Abstract
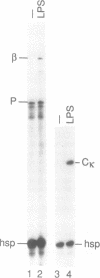
The first enhancers to be identified in the immunoglobulin gene loci are located in the J-C intron. However, deletion of the immunoglobulin kappa intron-enhancer has little effect on the transcription of kappa transgenes. Here we ask whether the second kappa enhancer which we recently identified at the 3'-end of the locus plays a role in kappa gene expression. We show that its omission leads to 20-40 fold lower expression of kappa transgenes and to poor allelic exclusion. Transfection experiments show that activity of the 3'-enhancer, like that of the kappa-intron enhancer, can be induced in a pre-B cell line by incubation with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Whereas induction of the kappa-intron enhancer is due to induction of NF-kappa B activity, deletion mapping of the 3'-enhancer localises its activity to a 50 nucleotide region that lacks an NF-kappa B site; indeed the 3'-enhancer allows kappa expression in a cell line which lacks NF-kappa B. Thus, both the 3'- and intron-enhancers can be induced at the same stage of differentiation but by distinct pathways. Furthermore, unlike the intron-enhancer, the 3'-enhancer plays a critical role in the transcription of rearranged immunoglobulin kappa genes.
Full text
PDF

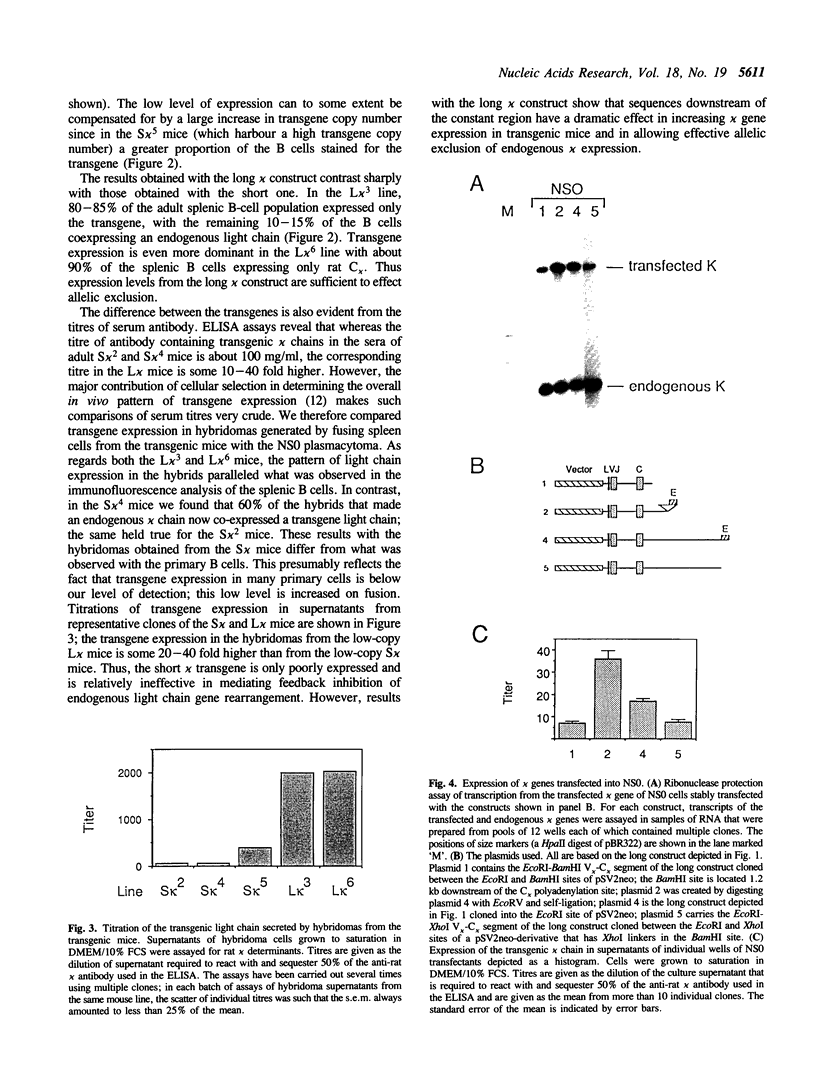



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilera R. J., Hope T. J., Sakano H. Characterization of immunoglobulin enhancer deletions in murine plasmacytomas. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3689–3693. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki K., Maeda H., Wang J., Kitamura D., Watanabe T. Purification of a nuclear trans-acting factor involved in the regulated transcription of a human immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):723–730. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. Complementation between two cell lines lacking kappa enhancer activity: implications for the developmental control of immunoglobulin transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4213–4220. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03318.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The role of the kappa enhancer and its binding factor NF-kappa B in the developmental regulation of kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasquez V. C., Xu M., Moses S. C., Garrard W. T. Immunoglobulin kappa gene expression after stable integration. I. Role of the intronic MAR and enhancer in plasmacytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21183–21189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Milstein C. Expression of spleen cell immunoglobulin phenotype in hybrids with myeloma cell lines. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Nov;7(6):657–666. doi: 10.1007/BF01538755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt L. A., Birshtein B. K. Independent immunoglobulin class-switch events occurring in a single myeloma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):856–868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlinger P., LeMeur M., Irrmann C., Renard P., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. B-lymphocyte targeting of gene expression in transgenic mice with the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6565–6577. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhardt M., Babinet C., Lutfalla G., Kallenbach S., Cavelier P., Rougeon F. Immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene promoter and enhancer are not responsible for B-cell restricted gene rearrangement. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7403–7415. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow C. C., Crosbie J., Adelstein S., Lavoie T. B., Smith-Gill S. J., Brink R. A., Pritchard-Briscoe H., Wotherspoon J. S., Loblay R. H., Raphael K. Altered immunoglobulin expression and functional silencing of self-reactive B lymphocytes in transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):676–682. doi: 10.1038/334676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagman J., Rudin C. M., Haasch D., Chaplin D., Storb U. A novel enhancer in the immunoglobulin lambda locus is duplicated and functionally independent of NF kappa B. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):978–992. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S., Sablitzky F., Radbruch A. Deletion of the IgH enhancer does not reduce immunoglobulin heavy chain production of a hybridoma IgD class switch variant. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2473–2476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Staudt L., Robbins P., Kuang A., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Repression of the IgH enhancer in teratocarcinoma cells associated with a novel octamer factor. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):544–546. doi: 10.1126/science.2536195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Involvement of a second lymphoid-specific enhancer element in the regulation of immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3155–3162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. O., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. Transcription cell type specificity is conferred by an immunoglobulin VH gene promoter that includes a functional consensus sequence. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The nucleotide sequence of a 5.5-kilobase DNA segment containing the mouse kappa immunoglobulin J and C region genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
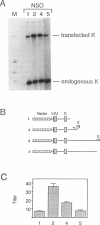
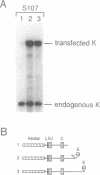
- Meyer K. B., Neuberger M. S. The immunoglobulin kappa locus contains a second, stronger B-cell-specific enhancer which is located downstream of the constant region. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1959–1964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelms K., Hromas R., Van Ness B. Identification of a second inducible DNA-protein interaction in the kappa immunoglobulin enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsen B., Kadesch T., Sen R. Complex regulation of the immunoglobulin mu heavy-chain gene enhancer: microB, a new determinant of enhancer function. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3145–3154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S. Expression and regulation of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene transfected into lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1373–1378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paige C. J., Kincade P. W., Ralph P. Independent control of immunoglobulin heavy and light chain expression in a murine pre-B-cell line. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):631–633. doi: 10.1038/292631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson S., Cook G. P., Brüggemann M., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. A second B cell-specific enhancer 3' of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):165–168. doi: 10.1038/344165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson S., Sharpe M. J., Gilmore D. R., Surani M. A., Neuberger M. S. Cellular selection leads to age-dependent and reversible down-regulation of transgenic immunoglobulin light chain genes. Int Immunol. 1989;1(5):509–516. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. Cell-type preference of immunoglobulin kappa and lambda gene promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2831–2838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Weir L., Leder P. Enhancer-dependent expression of human kappa immunoglobulin genes introduced into mouse pre-B lymphocytes by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7161–7165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Stafford J. Fine mapping of an immunoglobulin gene activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1042–1049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik W., Williams G., Barton S., Norris M., Neuberger M., Surani M. A. Provision of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer downstream of a test gene is sufficient to confer lymphoid-specific expression in transgenic mice. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Apr;17(4):465–469. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie K. A., Brinster R. L., Storb U. Allelic exclusion and control of endogenous immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in kappa transgenic mice. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):517–520. doi: 10.1038/312517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Köhler G. Transmission and expression of a specific pair of rearranged immunoglobulin mu and kappa genes in a transgenic mouse line. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):330–334. doi: 10.1038/314330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe M. J., Neuberger M., Pannell R., Surani M. A., Milstein C. Lack of somatic mutation in a kappa light chain transgene. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1379–1385. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard H. W., Gutman G. A. Allelic forms of rat kappa chain genes: evidence for strong selection at the level of nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7064–7068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Pinkert C., Arp B., Engler P., Gollahon K., Manz J., Brady W., Brinster R. L. Transgenic mice with mu and kappa genes encoding antiphosphorylcholine antibodies. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):627–641. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wabl M. R., Burrows P. D. Expression of immunoglobulin heavy chain at a high level in the absence of a proposed immunoglobulin enhancer element in cis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2452–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K. An enhancer element in the short unique region of human cytomegalovirus regulates the production of a group of abundant immediate early transcripts. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):406–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M., Hammer R. E., Blasquez V. C., Jones S. L., Garrard W. T. Immunoglobulin kappa gene expression after stable integration. II. Role of the intronic MAR and enhancer in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21190–21195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]