Abstract
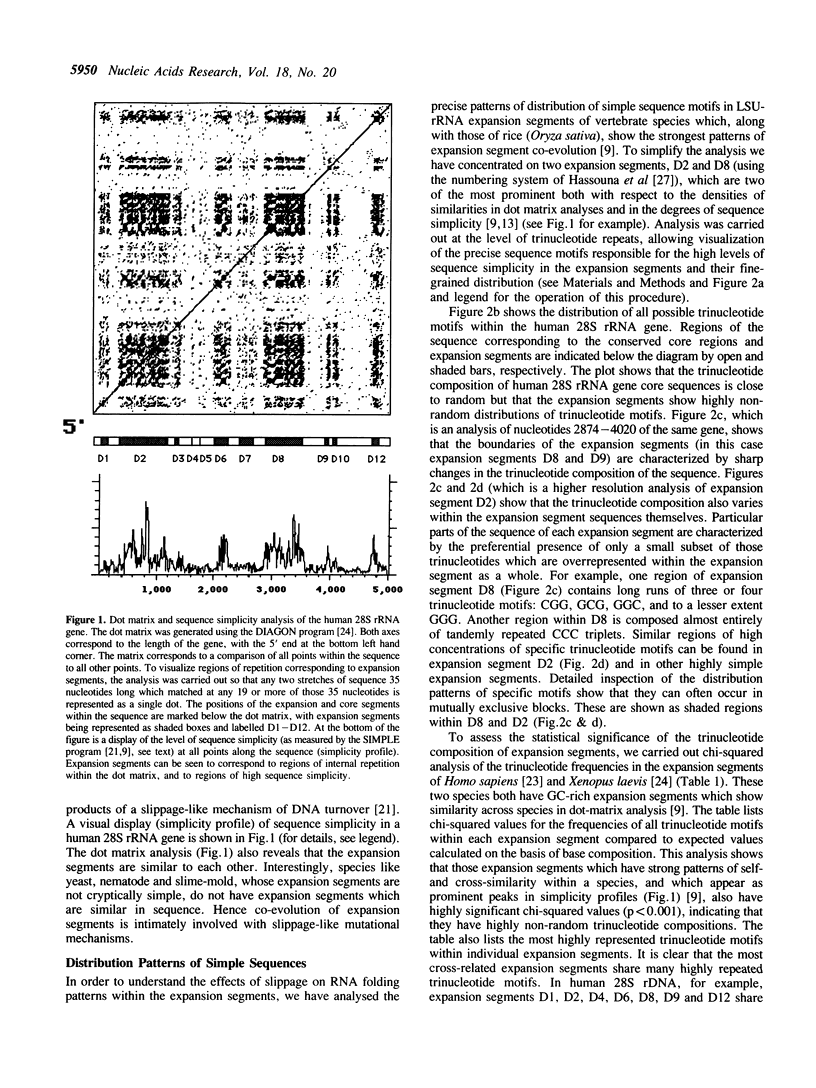
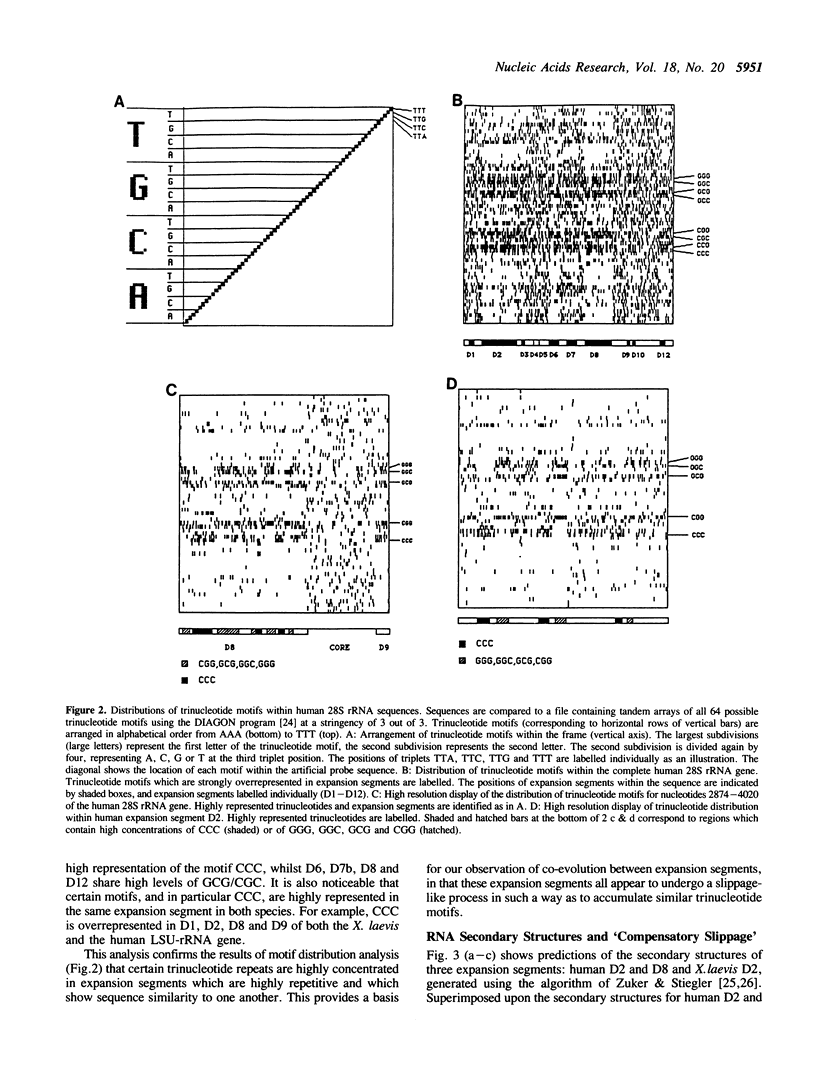
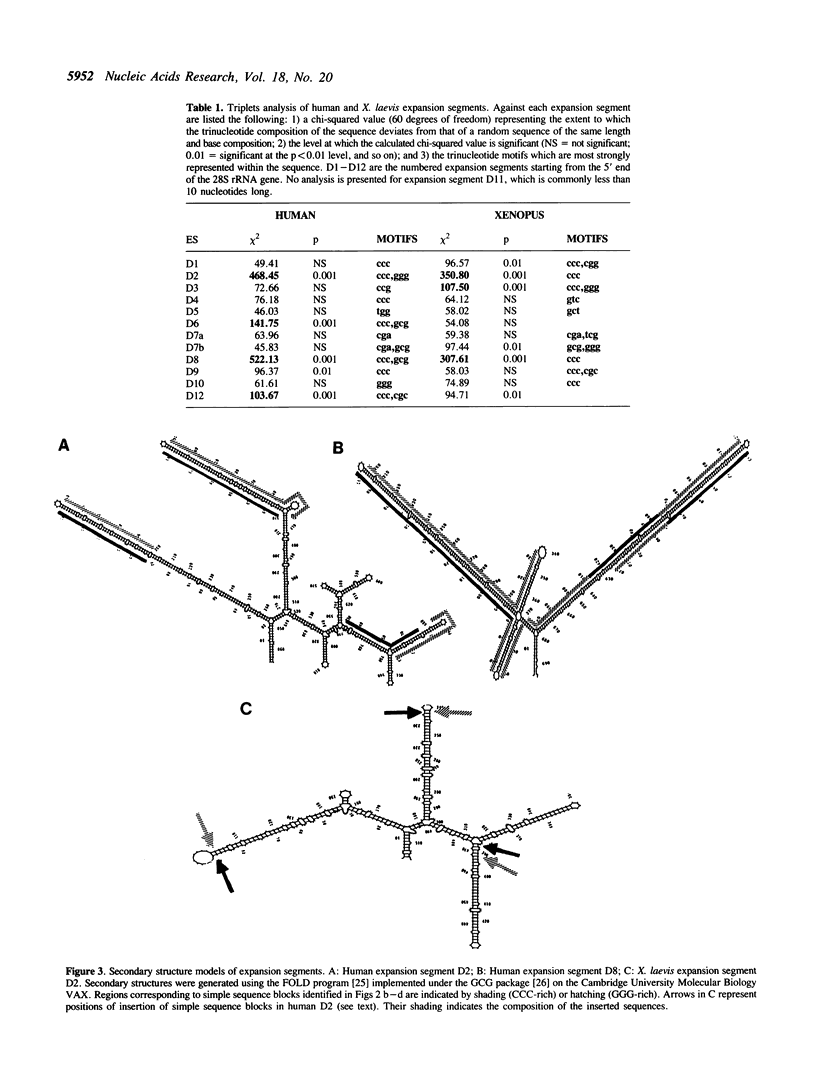
The distribution patterns of shared short repetitive motifs in the expansion segments of the large subunit rRNA genes of different species show that these segments are coevolving as a set and that in two examined vertebrate species the RNA secondary structures are conserved as a consequence of runs of motifs in one region being compensated by complementary motifs in another. These unusual processes, involving replication-slippage, have implications for the evolution of ribosomal RNA and for the use of the rDNA multigene family as a 'molecular clock' for assessing relationships between species.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boer P. H., Gray M. W. Genes encoding a subunit of respiratory NADH dehydrogenase (ND1) and a reverse transcriptase-like protein (RTL) are linked to ribosomal RNA gene pieces in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3501–3508. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03226.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer P. H., Gray M. W. Scrambled ribosomal RNA gene pieces in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):399–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgin A. B., Parodos K., Lane D. J., Pace N. R. The excision of intervening sequences from Salmonella 23S ribosomal RNA. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. G. On the evolution of ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):343–350. doi: 10.1007/BF02603119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. A. Linkage disequilibrium and molecular drive in the rDNA gene family. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):249–252. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. A. Molecular evolution. rDNA world falling to pieces. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):623–624. doi: 10.1038/336623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. A., Tautz D. Conservation and divergence in multigene families: alternatives to selection and drift. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Jan 29;312(1154):275–289. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1986.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field K. G., Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Ghiselin M. T., Raff E. C., Pace N. R., Raff R. A. Molecular phylogeny of the animal kingdom. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):748–753. doi: 10.1126/science.3277277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez I. L., Gorski J. L., Campen T. J., Dorney D. J., Erickson J. M., Sylvester J. E., Schmickel R. D. Variation among human 28S ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7666–7670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez I. L., Sylvester J. E., Schmickel R. D. Human 28S ribosomal RNA sequence heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10213–10224. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J. L., Gonzalez I. L., Schmickel R. D. The secondary structure of human 28S rRNA: the structure and evolution of a mosaic rRNA gene. J Mol Evol. 1987;24(3):236–251. doi: 10.1007/BF02111237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Li W. H. Phylogenetic analysis based on rRNA sequences supports the archaebacterial rather than the eocyte tree. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):145–147. doi: 10.1038/339145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. M., Dover G. A. Molecular coevolution among cryptically simple expansion segments of eukaryotic 26S/28S rRNAs. Mol Biol Evol. 1988 Jul;5(4):377–391. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. M., Tautz D., Dover G. A. Evolution of the secondary structures and compensatory mutations of the ribosomal RNAs of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol. 1988 Jul;5(4):393–414. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassouna N., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 28S rRNA gene. Implications for the process of size increase of the large subunit rRNA in higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3563–3583. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A. A rate-independent technique for analysis of nucleic acid sequences: evolutionary parsimony. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Mar;4(2):167–191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E., Dent C. L., Farrell T. E., Garde J., McCallum F. S., Wakeman J. A. Clones of human ribosomal DNA containing the complete 18 S-rRNA and 28 S-rRNA genes. Characterization, a detailed map of the human ribosomal transcription unit and diversity among clones. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):519–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2460519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian A., Dover G. A. Promoter variation in the ribosomal RNA genes in Drosophila melanogaster strains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3795–3801. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. Comparisons of large subunit rRNAs reveal some eukaryote-specific elements of secondary structure. Biochimie. 1987 Jan;69(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90267-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. How were introns inserted into nuclear genes? Trends Genet. 1989 Jul;5(7):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4731–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Trick M., Dover G. A. Cryptic simplicity in DNA is a major source of genetic variation. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):652–656. doi: 10.1038/322652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware V. C., Tague B. W., Clark C. G., Gourse R. L., Brand R. C., Gerbi S. A. Sequence analysis of 28S ribosomal DNA from the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7795–7817. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lanversin G., Jacq B. Sequence and secondary structure of the central domain of Drosophila 26S rRNA: a universal model for the central domain of the large rRNA containing the region in which the central break may happen. J Mol Evol. 1989 May;28(5):403–417. doi: 10.1007/BF02603076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



