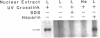Abstract
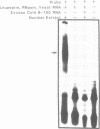
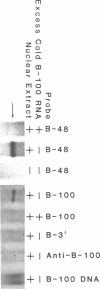
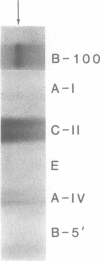
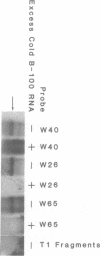
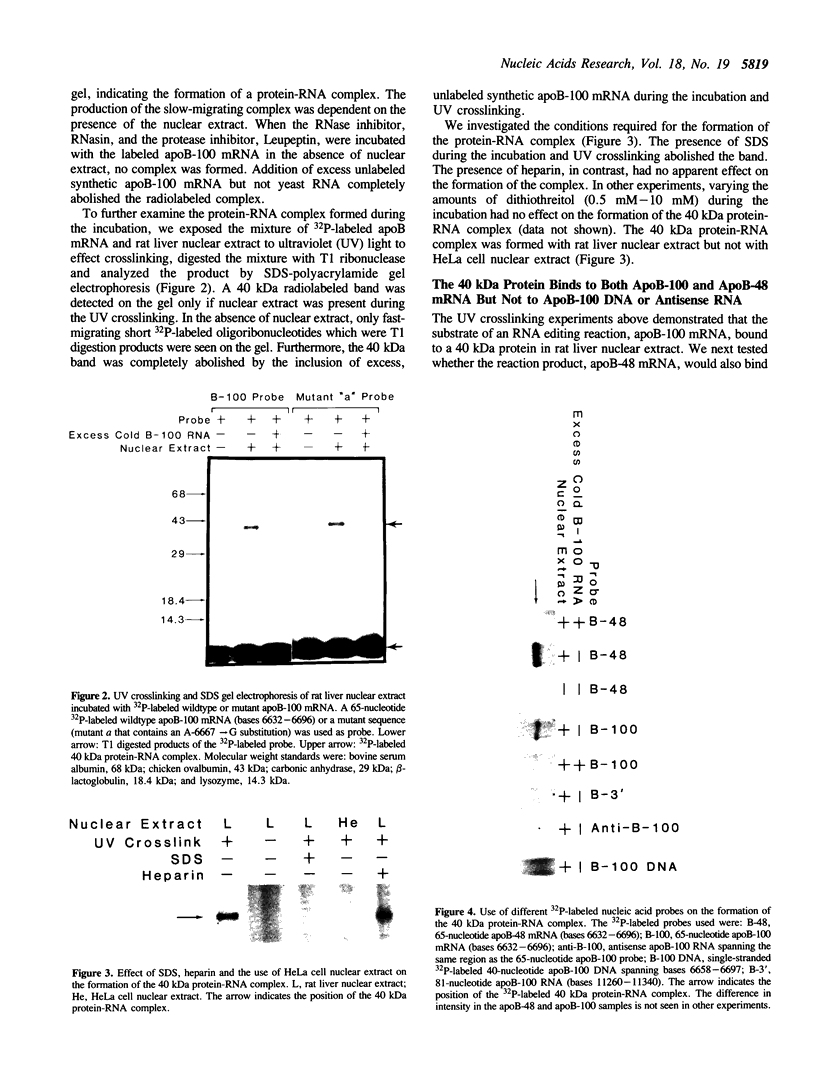
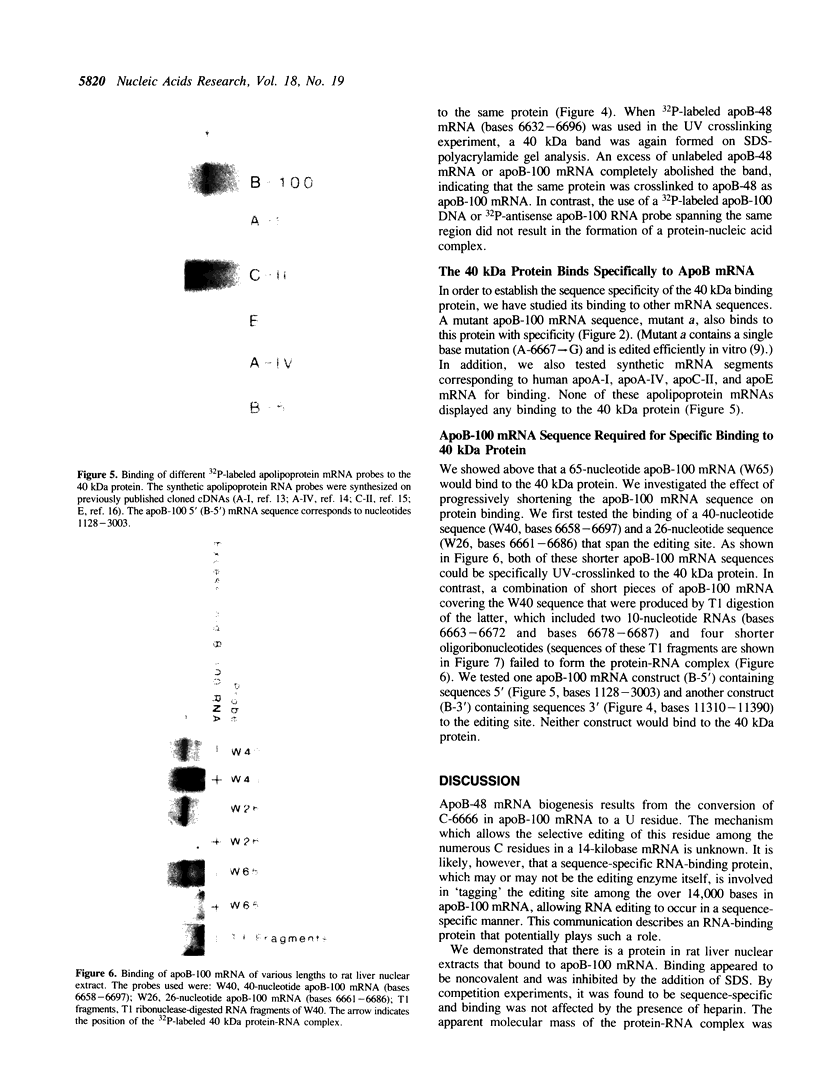
Apolipoprotein (apo) B-48 mRNA is the product of RNA editing which consists of a C----U conversion changing a CAA codon encoding Gln-2153 in apoB-100 mRNA to a UAA stop codon in apoB-48 mRNA. In the adult rat, RNA editing occurs both in the small intestine and the liver. We have studied the ability of rat liver nuclear extracts to bind to synthetic apoB mRNA segments spanning the editing site. Using an RNA gel mobility shift assay, we found the sequence-specific binding of a protein(s) to a 65-nucleotide apoB-100 mRNA. UV crosslinking followed by T1 ribonuclease digestion and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis demonstrated the formation of a 40 kDa protein-RNA complex when 32P-labeled apoB-100 mRNA was incubated with a rat liver nuclear extract but not with HeLa nuclear extract. Binding was specific for the sense strand of apoB mRNA, and was not demonstrated with single-stranded apoB DNA, or antisense apoB RNA. The complex also failed to form if SDS was present during the UV light exposure. Binding experiments using synthetic apoB mRNAs indicate that the 40 kDa protein would also bind to apoB-48 mRNA but not apoA-I, apoA-IV, apoC-II or apoE mRNA. Experiments using deletion mutants of apoB-100 mRNA indicate efficient binding of wildtype 65-nucleotide (W65), 40-nucleotide (W40) and 26-nucleotide (W26) apoB-100 mRNA segments, but not 10-nucleotide (or smaller) segments of apoB-100 mRNA to the 40 kDa protein. In contrast, two other regions of apoB-100 mRNA, B-5' (bases 1128-3003) and B-3' (bases 11310-11390), failed to bind to the protein. The 40 kDa sequence-specific binding protein in rat liver nuclear extract may play a role in apoB-100 mRNA editing.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Habib G., Yang C. Y., Gu Z. W., Lee B. R., Weng S. A., Silberman S. R., Cai S. J., Deslypere J. P., Rosseneu M. Apolipoprotein B-48 is the product of a messenger RNA with an organ-specific in-frame stop codon. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):363–366. doi: 10.1126/science.3659919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Li X. X., Liao W. S., Wu J. H., Chan L. RNA editing of apolipoprotein B mRNA. Sequence specificity determined by in vitro coupled transcription editing. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6811–6816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung P., Chan L. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA of human apolipoprotein A-I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3703–3715. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. O., Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Scott J. Thyroid hormone modulates the introduction of a stop codon in rat liver apolipoprotein B messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13482–13485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. S., Wallis S. C., Driscoll D. M., Wynne J. K., Williams G. W., Powell L. M., Scott J. Sequence requirements for apolipoprotein B RNA editing in transfected rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13395–13398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. M., Wynne J. K., Wallis S. C., Scott J. An in vitro system for the editing of apolipoprotein B mRNA. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. Apolipoprotein B: structural and metabolic heterogeneity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:637–650. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott T. J., Rall S. C., Jr, Innerarity T. L., Jacobson S. F., Urdea M. S., Levy-Wilson B., Powell L. M., Pease R. J., Eddy R., Nakai H. Human apolipoprotein B: structure of carboxyl-terminal domains, sites of gene expression, and chromosomal localization. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):37–43. doi: 10.1126/science.2994225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Lee Y. C., Kao F. T., Cheung P., Chan L. Apolipoprotein E gene mapping and expression: localization of the structural gene to human chromosome 19 and expression of ApoE mRNA in lipoprotein- and non-lipoprotein-producing tissues. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3751–3756. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Chen J., Whoriskey J. Two proteins crosslinked to RNA containing the adenovirus L3 poly(A) site require the AAUAAA sequence for binding. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3159–3169. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Pease R. J., Edwards Y. H., Knott T. J., Scott J. A novel form of tissue-specific RNA processing produces apolipoprotein-B48 in intestine. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90510-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. F., Tsao Y. K., Robberson D. L., Gotto A. M., Jr, Brown K., Chan L. The structure of the human apolipoprotein C-II gene. Electron microscopic analysis of RNA:DNA hybrids, complete nucleotide sequence, and identification of 5' homologous sequences among apolipoprotein genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15211–15221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. Y., Chen S. H., Gianturco S. H., Bradley W. A., Sparrow J. T., Tanimura M., Li W. H., Sparrow D. A., DeLoof H., Rosseneu M. Sequence, structure, receptor-binding domains and internal repeats of human apolipoprotein B-100. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):738–742. doi: 10.1038/323738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. Y., Gu Z. W., Chong I. S., Xiong W. J., Rosseneu M., Yang H. X., Lee B. R., Gotto A. M., Jr, Chan L. The primary structure of human apolipoprotein A-IV. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 3;1002(2):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]