Abstract
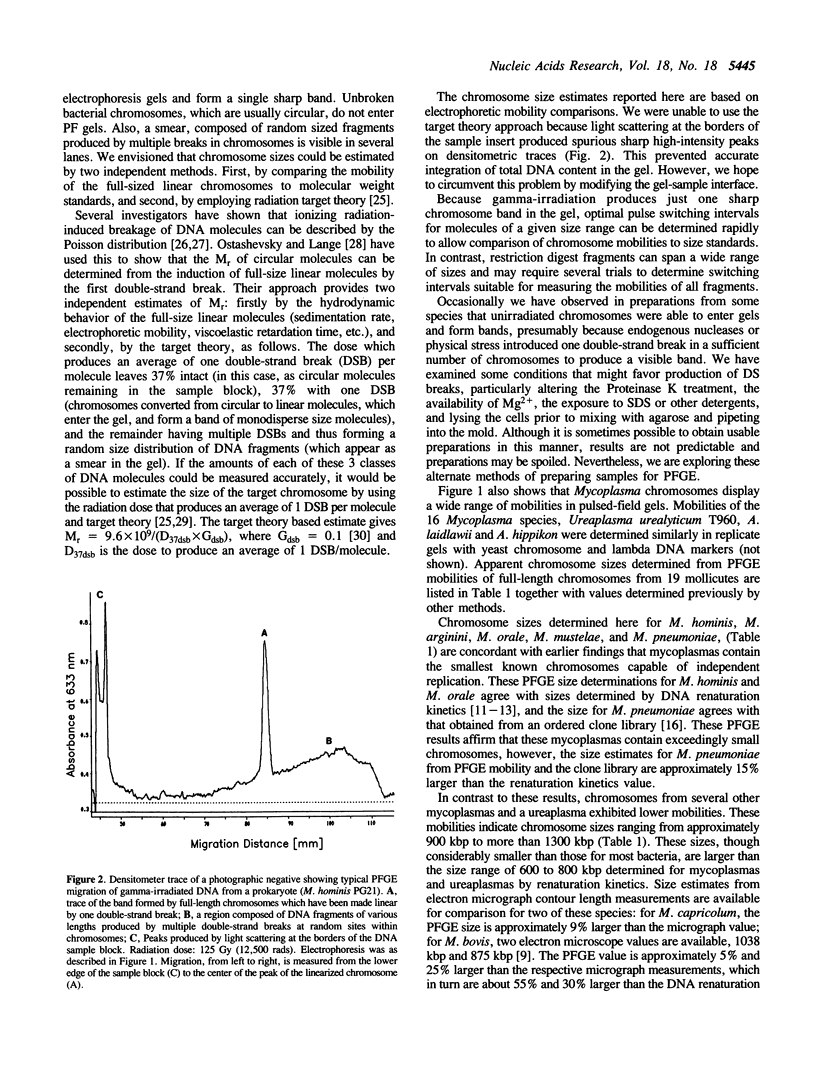
Full-size linear chromosomes were prepared from mycoplasmas by using gamma-irradiation to introduce one (on average) double-strand break in their circular chromosomes. Chromosome sizes were estimated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) from the mobilities of these full-length molecules relative to DNA size references. Sizes estimated for Ureaplasma urealyticum T960 and 16 Mycoplasma species ranged from 684 kbp (M. hominis) to 1315 kbp (M. iowae). Using this sample, we found no correlation between the mobility of the full-size linear chromosomes and their G + C content. Sizes for A. laidlawii and A. hippikon were within the range expected from renaturation kinetics. PFGE size estimates are in good agreement with sizes determined by other methods, including electron microscopy, an ordered clone library, and summation of restriction fragments. Our estimates also agree with those from renaturation kinetics for both the largest and some of the smallest chromosomes, but in the intermediate size range, renaturation kinetics consistently provides lower values than PFGE or electron microscopy. Our PFGE estimates show that mycoplasma chromosomes span a continual range of sizes, with several intermediate values falling between the previously recognized large and small chromosome size clusters.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askaa G., Christiansen C., Erno H. Bovine mycoplasmas: genome size and base composition of DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):283–286. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bak A. L., Black F. T., Christiansen C., Freundt E. A. Genome size of mycoplasmal DNA. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1209–1210. doi: 10.1038/2241209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bak A. L., Christiansen C., Stenderup A. Bacterial genome sizes determined by DNA renaturation studies. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):377–380. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautsch W. Rapid physical mapping of the Mycoplasma mobile genome by two-dimensional field inversion gel electrophoresis techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11461–11467. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergemann A. D., Whitley J. C., Finch L. R. Homology of mycoplasma plasmid pADB201 and staphylococcal plasmid pE194. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):593–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.593-595.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bove J. M. Spiroplasmas: from pathology to biology and vice versa. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Sep;20(9):817–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Smith C. L., Mathew M. K. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of very large DNA molecules. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:287–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman S. D., Hu P. C., Bott K. F. Prevalence of novel repeat sequences in and around the P1 operon in the genome of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Gene. 1990 Mar 1;87(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90498-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehmann U. K., Lett J. T. Review and evaluation of molecular weight calculations from the sedimentation profiles of irradiated DNA. Radiat Res. 1973 Apr;54(1):152–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frutos R., Pages M., Bellis M., Roizes G., Bergoin M. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis determination of the genome size of obligate intracellular bacteria belonging to the genera Chlamydia, Rickettsiella, and Porochlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4511–4513. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4511-4513.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis M., de Ley J. Determination of the molecular complexity of double-stranded phage genome DNA from initial renaturation rates. The effect of DNA base composition. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):447–464. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence-directed curvature of DNA. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):449–450. doi: 10.1038/321449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauc L., Mitchell M., Goodgal S. H. Size and physical map of the chromosome of Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2474–2479. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2474-2479.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Asai T., Imai M., Takanami M. Methylation strongly enhances DNA bending in the replication origin region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):69–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00261159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange C. S., Ostashevsky J., Perlmutter E., DeLeon J., Grossman G. The use of viscoelastometry to determine survival curves for intact genomes. Radiat Res. 1984 Oct;100(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Smith H. O. Sizing of the Haemophilus influenzae Rd genome by pulsed-field agarose gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4402–4405. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4402-4405.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Zimm B. H. Understanding the anomalous electrophoresis of bent DNA molecules: a reptation model. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):396–399. doi: 10.1126/science.2756426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J. Anomalous values of Mycoplasma genomes sizes determined by pulse-field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1268–1268. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroun R. C., Olson W. K. Base sequence effects in double-helical DNA. II. Configurational statistics of rodlike chains. Biopolymers. 1988 Apr;27(4):561–584. doi: 10.1002/bip.360270403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neimark H. C. Division of mycoplasmas into subgroups. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):249–263. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neimark H., London J. Origins of the mycoplasmas: sterol-nonrequiring mycoplasmas evolved from streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1259–1265. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1259-1265.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nur I., LeBlanc D. J., Tully J. G. Short, interspersed, and repetitive DNA sequences in Spiroplasma species. Plasmid. 1987 Mar;17(2):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostashevsky J. Y. A model relating cell survival to DNA fragment loss and unrepaired double-strand breaks. Radiat Res. 1989 Jun;118(3):437–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostashevsky J. Y., Lange C. S. A model of the hydrodynamic behavior of irradiated DNA: dependence on molecular conformation. Biopolymers. 1987 Jan;26(1):59–82. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poddar S. K., Maniloff J. Determination of microbial genome sizes by two-dimensional denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):2889–2895. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.2889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proceedings of the eighth annual Mid-Atlantic Regional Extrachromosomal Genetic Elements Conference. October 12-14, 1984, Virginia Beach, Virginia. Plasmid. 1985 May;13(3):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Corcoran L. N., Cocks B. G., Bergemann A. D., Whitley J. C., Finch L. R. Pulsed-field electrophoresis indicates larger-than-expected sizes for mycoplasma genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6015–6025. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Razin S. Methylated bases in mycoplasmal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1383–1390. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Barile M. F., Harasawa R., Amikam D., Glaser G. Characterization of the mycoplasma genome. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):357–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
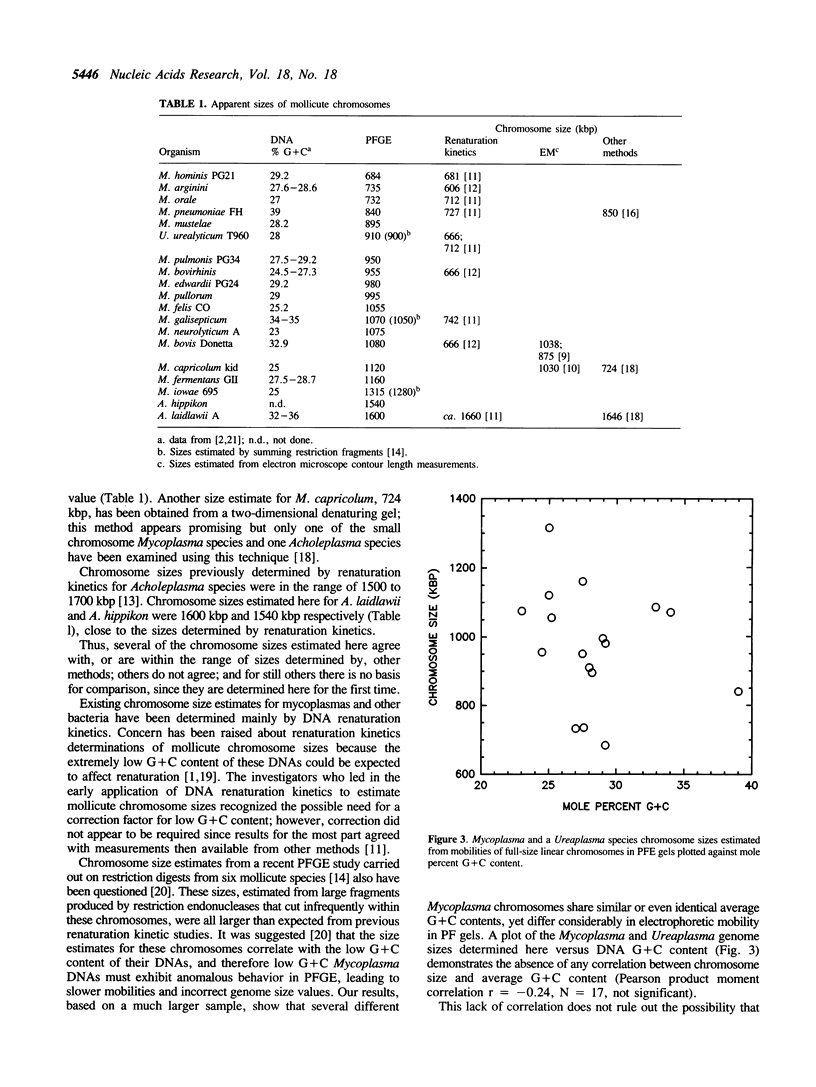
- Razin S. Molecular biology and genetics of mycoplasmas (Mollicutes). Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):419–455. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.419-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A., Pyle L. E., Stemke G. W., Finch L. R. Human ureaplasmas show diverse genome sizes by pulsed-field electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1451–1455. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. J., Simmons J., Walker R. T., Weisburg W. G., Woese C. R., Tanner R. S., Robinson I. M., Stahl D. A., Olsen G., Leach R. H. Construction of the mycoplasma evolutionary tree from 5S rRNA sequence data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1160–1164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. L., Morowitz H. J. Partial purification of native rRNA and tRNA cistrons from mycoplasma sp. (Kid). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1282–1289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Becker Y. Trachoma agent DNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 28;42(3):581–589. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90245-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. J., Chavoya A., Baseman J. B. Regions of Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadhesin P1 structural gene exist as multiple copies. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3157–3161. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3157-3161.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. A., Ferrell R. V., Wise K. S., McIntosh M. A. Reiterated DNA sequences defining genomic diversity within the species Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):665–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W., Connelly C., Hieter P. Physical mapping of large DNA by chromosome fragmentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6027–6031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7865–7876. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Tully J. G., Rose D. L., Petzel J. P., Oyaizu H., Yang D., Mandelco L., Sechrest J., Lawrence T. G., Van Etten J. A phylogenetic analysis of the mycoplasmas: basis for their classification. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6455–6467. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6455-6467.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R., Herrmann R. Cloning of the complete Mycoplasma pneumoniae genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 12;17(17):7029–7043. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.17.7029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R., Herrmann R. Repetitive DNA sequences in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8337–8350. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Maniloff J., Zablen L. B. Phylogenetic analysis of the mycoplasmas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):494–498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




