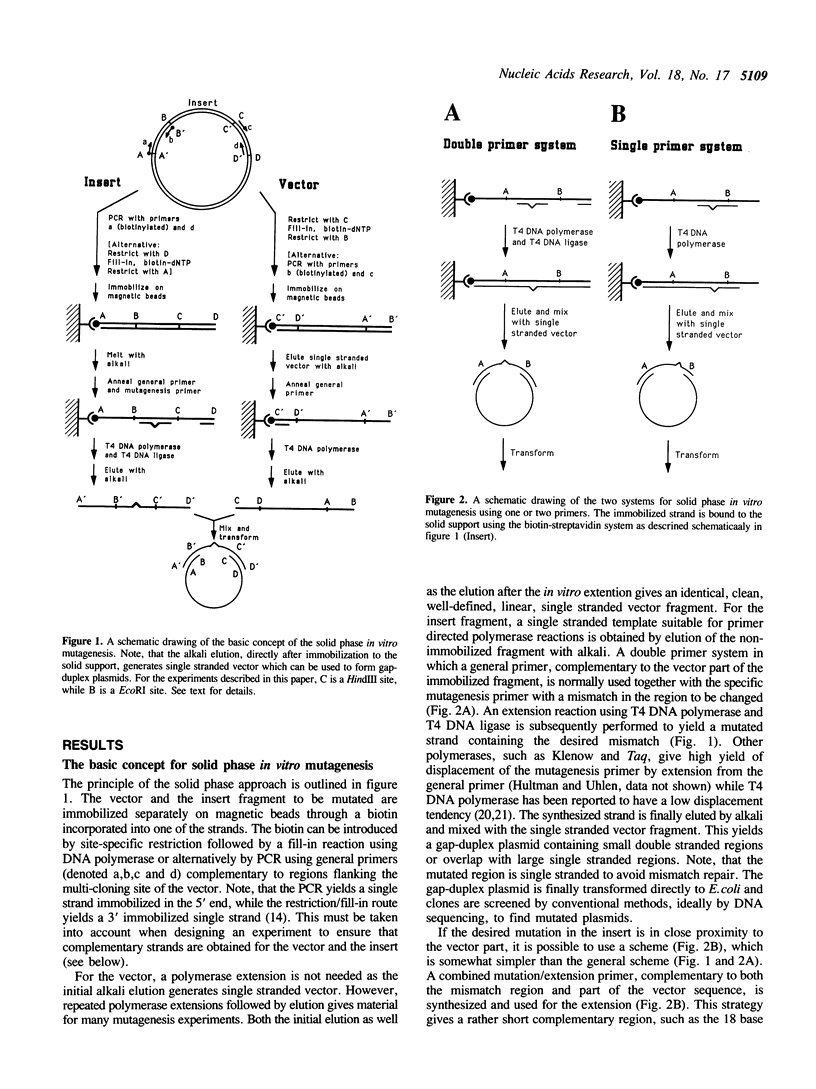
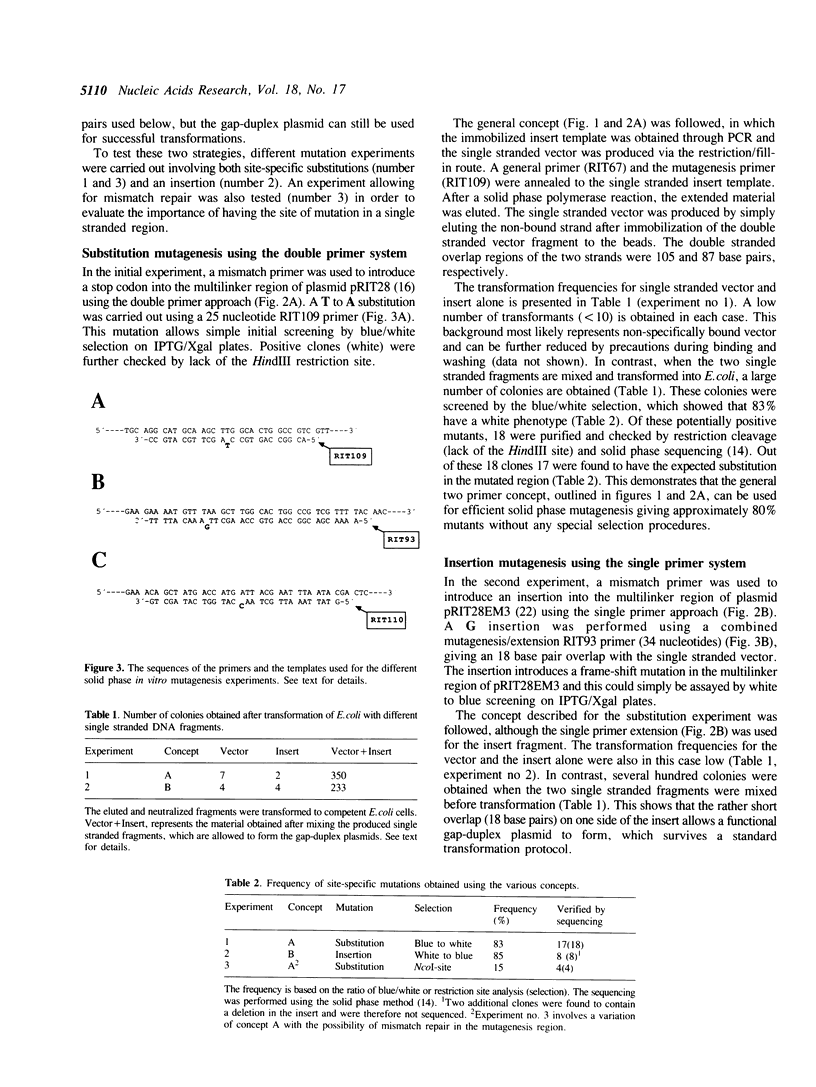
Site-specific mutagenesis was accomplished using a solid support to generate single stranded vector and insert fragments which can be used to form gap-duplex plasmids through flanking, complementary double stranded regions. More than 80% mutants were obtained in both a single and a double primer approach. No special vectors or strains are needed and mismatch repair is avoided as the mutagenesis region is in a single stranded form when transformed into the Escherichia coli host cell. The fragments to be immobilized can be produced either by a polymerase chain reaction using general primers or by a site-specific restriction followed by a fill-in reaction. This novel method is rapid, simple and flexible and well suited for both manual and semi-automated in vitro mutagenesis protocols.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultman T., Ståhl S., Hornes E., Uhlén M. Direct solid phase sequencing of genomic and plasmid DNA using magnetic beads as solid support. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):4937–4946. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Howard B. H. A rapid method for site-specific mutagenesis and directional subcloning by using the polymerase chain reaction to generate recombinant circles. Biotechniques. 1990 Feb;8(2):178–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Schughart K., Fritz H. J. Directed mutagenesis of DNA cloned in filamentous phage: influence of hemimethylated GATC sites on marker recovery from restriction fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6475–6485. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley K. E., Villarejo M. R., Fowler A. V., Zamenhof P. J., Zabin I. Molecular basis of beta-galactosidase alpha-complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1254–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masamune Y., Richardson C. C. Strand displacement during deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis at single strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2692–2701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal N. G. DNA synthesis on a double-stranded DNA template by the T4 bacteriophage DNA polymerase and the T4 gene 32 DNA unwinding protein. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5668–5676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen D. B., Eckstein F. High-efficiency oligonucleotide-directed plasmid mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1451–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U. pUR 250 allows rapid chemical sequencing of both DNA strands of its inserts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5765–5772. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. In vitro mutagenesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:423–462. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhl S., Hultman T., Olsson A., Moks T., Uhlén M. Solid phase DNA sequencing using the biotin-avidin system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):3025–3038. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.3025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhl S., Sjölander A., Hansson M., Nygren P. A., Uhlén M. A general strategy for polymerization, assembly and expression of epitope-carrying peptides applied to the Plasmodium falciparum antigen Pf155/RESA. Gene. 1990 May 14;89(2):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90005-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Huber H. E., Richardson C. C. Escherichia coli thioredoxin confers processivity on the DNA polymerase activity of the gene 5 protein of bacteriophage T7. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16212–16223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindall K. R., Kunkel T. A. Fidelity of DNA synthesis by the Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):6008–6013. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomic M., Sunjevaric I., Savtchenko E. S., Blumenberg M. A rapid and simple method for introducing specific mutations into any position of DNA leaving all other positions unaltered. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1656–1656. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlen M. Magnetic separation of DNA. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):733–734. doi: 10.1038/340733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:329–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


