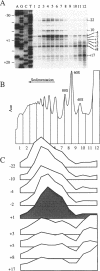
Abstract
The role of eukaryotic 5'-untranslated messenger RNA leaders is not entirely clear, since they share little sequence similarity among each other. The importance of the leader in determining the efficiency of translation initiation was addressed here by examining the polyribosome distribution of several leader-deletion alleles of the yeast tcm1 gene (coding for ribosomal protein L3). Shortening of this 22-nucleotide leader, or complete removal of it (the first nucleotide of the mRNA becoming the A of the translation initiation codon AUG) permitted translation, albeit reduced. Further deletion of as few as the first two nucleotides of the initiation codon leads to a substantial reduction in ribosome loading, which is compatible with inefficient initiation at the next downstream, out-of-frame, AUG triplet. A second measure of translation initiation was obtained by assaying qualitatively for the production of biologically active L3 protein using growth-resistance to trichodermin. This experiment indicates that ribosomes can recognize the correct initiation codon even in the complete absence of a leader. We conclude that the 5'-untranslated leader of the yeast tcm1 gene is not essential for accurate translation initiation, but enhances its efficiency.
Full text
PDF
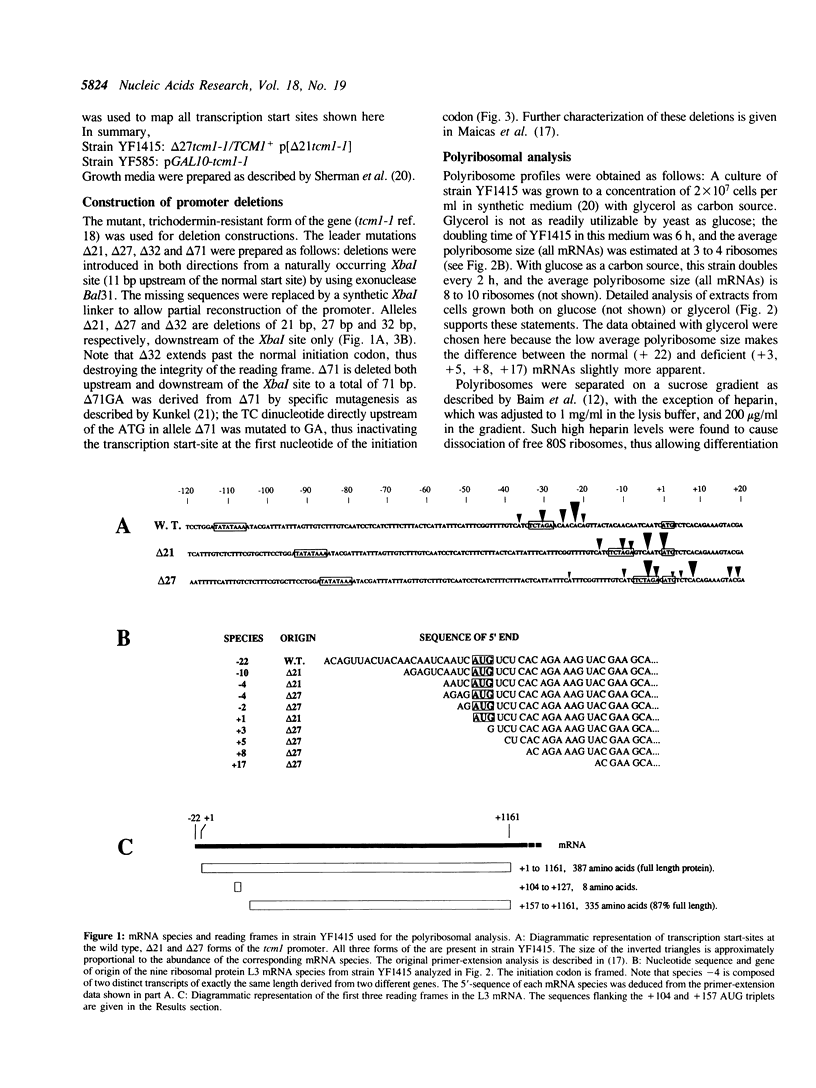
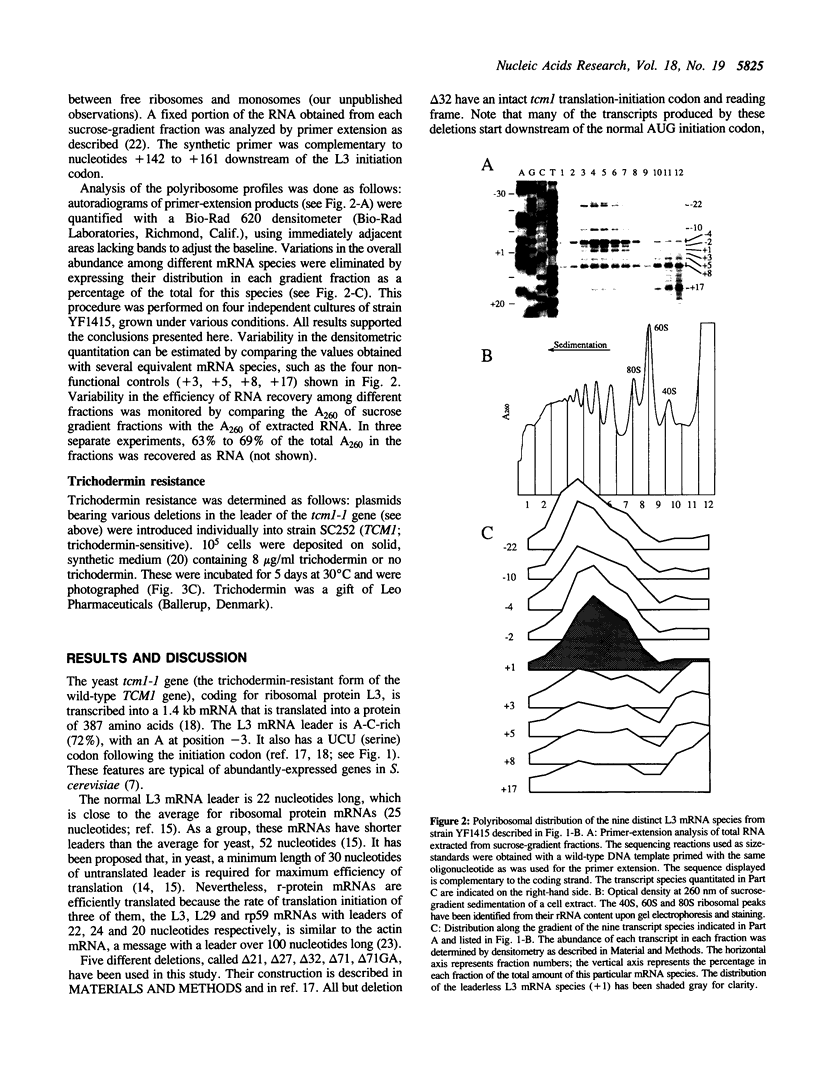
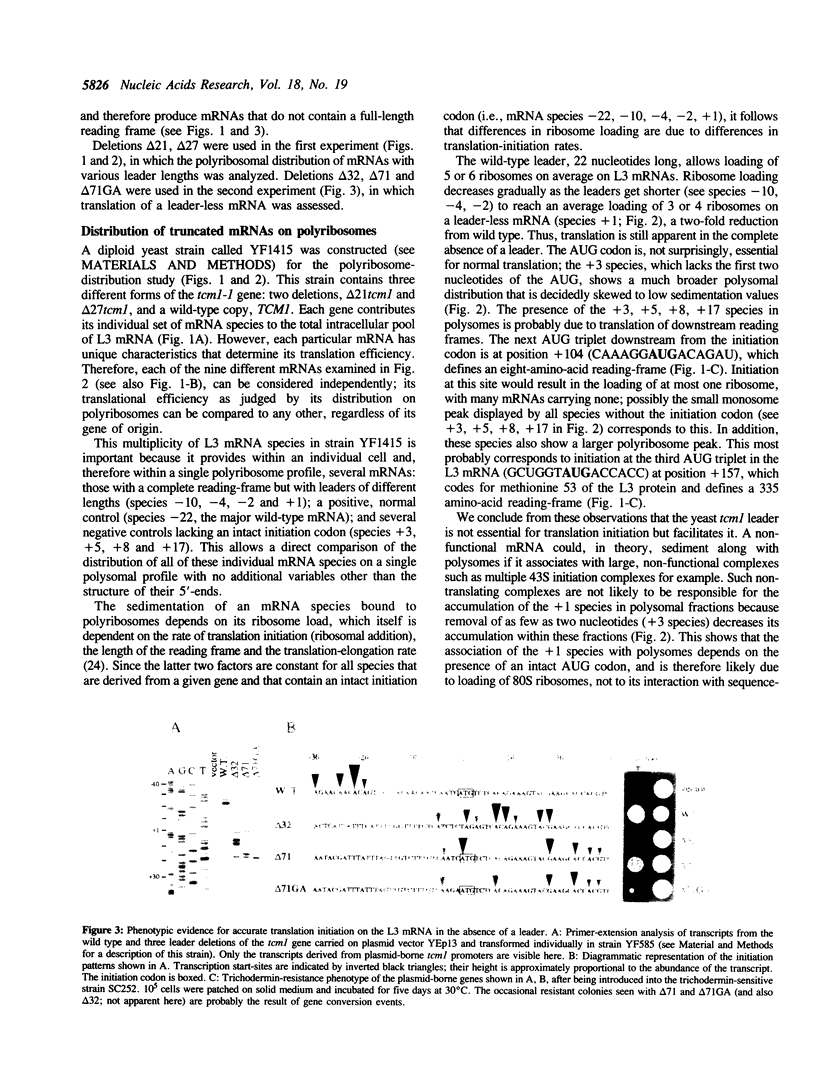


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baim S. B., Pietras D. F., Eustice D. C., Sherman F. A mutation allowing an mRNA secondary structure diminishes translation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae iso-1-cytochrome c. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1839–1846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baim S. B., Sherman F. mRNA structures influencing translation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1591–1601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann J. E., Lodish H. F. A kinetic model of protein synthesis. Application to hemoglobin synthesis and translational control. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11927–11937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R. Construction of high copy yeast vectors using 2-microns circle sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:307–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F. Sequence and structural features associated with translational initiator regions in yeast--a review. Gene. 1987;59(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Pabich E. K., Donahue T. F. Mutational analysis of the HIS4 translational initiator region in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2964–2975. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Cigan A. M. Genetic selection for mutations that reduce or abolish ribosomal recognition of the HIS4 translational initiator region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2955–2963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouser L. A., Friesen J. D. Mutations in a yeast intron demonstrate the importance of specific conserved nucleotides for the two stages of nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Warner J. R. Cloning of yeast gene for trichodermin resistance and ribosomal protein L3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):238–242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R., Watanabe C. K., de Boer H. A. Compilation and comparison of the sequence context around the AUG startcodons in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3581–3593. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Novel mechanisms of translational control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Trends Genet. 1988 Jun;4(6):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Leader length and secondary structure modulate mRNA function under conditions of stress. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2737–2744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maicas E., Friesen J. D. A sequence pattern that occurs at the transcription initiation region of yeast RNA polymerase II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3387–3393. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maicas E., Pluthero F. G., Friesen J. D. The accumulation of three yeast ribosomal proteins under conditions of excess mRNA is determined primarily by fast protein decay. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):169–175. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. D., Friesen J. D. Nucleotide sequence of the tcml gene (ribosomal protein L3) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.8-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedman S. A., Gelembiuk G. W., Mertz J. E. Translation initiation at a downstream AUG occurs with increased efficiency when the upstream AUG is located very close to the 5' cap. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):453–457. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.453-457.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Ribosome pausing and stacking during translation of a eukaryotic mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3559–3569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitomer R. S., Walthall D. A., Rymond B. C., Hollenberg C. P. Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomes recognize non-AUG initiation codons. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1191–1197. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel J. J., Bergkamp R. J., Planta R. J., Raué H. A. Effect of deletions in the 5'-noncoding region on the translational efficiency of phosphoglycerate kinase mRNA in yeast. Gene. 1989 Jun 30;79(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]