Abstract
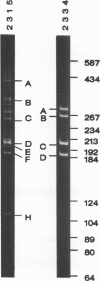
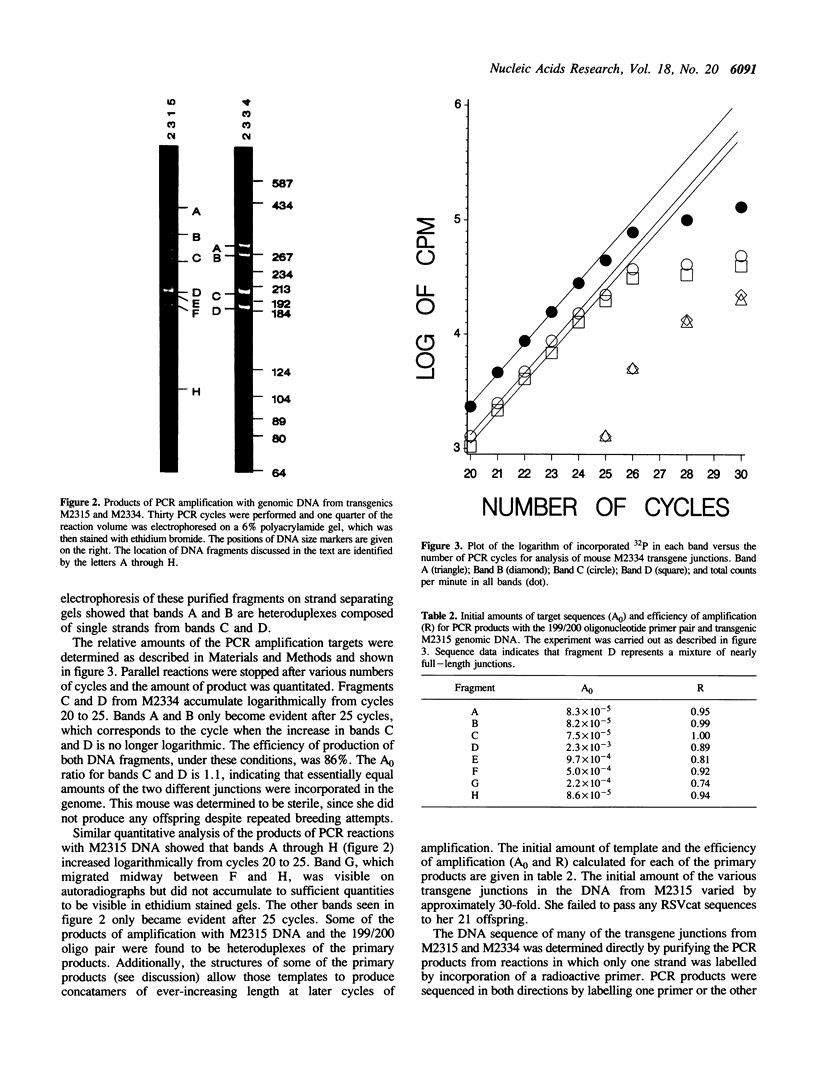
When microinjected foreign genes integrate into the genomes of mice, multiple copies are frequently found clustered together at one location. How they concatamerize--by the integration of large linearized concatamers that are formed by simple end-to-end linkage, by circularization of individual DNA fragments and recombination, or by some other means--is not understood. In the transgenic animals studied thus far by ourselves and others, integration frequency and transgene copy number do not seem to be significantly influenced by the complementarity of the ends of the DNA fragments that have been microinjected. We have utilized PCR amplification and DNA sequence analysis to study selected transgene junctions at the nucleotide level. In two transgenic mice carrying the synthetic RSVcat gene (injected with noncomplementary overhangs on the fragment ends), ends were 'nibbled' from 1 to 62 bases before being joined to an adjacent gene copy. Repeated dinucleotides, providing the most minimal of homologies, are present in half of the characterized junctions. Determination of the relative copy number of the junctions in each mouse supports the idea that transgene complexes can undergo additional rearrangements after the initial formation event.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Been M. D., Burgess R. R., Champoux J. J. Nucleotide sequence preference at rat liver and wheat germ type 1 DNA topoisomerase breakage sites in duplex SV40 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3097–3114. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya A., Lilley D. M. The contrasting structures of mismatched DNA sequences containing looped-out bases (bulges) and multiple mismatches (bubbles). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 12;17(17):6821–6840. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.17.6821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Smith P. Mechanism of chromosomal integration of microinjected DNA. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Aug;6(4):283–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M., Senear A. W., Warren R., Palmiter R. D. Somatic expression of herpes thymidine kinase in mice following injection of a fusion gene into eggs. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90376-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock P., Champoux J. J., Botchan M. Association of crossover points with topoisomerase I cleavage sites: a model for nonhomologous recombination. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):954–958. doi: 10.1126/science.2997924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canning S., Dryja T. P. Short, direct repeats at the breakpoints of deletions of the retinoblastoma gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5044–5048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Kaplan J. C., Maire P., Gautron S., Kahn A. Transcription of the dystrophin gene in human muscle and non-muscle tissue. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):858–860. doi: 10.1038/333858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias L., Nishida Y., Mintz B. Early postimplantation embryo lethality due to DNA rearrangements in a transgenic mouse strain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6020–6024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias L., Nishida Y., Terao M., D'Eustachio P., Mintz B. Cellular DNA rearrangements and early developmental arrest caused by DNA insertion in transgenic mouse embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2243–2247. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Wong E. A., Wahl G., Capecchi M. R. Patterns of integration of DNA microinjected into cultured mammalian cells: evidence for homologous recombination between injected plasmid DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1372–1387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. W., Scangos G. A., Plotkin D. J., Barbosa J. A., Ruddle F. H. Genetic transformation of mouse embryos by microinjection of purified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7380–7384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halligan B. D., Davis J. L., Edwards K. A., Liu L. F. Intra- and intermolecular strand transfer by HeLa DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3995–4000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. H., Griffith J. D. Deletions of bases in one strand of duplex DNA, in contrast to single-base mismatches, produce highly kinked molecules: possible relevance to the folding of single-stranded nucleic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Neumann R., Keyte J. Amplification of human minisatellites by the polymerase chain reaction: towards DNA fingerprinting of single cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):10953–10971. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.10953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khillan J. S., Overbeek P. A., Westphal H. Drosophila P element integration in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1985 May;109(1):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90365-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopchick J. J., Stacey D. W. Differences in intracellular DNA ligation after microinjection and transfection. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):240–246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., DuBridge R. B., Antell E. A., Greisen K. S., Calos M. P. Transfected DNA is mutated in monkey, mouse, and human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1951–1960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahon K. A., Overbeek P. A., Westphal H. Prenatal lethality in a transgenic mouse line is the result of a chromosomal translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1165–1168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhans A., Vartanian J. P., Wain-Hobson S. DNA recombination during PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1687–1691. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita S., Rizzuto R., Moraes C. T., Shanske S., Arnaudo E., Fabrizi G. M., Koga Y., DiMauro S., Schon E. A. Recombination via flanking direct repeats is a major cause of large-scale deletions of human mitochondrial DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):561–567. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Hammer R. E., Trumbauer M. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Birnberg N. C., Evans R. M. Dramatic growth of mice that develop from eggs microinjected with metallothionein-growth hormone fusion genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):611–615. doi: 10.1038/300611a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. DNA bending by the bulge defect. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4512–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells: role for short sequence homologies in the joining reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4295–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuldiner A. R., Nirula A., Roth J. Hybrid DNA artifact from PCR of closely related target sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4409–4409. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Kunes S. M., Schultz D. W., Taylor A., Triman K. L. Structure of chi hotspots of generalized recombination. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W. Special sites in generalized recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:7–24. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. F., Covarrubias L., Stewart T. A., Mintz B. Prenatal lethalities in mice homozygous for human growth hormone gene sequences integrated in the germ line. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):647–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Gudewicz T., Porter T., White A., Wilson J. H. How damaged is the biologically active subpopulation of transfected DNA? Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):387–398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie T. M., Palmiter R. D. Analysis of the integrant in MyK-103 transgenic mice in which males fail to transmit the integrant. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1646–1655. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang X., Benson K. F., Chada K. Mini-mouse: disruption of the pygmy locus in a transgenic insertional mutant. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):967–969. doi: 10.1126/science.2305264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura K., Miki T., Suzuki N., Ebihara T., Kawai K., Kumahara Y., Honjo T. Introduction of mouse C epsilon genes into Cos-7 cells and fertilized mouse eggs. J Biochem. 1985 Jan;97(1):333–339. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]