Abstract
High-resolution mapping of cofactor-specific photochemistry in photosynthetic reaction centers (RCs) from Rhodobacter sphaeroides was achieved by polarization selective ultrafast spectroscopy in single crystals at cryogenic temperature. By exploiting the fixed orientation of cofactors within crystals, we isolated a single transition within the multicofactor manifold, and elucidated the site-specific photochemical functions of the cofactors associated with the symmetry-related active A and inactive B branches. Transient spectra associated with the initial excited states were found to involve a set of cofactors that differ depending upon whether the monomeric bacteriochlorophylls, BChlA, BChlB, or the special pair bacteriochlorophyll dimer, P, was chosen for excitation. Proceeding from these initial excited states, characteristic photochemical functions were resolved. Specifically, our measurements provide direct evidence for an alternative charge separation pathway initiated by excitation of BChlA that does not involve P*. Conversely, the initial excited state produced by excitation of BChlB was found to decay by energy transfer to P. A clear sequential kinetic resolution of BChlA and the A-side bacteriopheophytin, BPhA, in the electron transfer proceeding from P* was achieved. These experiments demonstrate the opportunity to resolve photochemical function of individual cofactors within the multicofactor RC complexes using single crystal spectroscopy.
Keywords: photosynthesis, transient absorption, light-harvesting
In contrast to the diverse array of structures that have evolved for photosynthetic light-harvesting, a conserved feature of photosynthetic reaction centers (RCs) is the hexameric cofactor core that converts optical excited states to charge-separated states as the first chemical reaction in photosynthesis (1–3). Crystal structures from both oxygenic and nonoxygenic photosynthetic reaction center complexes show the hexameric cofactor core to be arranged with a pseudo twofold axis of symmetry consisting of the primary electron donor special pair (P), a dimer of (bacterio)chlorophyll molecules, and two branches, labeled A and B, that are equivalently positioned to serve as electron acceptor chains that extend across the membrane as depicted in the inset of Fig. 1 (4–6). The primary light-initiated electron transfer steps have been extensively investigated in bacterial Type II RCs and are considered to proceed from the excited singlet state P* to A side bacteriopheophytins (BPhA) using A side bacteriochlorophyll (BChlA) as a largely kinetically unresolved first electron acceptor (7–9) with the reaction directionality understood to be determined primarily by differences in local protein-site determined energetics for electron transfer along the two cofactor branches (10–12).
Fig. 1.
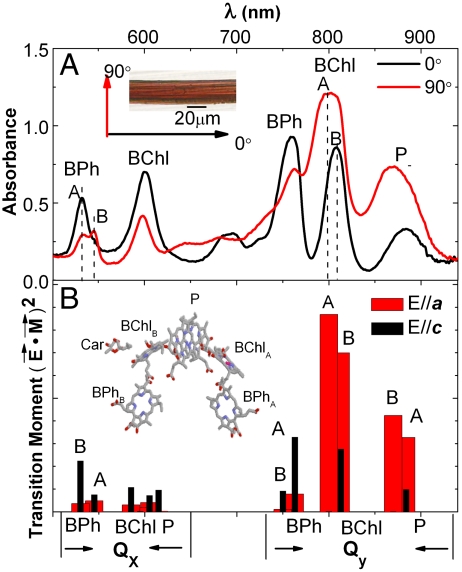
Polarized ground state optical absorption for a single R. sphaeroides R26 RC crystal (P212121) at 100 K. Part (A) shows ground state absorption spectra measured with light polarized perpendicular (90°) and parallel (0°) to the long axis of the crystal. The inset in part (A) shows a representative photograph of the wild-type (WT) crystals used in the experiments. The (B) box shows transition moment projections along the crystal a (red) and c (black) axes, respectively. The inset in (B) illustrates the arrangement of the cofactors in RCs. Letters A and B denote branches in RC molecule.
The above view leaves in question the role for the conserved, but nominally inactive B-side pigments. Possible complexities in primary photochemistry for the bacterial RC multicofactor core have been suggested by findings of excitation energy-dependent variation photochemical pathways (13, 14), including those that do not involve P* (15, 16) that are analogous to the primary processes identified in Photosystem I and II reaction centers in oxygenic photosynthesis.(17–20). Analysis of a broad range of spectroscopic, excitation energy transfer, and electron transfer properties based on modeling the electronic structure of RCs have led to the concept that the hexameric cofactor core should be considered as a supermolecule with a ladder of exciton states composed of various contributions from each of the individual cofactors (21–23). Further, recent 2D electronic spectroscopic studies revealed surprisingly long-lived excited-state quantum coherence between cofactors preserved by correlated protein environments in photosynthetic light-harvesting and reaction center complexes (24–29). This intercofactor electronic coherence is significant as a conduit for energy transfer that is potentially relevant to electron transfer as well. Interpigment electronic coupling has been studied by ultrafast pump-probe anisotropy spectroscopy in solution (28, 30, 31). Interpigment couplings in these measurements are detected through delocalized excited-state absorption changes, including coherent wave-packet motion, (25, 31–33) and by polarization studies that resolve transition moment anisotropies that deviate from the individual molecular reference frames (30, 31, 34, 35). Limitations for photo-selection spectroscopy arise from the inability of excitation pulses to selectively isolate a single transition in regions of spectral congestion.
Ultrafast transient absorption spectroscopy on single crystals of the bacterial RC (36) and a cyanobacterial cytochrome b6/f (37) has been used to resolve cofactor photochemistry directly related to crystal coordinate data. Further, in contrast to photo-selection spectroscopy in solution, polarized ultrafast spectroscopy on single crystals offers the additional opportunity to exploit the fixed orientation of cofactors for both pump and probe measurements. For example, the A-and B-branch cofactors have different projections along the unit cell axes of orthorhombic crystals, allowing both pump and probe to isolate individual transitions of the normally symmetry degenerate pairs (36).
In this paper, we report on polarization selective femtosecond transient absorption spectroscopy of cryogenically cooled (100 K) single reaction center crystals from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Combinations of pump wavelength and polarization were used to selectively excite optical transitions of P- (the lower exciton state of P), BChlA and BChlB in the Qy spectral region. By isolating a single transition within the cofactor manifold at a time, we are able to map cofactor-specific charge separation pathways. This approach provides unique opportunities to exploit the fixed orientation of cofactors within crystals to achieve site-specific excitation and detection of cofactors, and to elucidate photochemical functions of cofactors associated with the active A branch and inactive B branch in bacterial RCs.
Results
Ground state polarized absorption spectra for cryogenically cooled (100 K) crystals are shown in Fig. 1. Extinction coefficient weighted projections for each of the RC cofactor optical transitions along the a and c crystal axes are plotted with wavelength positions according to cofactor peak assignments (23, 38, 39) in Fig. 1B. Magnitudes for polarized optical absorption for the RC P212121 unit cell were calculated from the transition moment, the polarized light electric field, and unit vectors as described previously (36). Absorption spectra were measured with light polarized either parallel (0°) or perpendicular (90°) to the long axis of the needle-shaped crystal (inset of Fig. 1A). X-ray alignment measurements show that the unit cell directions lie parallel to the crystal axes (40, 41). The agreement between the measured spectra and calculated transition moment projections allows the experimental 0° and 90° directions to be identified as lying along the 4RCR crystal unit cell c and a axes, respectively (36). Further details are provided in the SI Text.
As illustrated in Fig. 1A, the ground state polarized absorption spectra show pronounced variation in both absorption peak positions and amplitudes as the polarization angle for the measuring beam is rotated from 0° to 90°. For instance, the BPh Qx peak at 530 nm reflects predominate contribution from BPhB at 0° polarization, while the spectrum recorded with 90° polarized light shows split absorption bands corresponding to the BPhB (530 nm) and BPhA (545 nm) contributions, respectively. The spectrum recorded with 90° polarized light shows a peak centered at 800 nm that reflects the greater contribution of BChlA. With 0° polarized light, the BChl peak absorption shifts to 810 nm, and based on the agreement with transition moment projection onto the crystal axes can be understood to be contributed mainly by BChlB. Note that the upper energy exciton component of P+ is known to have an absorption band that overlaps with BChlB around 810 nm but with only approximately 1/3 of the oscillation strength of the BChlB (42). The red-most absorption band arises from the lower energy exciton component of P, P- (43). Models have taken into account the effects of coupling between all of the cofactor transition dipoles within the RC and charge transfer states between BChl comprising P.(22, 23). The polarized spectra recorded for P- is found to have a strong preferential absorption with 90° polarized light. The absorption spectra shown in Fig. 1 are from a R26 crystal. The experiments described below are performed on wild-type (WT) crystals. The ground state dichroism is similar for R26 and WT crystals and the absorption spectra for a typical WT crystal are shown in Fig. S1A.
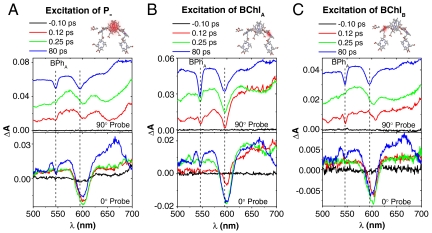
Based on the ground state dichroism discussed above, the polarization angle can be combined with wavelength to selectively excite and probe otherwise degenerate optical transitions of cofactors associated with the A and B branches (36). The opportunity to resolve cofactor-specific photochemical function by polarization selective transient spectroscopy measurements in single crystals is illustrated in Fig. 2. Three pump wavelength and polarization combinations were utilized to selectively excite the Qy transition of P- (900 nm, bandwidth approximately 28 nm, 90° polarization Fig. 2A), BChlA (790 nm, bandwidth approximately 20 nm, 90°polarization, Fig. 2B), and BChlB (824 nm, bandwidth approximately 23 nm, 0° polarization, Fig. 2C). The spectra of the pump pulses are shown in Fig. S1B. The white-light probe polarization was set to be either 90° (top graphs) or 0° (bottom graphs). Probing at 0° and 90° produced dramatically different spectra, demonstrating the ability to selectively probe different transitions in the manifold (36). Specifically, bleaching of the Qx transition of BPhA around 545 nm is observed almost exclusively with the 90° polarized probe. This observation is consistent with the experimental polarized ground state spectra, in that the BPhA Qx transition moment is aligned preferentially with the a axis. Transient spectra for each pump and probe combination are compared at four delay times in Fig. 2. The corresponding 2D graphs illustrating the full time progression for the transient absorption measured during the experimental time frame are shown in Fig. S2.
Fig. 2.
Pump wavelength-dependent patterns of transient optical absorption changes in a single Rb. sphaeroides-wt crystal at 100 K. The pump is adjusted to 900 nm (90°), 790 nm (90°), and 824 nm (0°), in boxes (A, B, and C), to selectively pump Qy optical transitions of P-, BChlA and BChlB, respectively. The top spectra are for probing at 90° with respect to the crystal c axis and the spectra are offset for clarity. The vertical lines are placed at 545 and 595 nm. The bottom spectra are the spectra for probing at 0°.
The initial transient states and progression of subsequent energy and electron transfer events show clear differences that depend upon the cofactor-specific excitation. The position of the initial BChl Qx transition bleach near 600 nm accompanying excitation in the near-IR Qy region was found to shift characteristically depending upon the BChl cofactor selected for photoexcitation. For example, when the Qy transition of P- is selectively excited, the initial bleaching is at 604 nm corresponding to the Qx transition of P (Fig. 2A, 0.1 ps trace). We note that the P Qx transition makes only a minor projection onto the crystal axis probe by the 90° probe orientation. The bottom graph of Fig. 2A shows the transient spectrum measured with 0° probe following 900 nm, 90° excitation, and the larger P Qx bleaching. When BChlA is selectively excited, the initial bleaching occurs at 595 nm consistent with the Qx transition of BChlA (Fig. 2B, 0.1 ps trace). Finally, an initial bleaching at 609 nm is observed with an excitation wavelength of 824 nm and a polarization at 0° (Fig. 2C, 0.1 ps trace). This position is different from the Qx transition of P at 604 nm and if the P+ transition were excited, one would expect the bleach to be at 604 nm. Therefore, we assign the bleach observed at 609 nm to the Qx transition of BChlB. Even though there is significant spectral overlap between Qy transition of BChlB and P+ state, the instantaneous bleach at 609 nm instead of at 604 nm indicates that the pump wavelength of 824 nm at 0° polarization excites mostly the Qy transition of BChlB instead of P+.
In addition to the resolution of BChl Qx bleaching components, the earliest transient spectra show initial excite states to involve a set of cofactors that differ depending upon whether BChlA, BChlB, or P- was chosen for excitation. For example, with the selective excitation of P-, a partial absorption decrease of the BPhA Qx transition at 545 nm is seen in the transient spectrum recorded with a 100 fs delay (Fig. 2A). This instantaneous BPhA bleach recovers, and by 200 fs the transient spectrum reflects a localized P* state. When BChlA is selectively excited by the 790 nm pump, a larger magnitude of bleach at 545 nm is observed to coincide with excitation. In addition to the instantaneous bleach of BPhA, bleaching of carotenoid (Car) transition at 510 nm is also evident, suggesting that the initial excited-state perturbation extents to the Car cofactor. With BChlB excitation by pump wavelength of 824 nm (Fig. 2C), instantaneous bleaching of both the BPhA (545 nm) and Car (510 nm) cofactors is also observed. Remarkably, no involvement of BPhB is observed upon excitation of any of the BChls, even the adjacent BChlB. A small absorption loss at 530 nm is observed in the 100 fs transient spectra upon BChlA and BChlB excitation (e.g., Fig. 2 B and C) that corresponds to the position of the BPhB Qx absorption. However this feature is only detected with 90°, but not 0° probe polarization, Fig. 2. This polarization pattern matches that measured for the BPhA Qx, in the ground state spectrum, and is the opposite of that measured and predicted from the crystal coordinates for the BPhB Qx direction, Fig. 1.
Proceeding from these different initial excited states, distinguishable photochemical pathways are also resolved. When P- (Fig. 2A) or BChlB (Fig. 2C) are selectively excited, the initial excited states that include different amounts of BPhA and Car contributions, relax in 250 fs to have characteristics of a localized P*. In both cases, the P* state in turn evolves to the 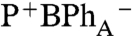 state, marked by characteristic BPhA and BChlA
Qx bleaching at 545 nm and 595 nm, respectively and an absorption of
state, marked by characteristic BPhA and BChlA
Qx bleaching at 545 nm and 595 nm, respectively and an absorption of 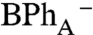 at 670 nm. In contrast, when BChlA is excited, the initial BPhA
Qx bleach does not recover fully; i.e., the bleaching at 545 nm persists at 0.25 ps (Fig. 2B, 90° probe 0.25 ps trace), suggesting formation of a possible initial
at 670 nm. In contrast, when BChlA is excited, the initial BPhA
Qx bleach does not recover fully; i.e., the bleaching at 545 nm persists at 0.25 ps (Fig. 2B, 90° probe 0.25 ps trace), suggesting formation of a possible initial 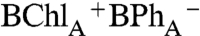 charge-separated state that forms directly, and does not evolve from P*. This interpretation is supported by the companion 0° probe spectrum (Fig. 2B, 0° probe), which measures the broad 650–700 nm bacteriochlorin anion absorption band at 0.25 ps (44). The absorption band at 650–700 nm at early delay time (0.12 ps and 0.25 ps traces) is broader than at 80 ps (Fig. 2B, 0° probe), which may reflect the biradical
charge-separated state that forms directly, and does not evolve from P*. This interpretation is supported by the companion 0° probe spectrum (Fig. 2B, 0° probe), which measures the broad 650–700 nm bacteriochlorin anion absorption band at 0.25 ps (44). The absorption band at 650–700 nm at early delay time (0.12 ps and 0.25 ps traces) is broader than at 80 ps (Fig. 2B, 0° probe), which may reflect the biradical 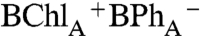 charge-transfer state formed initially upon BChlA excitation. In contrast, upon excitation of either BChlB or P- , a BPh anion absorption band is not observed until charge separation is completed and the P+
charge-transfer state formed initially upon BChlA excitation. In contrast, upon excitation of either BChlB or P- , a BPh anion absorption band is not observed until charge separation is completed and the P+
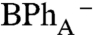 state is formed.
state is formed.
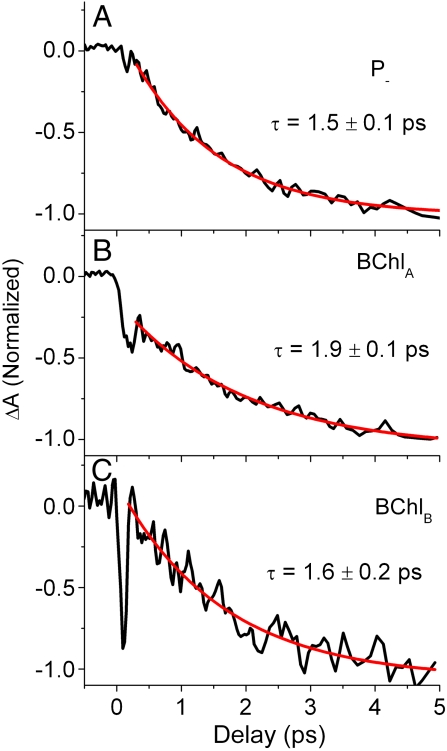
Fig. 3 shows the single-wavelength kinetics of the BPhA
Qx transition (545 nm - 540 nm, 90° probe), taken from the data shown in Fig. 2, and measured following selective excitation of P-, BChlA, and BChlB, that also reflect the site-specific charge separation pathways. At the earliest observable time (approximately 100 fs), a dip with a width of the time resolution of the experiments (approximately 150 fs) is present in all three decay curves corresponding to the instantaneous bleach observed in the spectra. The magnitude of initial BPhA transient is 10%, 45%, and 85% of the total absorption change following excitation of P-, BChlA, and BChlB, respectively. The dynamics after the initial bleach are fitted with a single exponential function. When P and BChlB are selectively excited, the initial BPhA bleach fully recovers (i.e., ΔA recovers to 0 at approximately 0.25 ps) to a P* state that subsequently decays with a time constant of approximately 1.5 ps to the 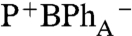 state. When BChlA is selectively excited, the initial BPhA bleach does not recover fully (i.e., ΔA does not recover to 0), which is attributed to a mixture of
state. When BChlA is selectively excited, the initial BPhA bleach does not recover fully (i.e., ΔA does not recover to 0), which is attributed to a mixture of 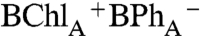 and P* states. The formation of
and P* states. The formation of 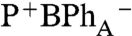 following these excited states is fitted with a time constant of 1.9 ± 0.1 ps.
following these excited states is fitted with a time constant of 1.9 ± 0.1 ps.
Fig. 3.
Pump wavelength-dependent kinetics for the BPhA Qx absorption (545 nm - 540 nm) in the same Rb. spheroides-wt crystal as in Fig. 2. The pump was adjusted to selectively excite different RC optical transitions P- (A), BChlA (B) and BChlB (C). The crystal temperature was 100 K. The red lines show single exponential decay fits.
The resolution of 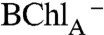 as an intermediate in the electron transfer from P* to BPhA is also resolved in these measurements. Although resolvable in the spectra shown above, this is most clearly illustrated with a crystal that exhibited a blue shift of the BChlA
Qx peak that allowed a very clear resolution of transient function shown in, Fig. S3. With excitation of P-, the initial BChl Qx bleach shows a single band with a peak at 604 nm associated with P*. During the subsequent electron transfer to form
as an intermediate in the electron transfer from P* to BPhA is also resolved in these measurements. Although resolvable in the spectra shown above, this is most clearly illustrated with a crystal that exhibited a blue shift of the BChlA
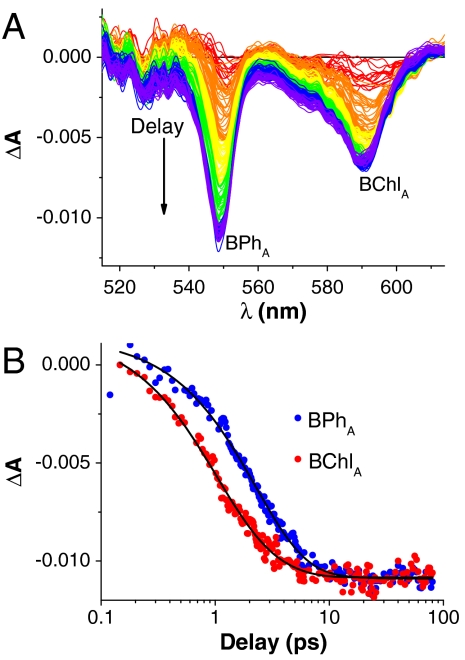
Qx peak that allowed a very clear resolution of transient function shown in, Fig. S3. With excitation of P-, the initial BChl Qx bleach shows a single band with a peak at 604 nm associated with P*. During the subsequent electron transfer to form 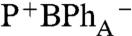 , an additional bleaching band builds in at 590 nm resulting in a final double peaked BChl Qx absorption decrease, Fig. S3. The individual contributions of BChlA and BPhA can be tracked, in difference transient spectra using the 150 fs P* as a reference spectrum, Fig. 4A, and corresponding single wavelength kinetics are plotted in Fig. 4B. The 2.2 ± 0.2 ps single exponential bleaching kinetics associated with BPhA reduction in this crystal lag behind the bleaching of BChlA, which shows biexponential kinetics with decay times of 0.9 ± 0.2 ps and 2.3 ± 0.8 ps, as described Fig. 4. Similar lag time of approximately 0.9 ps for reduction of BPhA compared to that of BChlA is also found from difference transient spectra obtained for the crystal shown in Fig. 2, plotted in Fig. S4. We note that many experimental parameters can cause shifts in the absorption peaks for the RC cofactors (45, 46). In the case of the crystal used in Fig. 4, these perturbations allowed the transient kinetics for BChlA to be more readily recognized, but comparable kinetics are observed in crystals without these perturbations, Fig. S4.
, an additional bleaching band builds in at 590 nm resulting in a final double peaked BChl Qx absorption decrease, Fig. S3. The individual contributions of BChlA and BPhA can be tracked, in difference transient spectra using the 150 fs P* as a reference spectrum, Fig. 4A, and corresponding single wavelength kinetics are plotted in Fig. 4B. The 2.2 ± 0.2 ps single exponential bleaching kinetics associated with BPhA reduction in this crystal lag behind the bleaching of BChlA, which shows biexponential kinetics with decay times of 0.9 ± 0.2 ps and 2.3 ± 0.8 ps, as described Fig. 4. Similar lag time of approximately 0.9 ps for reduction of BPhA compared to that of BChlA is also found from difference transient spectra obtained for the crystal shown in Fig. 2, plotted in Fig. S4. We note that many experimental parameters can cause shifts in the absorption peaks for the RC cofactors (45, 46). In the case of the crystal used in Fig. 4, these perturbations allowed the transient kinetics for BChlA to be more readily recognized, but comparable kinetics are observed in crystals without these perturbations, Fig. S4.
Fig. 4.
Difference transient absorption spectra following formation of P*. Part (A) shows difference transient spectra recorded with delays from 150 fs to 80 ps, and following subtraction of the spectrum recorded with a 150 fs delay from the pump pulse. This subtraction removes contributions of ground state bleaching of P and highlights the time-progression of the BPh and BChl QX transient components. Part (B) shows single wavelength BPhA and BChlA QX transient kinetics measured at 548 nm and 590 nm, respectively. The 590 nm transient was normalized to match the 548 nm amplitude. The BPhA 548 nm kinetics were fit (solid line) using a single exponential 2.2 ± 0.2 ps decay. The BChlA 590 nm kinetics were fit (solid line) using a biexponential with 0.9 ± 0.2 ps and 2.3 ± 0.8 ps decay times corresponding amplitudes of 0.0085 ± 0.002 and 0.004 ± 0.003, respectively. Excitation was provided by 890 nm pump pulse, and both pump and probe with 90° polarized, using the transient spectra shown in Fig. S3.
As shown here, polarization selective single crystal spectroscopy offers opportunities to resolve photochemical pathways within multicofactor photosynthetic complexes. For comparison, Fig. S5 provides an example of comparable wavelength selected excitation of detergent solubilized RCs in solution. A more complete analysis has been carried out earlier by van Grondelle and coworkers demonstrating charge-separation that did not initiate from P* (15, 16). Overall the transient absorption spectra and lifetimes measured in solution agree with those of single RC crystals, implying that the photochemical pathways are retained upon RC crystallization. The cofactor spacing between RCs within the crystal unit cell is greater than 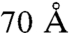 , and crystallographic packing is unlikely to alter primary photochemistry. Spectra recorded with 0.1 ps delay show initial excited-state spectra that include contributions from BPhA and the carotenoid cofactors, along with those of the BChl or P cofactors used for excitation. The initial excited-state spectra relax to a more localized on P* by 0.25 ps. However, because of the absence of dichroic selection, 790 nm femtosecond pump pulses excite both BChlA and BChlB. The responses of BChlA and BChlB are convoluted, and the different photochemical functions of BChlA and BChlB are not readily resolved.
, and crystallographic packing is unlikely to alter primary photochemistry. Spectra recorded with 0.1 ps delay show initial excited-state spectra that include contributions from BPhA and the carotenoid cofactors, along with those of the BChl or P cofactors used for excitation. The initial excited-state spectra relax to a more localized on P* by 0.25 ps. However, because of the absence of dichroic selection, 790 nm femtosecond pump pulses excite both BChlA and BChlB. The responses of BChlA and BChlB are convoluted, and the different photochemical functions of BChlA and BChlB are not readily resolved.
Discussion
Nature of the Initial Excited-States.
The instantaneous bleach of BPh upon excitation of BChl has been observed previously in decay associated spectral analysis of the spectra of RC solution (47). Here we are able to observe directly from the raw data of single crystal spectroscopy, and further discriminate between the involvement of BPhA as part of a charge-transfer state created by excitation of BChlA, and the different involvement of BPhA as part of an excited state produced by excitation of either BChlB or P.
The involvement of multiple cofactors upon single cofactor excitation can possibly be explained by strongly correlated electronic levels, possibly including charge-transfer mixing, among the individual cofactors in the RC (21, 28). Long-lived electronic coherence between the excited states of BPh and BChl was observed recently with 2-color photon echo experiments and was attributed to strong correlation between the protein-induced fluctuations in the transition energy levels of BChl and BPh (28). Electronic coherence between the cofactors allows the excitation to move coherently in space, enabling excited populations moving between different cofactors (24–29). Based on the observation of electronic coherence is much longer lived at low temperature (28), the fact that we observe multicofactor transitions in the initial excited states only at cryogenic temperature suggests that electronic coherence might play an important role. We also observe instantaneous bleaching of Car upon excitation of BChls and P, indicating Car participates in excitation energy transfer in the RC manifold. This observation is in accordance with the recent study of PSII reaction centers in which Car was suggested to act as an electronic coupling bridge and enhance energy transfer from the antenna to the reaction centers (48).
A possible alternative mechanism to explain the instantaneous bleaching of BPhA and Car cofactors coupled to BChl excitation is through electrochromic Stark effects (49), associated with charge-transfer dipole character of initial BChl excited states. However, a Stark effect alone cannot satisfactorily explain our observations for two reasons. First, the Stark effect for an internal electric field would typically be expected to produce transient spectra with a derivative band shape, (50) but neither the instantaneous BPhA nor Car transient bands appear to have such shapes. Secondly, a comparison of BPhA and BPhB Qx directions shows that both cofactors have comparable alignments with respect to possible excited charge-transfer state directions, Table S1, Fig. S6. Measurements using internal and external electric fields show that the B-side cofactors have a markedly enhanced electrochromic response, indicative of a dielectric asymmetry in the RC (49). We find that the opposite effect, that only BPhA, and not BPhB, response to BChl initial excited states.
These considerations suggest that the instantaneous bleach of multiple cofactor transitions upon single cofactor excitation of BChlA,B and P is most likely due to electronic coupling between the cofactor and not due to Stark effect. The lack of an involvement of the inactive BPhB with the initial excited state formed upon excitation of BChlA, BChlB, or P implies an inherent asymmetry in electronic coupling between cofactors. Mutagenesis experiments have shown that directional electron transfer in RCs is largely determined by protein-tuned energies of the cofactor molecular orbitals (10, 12). Such energy level tuning can be expected to regulate the magnitudes of exciton, charge transfer, and coherent couplings between cofactors.
Photochemistry Initiated from P.
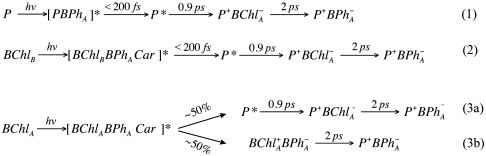
Following excitation of P, the consensus view is that BChlA functions as the initial electron acceptor for P*, forming the 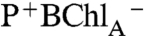 transient state with a 3 ps risetime (room temperature), but is rapidly converted by electron transfer to BPhA with a 0.9 ps time constant (7). However the overlap of the ground and excited-state optical absorptions of the cofactors has posed challenges for easy verification of this reaction scheme. The spectral resolution offered by polarized transient spectroscopy on crystals shown here provides a very clear resolution of biphasic transients of the BChlA cofactor prior to BPhA reduction. Pathway 1 in Scheme 1 summarizes the photochemistry initiated from P. These results are consistent with the kinetic scheme in which BChlA functions as the initial electron acceptor (7), but also with a more complex function discussed below.
transient state with a 3 ps risetime (room temperature), but is rapidly converted by electron transfer to BPhA with a 0.9 ps time constant (7). However the overlap of the ground and excited-state optical absorptions of the cofactors has posed challenges for easy verification of this reaction scheme. The spectral resolution offered by polarized transient spectroscopy on crystals shown here provides a very clear resolution of biphasic transients of the BChlA cofactor prior to BPhA reduction. Pathway 1 in Scheme 1 summarizes the photochemistry initiated from P. These results are consistent with the kinetic scheme in which BChlA functions as the initial electron acceptor (7), but also with a more complex function discussed below.
Scheme 1.
Cofactor-specific charge separation pathways revealed by single crystal spectroscopy. The brackets list the combination of cofactor optical transitions observed for the different initial excited-states, but not the levels of their contributions.
Photochemistry Initiated from BChlA and BChlB.
While selective excitation of BChlB was found to create a delocalized excited state that uniformly decayed (< 200 fs) to form a localized excited state on P as described above (pathway 2 in Scheme 1), more complex, dual photochemical pathways were found to accompany BChlA excitation (pathways 3a and 3b in Scheme 1). With up to 50% yield, BChlA excitation was seen to create an initial charge-separated state, 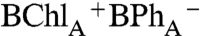 , that did not evolve from P*, that persists, apparently decaying by hole transfer to form
, that did not evolve from P*, that persists, apparently decaying by hole transfer to form 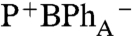 (Pathway 3b). We note that 650 nm -670 nm BPh “anion band” absorption for this initial state differs from that detected during the transient
(Pathway 3b). We note that 650 nm -670 nm BPh “anion band” absorption for this initial state differs from that detected during the transient 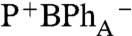 state, possibly a reflection of the coupled biradical natural of this initial charge-separated state. The remaining portion of the BChlA excitation appeared to decay to create P*, from which sequential electron transfer to BPhA occurs with approximately 2 ps time constant. The presence of dual pathways suggests heterogeneity in the coupling of BChlA and BPhA that might add complexity to the sequential electron transfer pathway.
state, possibly a reflection of the coupled biradical natural of this initial charge-separated state. The remaining portion of the BChlA excitation appeared to decay to create P*, from which sequential electron transfer to BPhA occurs with approximately 2 ps time constant. The presence of dual pathways suggests heterogeneity in the coupling of BChlA and BPhA that might add complexity to the sequential electron transfer pathway.
A component of primary charge separation occurring within the BChlABPhA pair that does not evolve from P* was suggested previously based on decay associated spectral analysis of transients recoded from solutions at low temperature (15, 16). However, the broadness of ultrafast pump pulses and overlap of the BChlA and BChlB absorptions prevents exclusive cofactor excitation. The polarization selective spectroscopy in single crystals shown here resolves these cofactor-specific pathways with greater precision, and allows direct resolution of cofactor-specific photochemistry in the polarized transient spectra. The confirmation of alternative photochemical pathways in the bacterial RC, including those that do not involve P, provides a relevant model system for comparative analysis of photochemistry in RCs from oxygenic photosynthesis.
Single crystal ultrafast transient spectroscopy is shown to provide a means to deepen our understanding of the photophysical function of the multicofactor RC core, and establish the foundation for extending this approach to probe energy and electron transfer pathways in RC-light harvesting, PSI, PSII crystalline complexes.
Materials and Methods
Details regarding preparation of reaction center crystals, sample preparation for low temperature optical measurements, ground state absorption and transient absorption spectroscopies are presented in SI Text.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments.
The authors gratefully acknowledge discussions with Dr. O. Kokhan on kinetic fitting using sequential electron transfer schemes that were not presented in the manuscript. L.H. was supported by the Division of Chemical Sciences, Geosciences and Biosciences, Office of Basic Energy Sciences of the Department of Energy through Grant DE-FC02-04ER15533. N.P. and D.M.T. were supported by the Division of Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and Biosciences, Office of Basic Energy Sciences of the Department of Energy under Contract DE-AC02-06CH11357. Use of the Center for Nanoscale Materials was supported by the Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. This publication is contribution No. NDRL 4893 from the Notre Dame Radiation Laboratory.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1116862109/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Kern J, Renger G. Photosystem II: Structure and mechanism of the water: plastoquinone oxidoreductase. Photosynth Res. 2007;94:183–202. doi: 10.1007/s11120-007-9201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sadekar S, Raymond J, Blankenship RE. Conservation of distantly related membrane proteins: photosynthetic reaction centers share a common structural core. Mol Bio Evol. 2006;23:2001–2007. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msl079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Amunts A, Nelson N. Plant photosystem I design in the light of evolution. Structure. 2009;17:637–650. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2009.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Deisenhofer J, Epp O, Miki K, Huber R, Michel H. X-ray structure analysis of a membrane protein complex Electron density map at 3 A resolution and a model of the chromophores of the photosynthetic reaction center from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. J Mol Bio. 1984;180:385–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jordan P, et al. Three-dimensional structure of cyanobacterial photosystem I at 2.5 angstrom resolution. Nature. 2001;411:909–917. doi: 10.1038/35082000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zouni A, et al. Crystal structure of photosystem II from Synechococcus elongatus at 3.8 angstrom resolution. Nature. 2001;409:739–743. doi: 10.1038/35055589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zinth W, Wachtveitl J. The first picoseconds in bacterial photosynthesis—Ultrafast electron transfer for the efficient conversion of light energy. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2005;6:871–880. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200400458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kirmaier C, Holten D. An assessment of the mechanism of initial electron-transfer in bacterial reaction centers. Biochemistry. 1991;30:609–613. doi: 10.1021/bi00217a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Blankenship R. Molecular mechanisms of photosynthesis. London: Blackwell Science; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Heller BA, Holten D, Kirmaier C. Control of electron-transfer between the L-side and M-side of photosynthetic reaction centers. Science. 1995;269:940–945. doi: 10.1126/science.7638616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Haffa A, et al. High yield of long-lived B-side charge separation at room temperature in mutant bacterial reaction centers. J Phys Chem B. 2003;107:12503–12510. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kirmaier C, Bautista J, Laible P, Hanson D, Holten D. Probing the contribution of electronic coupling to the directionality of electron transfer in photosynthetic reaction centers. J Phys Chem B. 2005;109:24160–24172. doi: 10.1021/jp054726z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lin S, Katilius E, Haffa A, Taguchi A, Woodbury N. Blue light drives B-side electron transfer in bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers. Biochemistry. 2001;40:13767–13773. doi: 10.1021/bi015612q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Xin Y, Lin S, Blankenship RE. Femtosecond spectroscopy of the primary charge separation in reaction centers of chloroflexus aurantiacus with selective excitation in the Q(Y) and soret bands. J Phys Chem A. 2007;111:9367–9373. doi: 10.1021/jp073900b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.van Brederode M, van Mourik F, van Stokkum I, Jones M, van Grondelle R. Multiple pathways for ultrafast transduction of light energy in the photosynthetic reaction center of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:2054–2059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.5.2054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.van Brederode M, Van Grondelle R. New and unexpected routes for ultrafast electron transfer in photosynthetic reaction centers. FEBS Letts. 1999;455:1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00810-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Holzwarth AR, et al. Kinetics and mechanism of electron transfer in intact photosystem II and in the isolated reaction center: Pheophytin is the primary electron acceptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:6895–6900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505371103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Novoderezhkin VI, Romero E, Dekker JP, Van Grondelle R. Multiple charge-separation pathways in photosystem ii: modeling of transient absorption kinetics. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2011;12:681–688. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201000830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Myers JA, et al. Two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy of the D1-D2-cyt b559 photosystem II reaction center complex. J Phys Chem Lett. 2010;1:2774–2780. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Muller MG, Slavov C, Luthra R, Redding KE, Holzwarth AR. Independent initiation of primary electron transfer in the two branches of the photosystem I reaction center. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:4123–4128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905407107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Parkinson DY, Lee H, Fleming GR. Measuring electronic coupling in the reaction center of purple photosynthetic bacteria by two-color, three-pulse photon echo peak shift spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B. 2007;111:7449–7456. doi: 10.1021/jp070029q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Warshel A, Parson W. Spectroscopic properties of photosynthetic reaction centers .1. theory. J Am Chem Soc. 1987;109:6143–6152. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Parson W, Warshel A. Spectroscopic properties of photosynthetic reaction centers .2. application of the theory to Rhodopseudomonas-viridis. J Am Chem Soc. 1987;109:6152–6163. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Novoderezhkin V, Yakovlev A, Van Grondelle R, Shuvalov V. Coherent nuclear and electronic dynamics in primary charge separation in photosynthetic reaction centers: A redfield theory approach. J Phys Chem B. 2004;108:7445–7457. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yakovlev A, et al. Primary charge separation between P* and BA: electron-transfer pathways in native and mutant GM203L bacterial reaction centers. Chem Phys. 2005;319:297–307. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brixner T, et al. Two-dimensional spectroscopy of electronic couplings in photosynthesis. Nature. 2005;434:625–628. doi: 10.1038/nature03429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Engel GS, et al. Evidence for wavelike energy transfer through quantum coherence in photosynthetic systems. Nature. 2007;446:782–786. doi: 10.1038/nature05678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee H, Cheng Y-C, Fleming GR. Coherence dynamics in photosynthesis: protein protection of excitonic coherence. Science. 2007;316:1462–1465. doi: 10.1126/science.1142188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Read EL, Lee H, Fleming GR. Photon echo studies of photosynthetic light harvesting. Photosynth Res. 2009;101:233–243. doi: 10.1007/s11120-009-9464-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jonas D, Lang M, Nagasawa Y, Joo T, Fleming G. Pump-probe polarization anisotropy study of femtosecond energy transfer within the photosynthetic reaction center of Rhodobacter sphaeroides R26. J Phys Chem. 1996;100:12660–12673. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Haran G, Wynne K, Moser C, Dutton P, Hochstrasser R. Level mixing and energy redistribution in bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers. J Phys Chem. 1996;100:5562–5569. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Vos MH, Breton J, Martin JL. Electronic energy transfer within the hexamer cofactor system of bacterial reaction centers. J Phys Chem B. 1997;101:9820–9832. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Vos MH, Rappaport F, Lambry JC, Breton J, Martin JL. Visualization of coherent nuclear motion in a membrane-protein by femtosecond spectroscopy. Nature. 1993;363:320–325. [Google Scholar]
- 34.King BA, McAnaney TB, Alex deWinter a, Boxer SG. Excited state energy transfer pathways in photosynthetic reaction centers. 3. ultrafast emission from the monomeric bacteriochlorophylls. J Phys Chem B. 2000;104:8895–8902. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Klenina I, Borovykh I, Shkuropatov AY, Gast P, Proskuryakov I. Orientation of the Qy optical transition moment of bacteriopheophytin in Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction centers. Chem Phys. 2003;294:451–458. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Huang L, et al. Correlating ultrafast function with structure in single crystals of the photosynthetic reaction center. Biochemistry. 2008;47:11387–11389. doi: 10.1021/bi801026g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dashdorj N, Yamashita E, Schaibley J, Cramer W, Savikhin S. Ultrafast optical pump-probe studies of the cytochrome b6f complex in solution and crystalline States. J Phys Chem B. 2007;111:14405–14410. doi: 10.1021/jp076536p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Breton J. Orientation of the chromophores in the reactioncenter of Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Comparison of low-tempereture linear dichroism spectra with a model derived from X-ray crystallography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;810:235–245. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kirmaier C, Holten D. Primary photochemistry of reaction centers from photosyntheic purple bacteria. Photosynth Res. 1987;13:225–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00029401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chang C-H, Schiffer M, Tiede DM, Smith U, Norris JR. Characterization of bacterial photosynthetic reaction center crystals from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26 by X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1985;186:201–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chang C-H, et al. Structure of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26 reaction center. FEBS Letts. 1986;205:82–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80870-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jordanides X, Scholes G, Fleming G. The mechanism of energy transfer in the bacterial photosynthetic reaction center. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105:1652–1669. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lathrop EJP, Friesner RA. Simulation of optical spectra from the reaction center of Rb Sphaeroides. Effects of an internal charge-separated state of the special pair. J Phys Chem. 1994;98:3056–3066. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Fajer J, Brune DC, Davis MS, Forman A, Spaulding LD. Primary charge separation in bacterial photosynthesis: oxidized chlorophylls and reduced pheophytin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1975;72:4956–4960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang S, Lin S, Lin X, Woodbury NW, Allen JP. Comparative study of reaction centers from purple photosynthetic bacteria: Isolation and optical spectroscopy. Photosynth Res. 1994;42:203–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00018263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gast P, Hemelrijk PW, Van Gorkom HJ, Hoff AJ. The association of different detergents with the photosynthetic reaction center protein of Rhodobacter sphaeroides R26 and the effects on its photochemistry. Eur J Biochem. 1996;239:805–809. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0805u.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gibasiewicz K, Pajzderska M, Karolczak J, Dobek A. Excitation and electron transfer in reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides probed and analyzed globally in the 1-nanosecond temporal window from 330 to 700 nm. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2009;11:10484–10493. doi: 10.1039/b912431d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Romero E, van Stokkum IHM, Dekker JP, Van Grondelle R. Ultrafast carotenoid band shifts correlated with ChlZ excited states in the photosystem II reaction center: are the carotenoids involved in energy transfer? Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011;13:5573–5575. doi: 10.1039/c0cp02896g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Steffen MA, Lao KQ, Boxer SG. Dielectric asymmetry in the photosynthetic reaction-center. Science. 1994;264:810–816. doi: 10.1126/science.264.5160.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Boxer SG. Stark Realities. J Phys Chem B. 2009;113:2972–2983. doi: 10.1021/jp8067393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.