Abstract
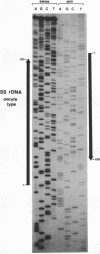
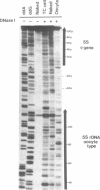
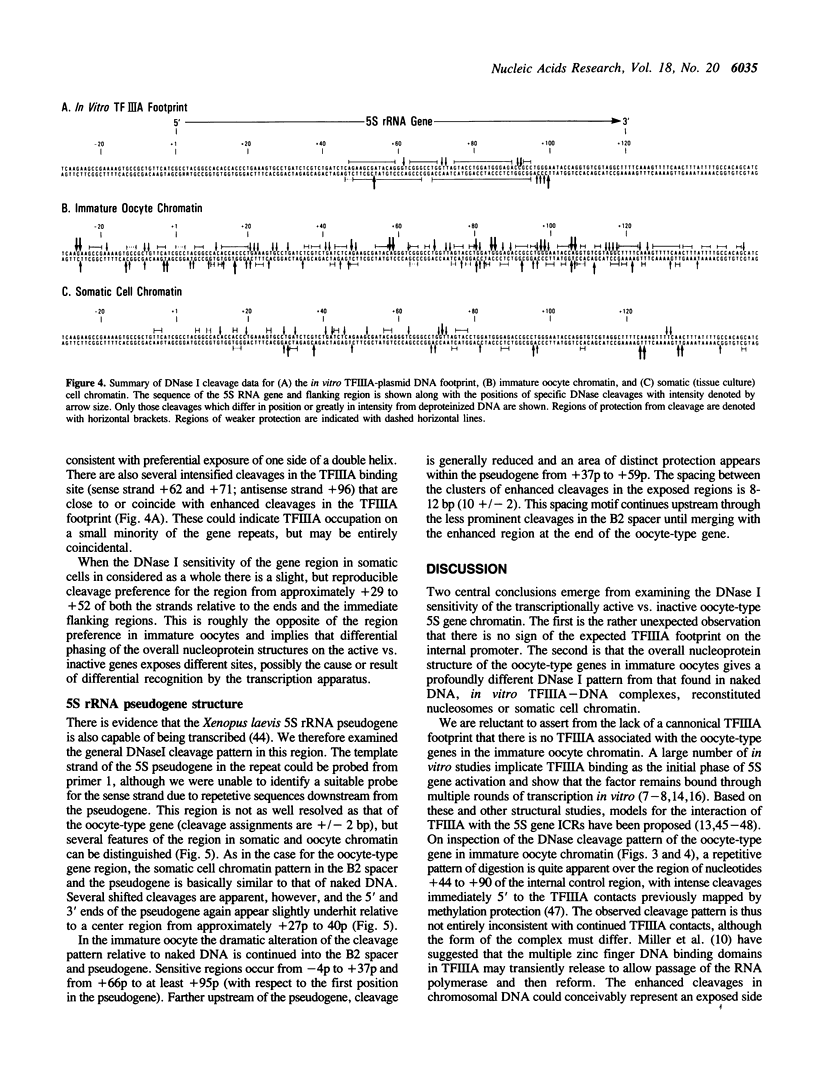
The chromatin structure of the Xenopus oocyte-specific 5S rRNA genes was examined at high resolution in immature oocyte and somatic cell chromosomes by DNase I footprinting. On oocyte chromatin, where the genes are active, the cleavage preferences over the entire gene region showed a periodic pattern of sensitivity and were dramatically different from the patterns obtained with deproteinized DNA or somatic cell chromatin. Further, the normal binding site for TFIIIA over the internal promoter region was preferentially sensitive to cleavage, indicating that TFIIIA was not bound in the manner predicted by in vitro experiments. In somatic cell chromatin, the oocyte-type 5S genes displayed a cleavage pattern largely similar to deproteinized DNA suggesting the absence of positioned nucleosomes on these inactive genes, although the presence of uncharacterized repressor complexes could not be ruled out. These data are discussed in terms of potential forms of the chromatin structure and alternative mechanisms of oocyte-type gene activation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews M. T., Brown D. D. Transient activation of oocyte 5S RNA genes in Xenopus embryos by raising the level of the trans-acting factor TFIIIA. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90640-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker J. J., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Formation of a rate-limiting intermediate in 5S RNA gene transcription. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco J., Millstein L., Razik M. A., Dilworth S., Cote C., Gottesfeld J. Two TFIIIA activities regulate expression of the Xenopus 5S RNA gene families. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1602–1612. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Gurdon J. B. Cloned single repeating units of 5S DNA direct accurate transcription of 5S RNA when injected into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2849–2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby M. K., Andrews M. T., Brown D. D. Transcription complexes that program Xenopus 5S RNA genes are stable in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5516–5520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Hoener P. A., Collins F. S. Direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified human genomic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):544–548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Rhodes D., Klug A. Mapping of the sites of protection on a 5 S RNA gene by the Xenopus transcription factor IIIA. A model for the interaction. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):577–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90278-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg A. M., King B. O., Roeder R. G. Xenopus 5S gene transcription factor, TFIIIA: characterization of a cDNA clone and measurement of RNA levels throughout development. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Bloomer L. S. Nonrandom alignment of nucleosomes on 5S RNA genes of X. laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):751–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M. DNA sequence-directed nucleosome reconstitution on 5S RNA genes of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1612–1622. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J., Bloomer L. S. Assembly of transcriptionally active 5S RNA gene chromatin in vitro. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):781–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla J. D. Rapid "footprinting" on supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3078–3081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinta D. R., Korn L. J. Differential order of replication of Xenopus laevis 5S RNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2536–2542. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinta D. R., Tso J. Y., Narayanswami S., Hamkalo B. A., Korn L. J. Early replication and expression of oocyte-type 5S RNA genes in a Xenopus somatic cell line carrying a translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5150–5154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber P. W., Wool I. G. Identification of the binding site on 5S rRNA for the transcription factor IIIA: proposed structure of a common binding site on 5S rRNA and on the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1593–1597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Engelke D. R. Genomic footprinting of a yeast tRNA gene reveals stable complexes over the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3244–3252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Evans C. F., Engelke D. R. Comparison of tRNA gene transcription complexes formed in vitro and in nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3212–3220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Riggs D. L., Negri R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription factor IIIB generates extended DNA interactions in RNA polymerase III transcription complexes on tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2551–2566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Gurdon J. B. The reactivation of developmentally inert 5S genes in somatic nuclei injected into Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):461–465. doi: 10.1038/289461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J. Transcription of Xenopus 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):101–105. doi: 10.1038/295101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladiges W. C., Raff R. F., Brown S., Deeg H. J., Storb R. The canine major histocompatibility complex. Supertypic specificities defined by the primed lymphocyte test (PLT). Immunogenetics. 1984;19(4):359–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00345410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. R., Cartwright E. M., Brownlee G. G., Fedoroff N. V., Brown D. D. The nucleotide sequence of oocyte 5S DNA in Xenopus laevis. II. The GC-rich region. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):717–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millstein L., Eversole-Cire P., Blanco J., Gottesfeld J. M. Differential transcription of Xenopus oocyte and somatic-type 5 S genes in a Xenopus oocyte extract. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17100–17110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate transcription of the Xenopus laevis 5S RNA genes in isolated chromatin by purified RNA polymerase III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):44–48. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Related 5S RNA transcription factors in Xenopus oocytes and somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Hamm J., Roeder R. G. The 5S gene internal control region is composed of three distinct sequence elements, organized as two functional domains with variable spacing. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds W. F., Bloomer L. S., Gottesfeld J. M. Control of 5S RNA transcription in Xenopus somatic cell chromatin: activation with an oocyte extract. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):57–75. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. An underlying repeat in some transcriptional control sequences corresponding to half a double helical turn of DNA. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90866-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. Structural analysis of a triple complex between the histone octamer, a Xenopus gene for 5S RNA and transcription factor IIIA. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3473–3482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Brown D. D. The transcriptional regulation of Xenopus 5s RNA genes in chromatin: the roles of active stable transcription complexes and histone H1. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., Brown D. D. Formation and stability of the 5 S RNA transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2483–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Jackson I. J., Brown D. D. Domains of the positive transcription factor specific for the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. Selective oxidation of the exonuclease domain of bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15330–15333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana K. E., Churchill M. E., Tullius T. D., Brown D. D. Mapping functional regions of transcription factor TFIIIA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1684–1696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L., Gurdon J. B. Cytoplasmic regulation of 5S RNA genes in nuclear-transplant embryos. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1613–1619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01632.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. DNA replication in vitro erases a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Developmental regulation of two 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1626–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Differential 5S RNA gene expression in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):733–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Onset of 5 S RNA gene regulation during Xenopus embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1983 Sep;99(1):248–257. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing Y. Y., Worcel A. A 3' exonuclease activity degrades the pseudogene 5S RNA transcript and processes the major oocyte 5S RNA transcript in Xenopus oocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1008–1018. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Carroll D. Regular arrangement of nucleosomes on 5S rRNA genes in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):720–730. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]