Abstract
The crystal structures of the ligand-binding domain (LBD) of the vitamin D receptor complexed to 1α,25(OH)2D3 and the 20-epi analogs, MC1288 and KH1060, show that the protein conformation is identical, conferring a general character to the observation first made for retinoic acid receptor (RAR) that, for a given LBD, the agonist conformation is unique, the ligands adapting to the binding pocket. In all complexes, the A- to D-ring moieties of the ligands adopt the same conformation and form identical contacts with the protein. Differences are observed only for the 17β-aliphatic chains that adapt their conformation to anchor the 25-hydroxyl group to His-305 and His-397. The inverted geometry of the C20 methyl group induces different paths of the aliphatic chains. The ligands exhibit a low-energy conformation for MC1288 and a more strained conformation for the two others. KH1060 compensates this energy cost by additional contacts. Based on the present data, the explanation of the superagonist effect is to be found in higher stability and longer half-life of the active complex, thereby excluding different conformations of the ligand binding domain.
Keywords: 20-epi analogs, nuclear receptors, VDR
Vitamin D, a seco-steroid hormone (steroid with an opened B-ring) is active only in the metabolized form 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1α,25(OH)2D3]. The genomic action of this hormone, like other steroid hormones, is mediated by a nuclear receptor (NR): the vitamin D nuclear receptor (VDR). This receptor exhibits the characteristic modular organization of five to six domains of NRs but presents a rather short N-terminal A/B domain and an insertion in the ligand binding domain. VDR modulates the expression of numerous genes in target cells; these genes are involved in calcium metabolism and bone formation and in control of cell growth and cell differentiation (1, 2). VDR acts by binding to specific DNA sequences as a heterodimer with RXR and to the basal transcription machinery in a ligand-independent (TFIIB; ref. 3) and -dependent manner (TFIIA; ref. 4). Other direct contacts have been revealed between the receptor and TATA box-binding protein (TBP)-associated factors (TAFs; ref. 5), components of general factors required for accurate and regulated initiation of RNA polymerase II. These factors are specific transcriptional coactivators in mammalian cells. A different class of proteins has been characterized that stimulate the transcriptional activity of liganded NRs in an activation function 2 (AF2)-dependent way. These coactivators are thought to bridge the NRs to the transcriptional apparatus. In particular, VDR is regulated by coactivators belonging to the steroid receptor activator (SRC)/p160 family of proteins, which contain several LXXLL motifs (6). This motif has been shown to form an amphipatic α-helical structure that can interact with the AF2 region of NRs (7). Another class of coactivators [vitamin D receptor-interacting protein (DRIP), thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein (TRAP), activator-recruited cofactor (ARC); refs. 8–11] has been isolated as multiprotein complexes and strongly potentiated transcription mediated by VDR/RXR in a ligand-dependent manner on DNA templates assembled into chromatin (8). One of their components, DRIP205, interacts directly with the ligand-binding domain (LBD) in the presence of ligand and anchors the rest of the subunits to the receptor.
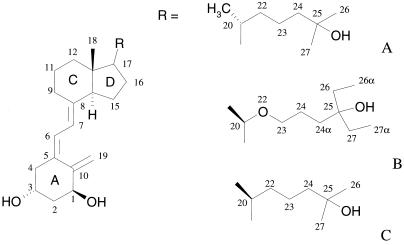
Among the several synthetic analogs of vitamin D, the 20-epi compounds, which exhibit an inverted stereochemistry at position 20 in the flexible aliphatic chain, have attracted much attention. They are potent growth inhibitors and inducers of cell differentiation, while showing an affinity similar to vitamin D for VDR (11). KH1060 (Fig. 1), a member of this 20-epi family, exhibits similar properties, with decreased calcemic side effects. These compounds induce VDR-dependent transcription at concentrations at least 100-fold lower than the natural ligand and present antiproliferative activity several orders of magnitude higher than the natural ligand (11–13). The differences in biological activity of 1α,25(OH)2D3 and the 20-epi molecules in general, and KH1060 in particular, are known to be VDR-LBD dependent, but are not yet understood. The ability of 20-epi analogs complexed to VDR to induce transcription correlates with the efficiency of these compounds to interact with coactivators (12). The different proteolysis pattern of VDR in the presence of the natural ligand and the 20-epi compounds has been interpreted as reflecting large conformational changes of the receptor on binding of the latter class of molecules. It has been suggested that the 20-epi compounds induce an alternate conformation of the VDR-LBD, rendering the receptor more resistant to protease digestion (8, 11, 12, 14–16). To investigate the binding mode of the 20-epi analogs to the VDR-LBD, we determined the high resolution crystal structures of the VDR in complex with MC1288 and KH1060 (Fig. 1) and compared them with that of the natural ligand. The comparison provides the rational basis to analyze the various contacts between the ligands and the receptor. These contacts are most likely responsible for the different biological responses.
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of 1α,25(OH)2D3 and the 20-epi analogs KH1060 and MC1288. (A) 1α,25(OH)2D3: 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. (B) KH1060: 1α,25-dihydroxy-20-epi-22-oxa-24,26,27-trihomovitamin D3. (C) MC1288: 20-epi-1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
Materials and Methods
The human LBD of VDR (118–427 Δ166–216) was purified following the protocol described by Rochel et al (17). Crystallization of VDR in the presence of each of the individual ligands 1α,25(OH)2D3 (1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3), MC1288 (20-epi-1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3), and KH1060 (1α,25-dihydroxy-20-epi-22-oxa-24,26,27-trihomovitamin D3; Fig. 1) was achieved in the same conditions as for the natural ligand as previously described, employing the hanging-drop vapor diffusion method. Crystals grew in a starting solution containing 10 mg/ml of VDR, a 5-fold molar excess of a specific agonist, 50 mM Mes-KOH, 5 mM Tris⋅HCl, 10 mM DTT, and 0.7 M ammonium sulfate equilibrated for 4 days at 4°C vs. a reservoir solution containing 100 mM Mes-KOH and 1.4 M ammonium sulfate at pH 6.0. The homogeneity of the protein and the formation of the complexes between the different ligands and the receptor were verified by SDS and native PAGE and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry.
The crystals were mounted in fiber loops and flash cooled in liquid nitrogen after cryoprotection with a solution containing the reservoir solution plus 30% glycerol and 5% polyethylene glycol (PEG) 400. In the case of the MC1288-VDR complex, the formation of ice rings explains the partial loss of reflections. The diffracting quality of the crystals was not affected. The data collection was performed at 100 K at the Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron (DESY) synchrotron facilities in Hamburg (BW7b beamline) for the MC1288-VDR complex and at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in Grenoble (beamline BM30) for the 1α,25(OH)2D3-VDR and KH1060-VDR complexes. For each of the characterized complexes, only one crystal was sufficient for obtaining a complete data set at a 1.5-Å resolution. The crystals were isomorphous and belonged to the orthorhombic space group P212121 with the unit cells parameters as specified in Table 1. Data were integrated and scaled by using the denzo-scalepack package (18). The program cns-solve was used throughout the structure determination and refinement calculations (19). All data were included in the refinement (no σ cutoff). Initial phase estimates were obtained by omitting the 1α,25(OH)2D3 from the structure of the VDR-1α,25(OH)2D3 complex previously solved at 4°C (17). A rigid body refinement was used to correctly place the model into the asymmetric units of all of the studied complexes. The phase bias of the initial model was reduced by torsion angle molecular dynamics simulated-annealing refinement (20), followed by Cartesian molecular dynamics simulated annealing (21) after fitting the ligand into the electron density. Subsequent refinement cycles alternated least-squares minimizations and manual model building by using the program O (22). Solvent molecules were then placed according to unassigned peaks in the Fourier difference maps. All of the refined models showed unambiguous chirality for the ligands and no Ramachandran plot outliers according to procheck (23). For the VDR-KH1060 complex, the weaker density of the electron density map at position C26α of the ligand clearly indicates a disorder of this methyl group and therefore the ability to adopt different conformations. The final models of VDR-1α,25(OH)2D3 and VDR-MC1288 complexes contain 255 residues, with no clear densities for the last four C-terminal residues, and also for the residue side chain of His-377. For the VDR-KH1060 complex, the final model contains 253 residues with no clear density for the two first N-terminal residues, the last four C-terminal residues, and residues 375–377 in loop 9–10. The volumes of the ligand-binding pockets and ligands were calculated as previously (17).
Table 1.
Data collection statistics
| Ligand | KH1060 | MC1288 | 1α,25(OH)2D3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Space group | P212121 | ||
| Cell dimensions | |||
| a | 44.49 Å | 44.94 Å | 44.93 Å |
| b | 51.87 Å | 51.42 Å | 51.32 Å |
| c | 131.39 Å | 132.52 Å | 132.32 Å |
| Resolution (last shell) | 20–1.52 Å | 15–1.4 Å | 20–1.52 Å |
| (1.56–1.52) | (1.43–1.4) | (1.56–1.52) | |
| Completeness (last shell) | 98.1% (97.3) | 73.4%* (81.1) | 96.2% (66.6) |
| Rsym (last shell) | 4.8% (29) | 4.3% (23.6) | 5% (12.2) |
| 〈I/σ(I)〉 (last shell) | 20.4 (4.6) | 23.4 (3.7) | 20.7 (9.8) |
| Unique reflections | 45,925 | 42,311 | 46,136 |
| Redundancy | 4.8 | 3.6 | 3.4 |
See Materials and Methods.
Results
Structure Determination.
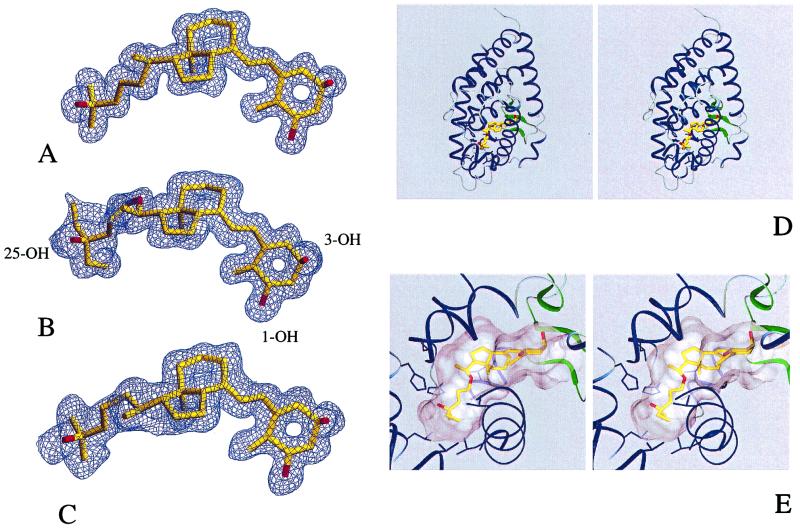
All observed crystal forms are isomorphous, with no significant changes in the protein conformation. To obtain crystals suitable for diffraction studies, the different ligands and the receptor must be present in the crystallization solution. The protein by itself failed to crystallize when incubated in the same conditions. The crystallization conditions (see Materials and Methods) are similar for the three complexes and do not represent any harsh change from physiological conditions, suggesting that the structural atomic model corresponds to the most stable dominant structure in solution. The structures were solved by molecular replacement (see Tables 1 and 2 and Materials and Methods). High resolution ligand-omit maps calculated from the refined structure of the three different complexes allowed to fit the ligands unequivocally (Fig. 2 A–C).
Table 2.
Statistics of structure refinement
| Ligand | KH1060 | M1288 | 1α,25(OH)2D3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rcryst | 21.2% (41,247) | 21.4% (38,055) | 19.5% (41,502) |
| Rfree | 23.0% (4,678) | 24.8% (4,256) | 21.6% (4,634) |
| rms bond length, Å | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.005 |
| rms bond angle, degrees | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.2 |
| Non-hydrogen protein atoms | 1,992 | 2,022 | 2,022 |
| Non-hydrogen ligand atoms | 33 | 30 | 30 |
| Solvent molecules | 214 | 225 | 271 |
| Average B factor protein | 23.5 | 14.4 | 13.9 |
| Ligand | 18.9 | 12.2 | 9.7 |
| Solvent molecules | 35.3 | 27.7 | 26.5 |
Figure 2.
Crystal structures of the VDR LBD complexed to 1α,25(OH)2D3, MC1288, and KH1060. Experimental electron density omit map contoured at 2.0 SD of (A) 1α,25(OH)2D3, (B) KH1060, and (C) MC1288. (D) Stereoview of KH1060 bound to the VDR LBD. (E) Close-up view of KH1060 in the ligand-binding pocket. Secondary structure features are represented in blue (α-helices) and green (β-strands). The ligand is colored in yellow with the oxygen atoms in red. The volume of the cavity is represented in gray.
The atomic models, when compared with VDR-1α,25(OH)2D3 complex, show rms deviations on Cα atoms of 0.08 Å and 0.14 Å for VDR-MC1288 complex and VDR-KH1060 complex, respectively. The rms deviations on all atoms are 0.38 Å and 0.51 Å for VDR-MC1288 complex and VDR-KH1060 complex, respectively. Variations concern only some side chains located at the surface of the protein. Contrary to the belief that the 20-epi analogs are inducing a different agonist conformation, the overall conformation and especially the position of helix H12 are strictly maintained in all three complexes. Furthermore the ligand-binding cavity is unique and conserved for the three complexes. The rms deviations of all atoms comprising the ligand pocket are 0.09 Å for VDR-MC1288 complex and 0.12 Å for theVDR-KH1060 complex. The sizes of the three ligands are 381 Å3, 375 Å3, and 392 Å3 for 1α,25(OH)2D3, MC1288 and KH1060, whereas the volume of the ligand pocket remains unaltered in the three complexes (660 Å3) and the ligands occupy only 57% of the volume of the pocket for the VDR-1α,25(OH)2D3 and VDR-MC1288 complexes and 59% for the VDR-KH1060 complex. This value can be compared with the retinoids that occupy 66% of the ligand-binding pocket of retinoic acid receptor (17).
Ligand–Protein Interactions.
The interactions between the ligands and the receptor involve both hydrophobic contacts and electrostatic interactions. The A, seco-B, and C/D rings form identical contacts as previously described for 1α,25(OH)2D3-VDR complex. The hydroxyl groups make the same hydrogen bonds, 1-OH with Ser-237 and Arg-274, 3-OH with Tyr-143 and Ser-278, and the 25-OH with His-305 and His-397. The deletion of 1-OH or 25-OH leads to the largest changes, with a significant decrease in binding (1/1000), whereas that of the 3-OH has a smaller effect (1/20) (1). This fact is consistent with the observation that the Ser-278 → Ala mutation decreases the transactivation by only 20% (24). The minor transactivation decrease observed for this mutation can be explained by the presence of Tyr-143, which maintains an anchoring link. A mutation of another residue close to the position C4 of the A-ring, Cys-288–Ala, results in a severe decrease in transcriptional activity (8, 24). Cys-288 is involved in numerous Van der Waals contacts with neighboring residues (Tyr-147, Phe-150, Ser-278, and Tyr-295). Its mutation affects Van der Waals contact with the ligand but, more importantly, destabilizes the protein architecture of the ligand pocket.
The specific interactions observed in the three ligand–protein complexes involve the hydrophobic contacts of the 17β-aliphatic chains summarized in Table 3. When comparing the natural ligand and MC1288, the main difference observed is the positioning of the methyl group C21, which results in different contacts with Val-300, Leu-309, and His-397 (Table 3). In MC1288, the C21 moiety is closer to His-397. Other protein–ligand contacts differ, but, to a lesser extent, they involve the methyl groups at positions 23 (His-305), 24 (His-397), and 27 (His-397 and Val-418). In these two complexes, the carbon C22 makes no contact at a distance closer than 4.2 Å. In the case of KH1060, the methyl group C21 is quite close to that of the corresponding atom in 1α,25(OH)2D3. Note that the oxygen atom at position 22 of KH1060 forms a van der Waals contact with Val-300. The major differences observed between KH1060 and the two other ligands are the tighter and more numerous ligand–protein contacts. The methyl groups C26α and C27α, specific to KH1060, form additional contacts with H3, loop 6–7, H11, and H12. A weak density is observed for the C26α methyl group, suggesting a structural disorder, whereas the C27α methyl group is clearly defined.
Table 3.
Protein/ligand aliphatic side chain distances observed in the 1α,25(OH)2D3, MC1288, and KH1060 VDR-LBD complexes
| Residue | Atom | 1α,25(OH)2D3 | MC1288 | KH1060 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leu-227(H3) | CD1 | C26(3.5) | C26(3.4) | C26(3.4) |
| Ala-231(H3) | CA | — | — | C27α(3.7) |
| Val-234(H3) | CB | — | — | C27α(3.7) |
| CG1 | — | — | C27α(3.8) | |
| CG2 | C24(3.9) | C24(3.9) | C24α(4.1), C27α(4.0) | |
| Val-300(H6) | CG1 | C21(4.0) | C21(5.4) | C21(4.2), O22(3.8) |
| His-305(L6–7) | NE2 | C23(3.6) | C23(3.4) | C24(3.4) |
| C26(3.8) | C26(3.8) | C24α(4.1), C26(3.8) | ||
| CD2 | C23(3.8) | C23(3.4) | C23(3.9) | |
| C24(4.6) | C24(4.5) | C24(3.6) | ||
| Leu-309(H7) | CD2 | C21(3.8) | C21(4.2) | C21(3.8) |
| His-397(H11) | NE2 | C24(3.7), C27(4.2) | C24(4.1), C27(4.0) | C24(4.1), C24α(4.3), C27(4.1) |
| CD2 | C21(4.5) | C21(3.9) | C21(4.4) | |
| Leu-404(H11) | CD2 | C26(4.3) | C26(4.4) | C26(3.8) |
| Val-418(H12) | CG1 | C27(3.9) | C27(4.2) | C27(4.1), C27α(3.9) |
A cutoff of 4.0 Å has been used. Underlined contacts in the table are included for comparison purposes. No distance is reported for the carbon atom at position 26α; this atomic position is not well resolved (see text).
Conformation of the Bound Ligands.
In the three complexes, the ligands adopt an elongated conformation (Fig. 3) similar to that described in the VDR-1α,25(OH)2D3 structure (17). The typical three ring structure of vitamin D and the position of the three hydroxyl groups are preserved among all of the analyzed molecules. In all complexes, the ligand is rather tightly bound to the receptor around the A-, seco-B, C-, and D-rings. In contrast, the aliphatic chain is less constrained, thus allowing alternative conformations of the 17β-chain for the natural and the 20-epi ligands. The distances between the 25-OH group and the 1-OH and 3-OH are similar for the three complexes. These represent the anchoring points that must be maintained to obtain an active conformation.
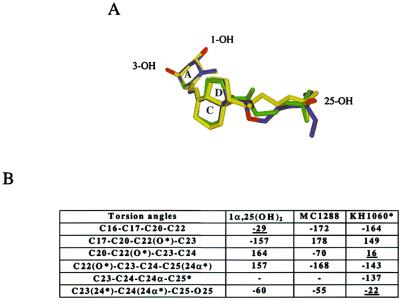
Figure 3.
(A) Superposition of 1α,25(OH)2D3 (yellow), MC1288 (green), and KH1060 (blue) ligands after superimposed VDR complexes. Oxygen atoms are colored in red. (B) Torsion angles of the 17β-aliphatic chains of 1α,25(OH)2D3, MC1288, and KH1060 in the VDR complexes.
In these complexes, the A-ring adopts a chair B conformation with the 19-methylene “up” and the 1α-OH and 3β-OH groups in an equatorial and axial orientation, respectively. Any alternative conformation would affect the H-bond interactions. A chair A conformation of the A-ring (1α-OH and 3β-OH groups in axial and equatorial orientations respectively) would disrupt the hydrogen bond network observed between the hydroxyl groups and the protein, and would therefore not fit in the VDR ligand-binding pocket because of a steric clash with Phe-150. Note that, in all three complexes, a water channel reaches the surface of the protein, starting at the position C2 of the A-ring, suggesting that a synthetic ligand could occupy this additional space without altering the conformation of the A- to D-ring conformation.
A tight channel around the seco-B ring is formed in all of the characterized structures by Ser-275 and Trp-286 on one side and Leu-233 on the other side. This channel accommodates an almost trans conformation of the triene system, connecting ring A to the C- and D-rings. The C6—C7 bond exhibits a torsion angle of −149° (C5—C6—C7—C8) that deviates significantly from the planar geometry toward the α face of the A-ring and confers a bent geometry to the molecule. The α face of the C-ring is lined by Trp-286 whereas the methyl C18 on the β face points toward Val-234. In the case of the VDR-MC1288 complex, the CD-rings are slightly tilted, revealing an additional degree of freedom to orient the 17β-chain.
The remaining section of the pocket is large enough to accommodate different variants of the long aliphatic chain of vitamin D analogs. The chain flexibility allows the different ligands to adapt to the pocket and to form the anchoring hydrogen bonds. Fig. 3 shows the dihedral transitions for each ligand side chain as observed in the complex. The aliphatic side chain of 1α,25(OH)2D3 adopts an extended conformation parallel to the C13—C18 bond with the C13—C17—C20—C22 torsion angle close to 90°. The two 20-epi analogs use different strategies to fit into the cavity. KH1060 accommodates its longer chain by adopting an eclipsed conformation around the O22—C23 bond whereas MC1288 adopts a gauche conformation and has to compensate for a chain that is too short to maintain the 25-OH interactions because of the C20 inverted stereochemistry. Our preliminary docking experiments of the 20-epi analogs have correctly positioned the methyl C21 in the same cavity as 1α,25(OH)2D3, but failed to give the correct geometry of the aliphatic chains. The crystallographic structures provide the exact information regarding these changes and the details of the interactions with the protein. Compared with the natural ligand, the aliphatic chains of the 20-epi analogs are lining the opposite side of the pocket. The different orientation of the chains is reflected by the different values of the torsion angles C16—C17—C20—C22 and C17—C20—C22(O22 for KH1060)—C23 (Fig. 3). Further down the chain, whereas 1α,25(OH)2D3 adopts an extended conformation, the MC1288 and KH1060 exhibit gauche and eclipsed conformations, respectively, to properly orient the 25 hydroxyl group. The energetically unfavorable eclipsed conformation observed in KH1060 (C20—O22—C23—C24 of KH1060 equal to 16°) is made possible by the strong interactions formed by O22 with C12 (2.9 Å) and C18 (3.24 Å). A methylene group at this position as in MC1301 would be shifted away from the D-ring. A crude modeling analysis suggests that the methylene group would move away from C12, adopting a gauche (+) conformation instead of the eclipsed one observed for KH1060. As a result, additional contacts with the protein pockets are formed (Val-300), which may contribute to the higher affinity of MC1301, and other contributions like solvation cannot be excluded. Similarly, the naturally occurring hydroxylation of C24α in KH1060 and C23 in 1α,25(OH)2D3 would form steric clashes with His-305, affecting the hydrogen bond network with 25-OH. The resulting conformational changes can thus explain the reported lack of transcriptional activity (25). Based on the crystal structures, this activity would depend on the capacity of the pocket to accommodate these additional groups.
Discussion
The high resolution structures of the VDR complexed to 1α,25(OH)2D3 and 20-epi analogs provide experimental images essential for a rational analysis of the interactions of these analogs with VDR and suggest how the 20-epi analogs enhance the stability of the receptor and stimulate the interaction with coactivator complexes like DRIP. Our data reveal that, contrary to what was previously thought, the interaction between the 20-epi agonists and the VDR does not result in significant variations from the LBD conformational change induced by the natural ligand. The protein structures are identical to that observed in the complex with the natural ligand. A similar observation has already been made for retinoic acid receptor, where numerous complexes with the two natural ligands (all-trans- and 9-cis-retinoic acid) and synthetic analogs revealed that the ligand-binding pocket was unchanged and that it is the ligand that adapts (26–29). Such observations should be valid not only for retinoic acid receptor and VDR but most likely also for other NRs. It will be interesting to check whether the Gemini analog follows that rule or constitutes an exception (30). A drug design strategy based on the lock and key concept by using the three-dimensional structure of the receptor in complex with any agonist is thus valid.
How can one correlate the present observation to the specific properties of the 20-epi ligands? The main differences between the complexes of the 20-epi analogs and that of 1α,25(OH)2D3 are a result of their capacity to fit into the “mold” of the ligand-binding site. The 20-epi analogs make new contacts with the protein as a consequence of the different path adopted by the aliphatic chain. Whereas for MC1288 the number of interactions is comparable to that of the natural ligand, for KH1060, additional interactions because of the 20-epimerization and the extra methylene groups could provide an explanation for the higher stability of this complex. The higher stability of the VDR-MC1288 complex has to be found in the low energy conformation of the ligand in the conserved pocket (Fig. 3) whereas the more tense conformation of 1α,25(OH)2D3 is energetically less favorable. For KH1060, the energetically unfavorable conformation is partially compensated for by the numerous contacts between the ligand and the protein. Both conformations and additional interactions of the 20-epi analogs would result in higher stability and longer half-life of the active complexes. Indeed within 3 hr, 60% of 1α,25(OH)2D3 dissociates from the VDR complex, when only 5–20% of MC1288 is dissociated (9). Furthermore receptors lacking the C-terminal helix 12 exhibit different dissociation behavior for the 20-epi analogs that are still capable to interact with a mutated receptor (11, 12). Limited digest proteolysis shows that the 20-epi analog-receptor complexes are more resistant to digestion and suggests that they are more stable. Additionally, an important role might be played by the rate of assimilation and how the synthetic agonists are metabolized vs. the natural ligand in different cell types (25, 31). Altogether, these data suggest that the life time of the active conformation is then the main factor responsible for the formation of a more potent complex with coactivators like DRIP and the subsequent higher transcription activity.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to A. Steinmeyer (Schering AG) for a generous gift of 1α,25(OH)2D3 and KH1060 and F. Bjoerkling (Leo Pharmaceutical Products) for providing us with MC1288. We are grateful to P. Egea for help with the figures. We also wish to thank B. Chevrier and L. Moulinier for helpful discussions and I. Davidson for critical reading of the manuscript. We thank the beamline staff at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF; Grenoble, France) and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL; Hamburg, Germany) for technical assistance during data collection. This work was supported by grants from the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), the Hôpital Universitaire de Strasbourg, the Ministère de la Recherche et de la Technologie, the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer, and the Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer.
Abbreviations
- NR
nuclear receptor
- VDR
vitamin D NR
- DRIP
VDR-interacting protein
- LBD
ligand-binding domain
- RAR
retinoic acid receptor
Footnotes
This paper was submitted directly (Track II) to the PNAS office.
Data deposition: The atomic coordinates and structure factors have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank, www.rcsb.org (PDB ID codes 1DB1, 1IE8, and 1IE9).
References
- 1.Bouillon R, Okamura W H, Norman A W. Endocr Rev. 1995;16:200–257. doi: 10.1210/edrv-16-2-200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.DeLuca H F, Zierold C. Nutr Rev. 1998;56:S4–S10. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1998.tb01686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Masuyama H, Jefcoat S C, Jr, MacDonald P N. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:218–228. doi: 10.1210/mend.11.2.9879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lemon B D, Fondell J D, Freedman L P. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:1923–1937. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.4.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lavigne A C, Mengus G, Gangloff Y G, Wurtz J M, Davidson I. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:5486–5494. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.8.5486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McKenna N J, Xu J, Nawaz Z, Tsai S Y, Tsai M J, O'Malley B W. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1999;69:3–12. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(98)00144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McInerney E M, Rose D W, Flynn S E, Westin S, Mullen T M, Krones A, Inostroza J, Torchia J, Nolte R T, Assa-Munt N, et al. Genes Dev. 1998;12:3357–3368. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.21.3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rachez C, Lemon B D, Suldan Z, Bromleigh V, Gamble M, Naar A M, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Freedman L P. Nature (London) 1999;398:824–828. doi: 10.1038/19783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rachez C, Gamble M, Chang C P, Atkins G B, Lazar M A, Freedman L P. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:2718–2726. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.8.2718-2726.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yuan C X, Ito M, Fondell J D, Fu Z Y, Roeder R G. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:7939–7944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.7939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Peleg S, Sastry M, Collins E D, Bishop J E, Norman A W. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:10551–10558. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liu Y Y, Collins E D, Norman A W, Peleg S. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:3336–3345. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.6.3336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yang W, Freedman L P. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:16838–16845. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.24.16838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vaisanen S, Juntunen K, Itkonen A, Vihko P, Maenpaa P H. Eur J Biochem. 1997;248:156–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-1-00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vaisanen S, Ryhanen S, Saarela J T, Maenpaa P H. Eur J Biochem. 1999;261:706–713. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.van den Bemd G C, Pols H A, Birkenhager J C, van Leeuwen J P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:10685–10690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.20.10685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rochel N, Wurtz J M, Mitschler A, Klaholz B, Moras D. Mol Cell. 2000;5:173–179. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Otwinowski Z, Minor W. Methods Enzymol. 1997;276:307–326. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(97)76066-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Brunger A T, Adams P D, Clore G M, DeLano W L, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve R W, Jiang J S, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu N S, et al. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1998;54:905–921. doi: 10.1107/s0907444998003254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rice L M, Brunger A T. Proteins. 1994;19:277–290. doi: 10.1002/prot.340190403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Brunger A T, Adams P D, Rice L M. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1999;72:135–155. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6107(99)00004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jones T A, Zou J Y, Cowan S W, Kjeldgaard Acta Crystallogr A. 1991;47:110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Laskowski R A, MacArthur M W, Moss D S, Thornton J M. J Appl Crystallogr. 1993;26:283–291. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yamamoto K, Masuno H, Choi M, Nakashima K, Taga T, Ooizumi H, Umesono K, Sicinska W, VanHooke J, DeLuca H F, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:1467–1472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.020522697. . (First Published February 4, 2000; 10.1073/pnas.020522697) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dilworth F J, Williams G R, Kissmeyer A M, Nielsen J L, Binderup E, Calverley M J, Makin H L, Jones G. Endocrinology. 1997;138:5485–5496. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.12.5594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Egea P F, Klaholz B P, Moras D. FEBS Lett. 2000;476:62–67. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01672-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Klaholz B P, Renaud J P, Mitschler A, Zusi C, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H, Moras D. Nat Struct Biol. 1998;5:199–202. doi: 10.1038/nsb0398-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Klaholz B P, Mitschler A, Belema M, Zusi C, Moras D. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:6322–6327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.12.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Klaholz B P, Mitschler A, Moras D. J Mol Biol. 2000;302:155–170. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Norman A W, Manchand P S, Uskokovic M R, Okamura W H, Takeuchi J A, Bishop J E, Hisatake J I, Koeffler H P, Peleg S. J Med Chem. 2000;43:2719–2730. doi: 10.1021/jm0000160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shankar V N, Dilworth F J, Makin H L, Schroeder N J, Trafford D J, Kissmeyer A M, Calverley M J, Binderup E, Jones G. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997;53:783–793. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(96)00815-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]