Abstract
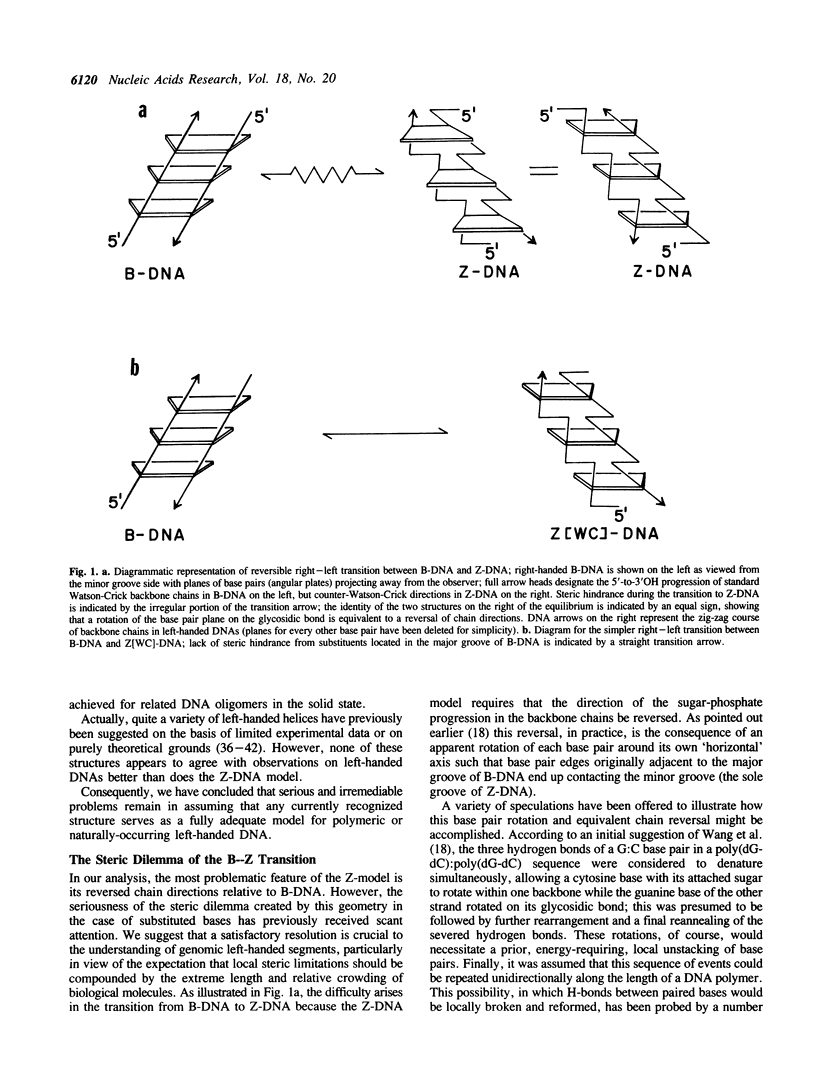
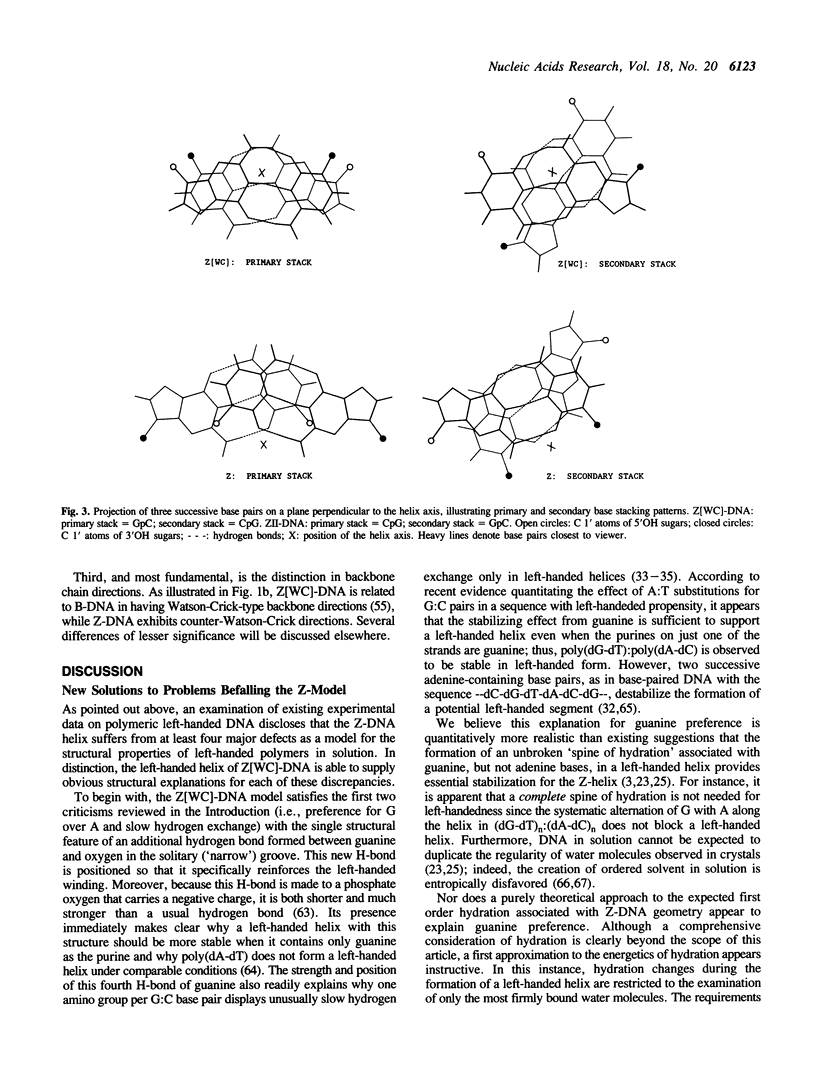
The structure of Z-DNA, currently accepted as a model for all left-handed DNAs, fails to provide convincing explanations for at least four well established properties of left-handed DNA polymers in solution. However, the major discrepancies between theory and experiment are resolved by the structure presently proposed for Z[WC]-DNA, a new left-handed, zig-zag double helix with Watson-Crick-type backbone directions. Structural features of Z[WC]-DNA include the presence of an additional H-bond between each guanine N2-amino group and an adjacent phosphate oxygen, the capacity to form four-stranded, base-matched complexes that should readily precipitate from solution, and backbone progressions that are the same as B-DNA (opposite to Z-DNA). However, since Z[WC]-DNA and Z-DNA have many parameters in common, they could be difficult to distinguish in a majority of existing experiments. In view of the close relationship of the new helix to B-DNA, which allows a relatively unhindered right-to-left transition in handedness, Z[WC]-DNA is theorized to be the left-handed structure preferentially generated in vivo by the torque available in naturally occurring DNA supercoils.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Birdsall D. L., Leslie A. G., Ratliff R. L. Left-handed DNA helices. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):743–745. doi: 10.1038/283743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effects of methylation on a synthetic polynucleotide: the B--Z transition in poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya D., Bansal M. Energetics of left and right handed models of DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Jun;4(6):1027–1040. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10507695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaho J. A., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA binding by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6082–6088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borah B., Cohen J. S., Bax A. Conformation of double-stranded polydeoxynucleotides in solution by proton two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser enhancement spectroscopy. Biopolymers. 1985 May;24(5):747–765. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castleman H., Hanau L. H., Zacharias W., Erlanger B. F. Z DNA and loop structures by immunoelectronmicroscopy of supercoiled pRW751, a plasmid containing left-handed helices. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3977–3996. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillès J. A., Neumann J. M., Tran-Dinh S., Huynh-Dinh T., d'Estaintot B. L., Igolen J. Influence of dA X dT and d(2aminoA) X dT base pairs on the B in equilibrium Z transition of DNA fragments. 1H-NMR study of d(C-G-C-A-m5C-G-T-G-m5C-G), d(m5C-G-C-A-m5C-G-T-G-C-G) and d(C-2aminoA-C-G-T-G). Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F. M. Effects of A:T base pairs on the B-Z conformational transitions of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2269–2281. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevrier B., Dock A. C., Hartmann B., Leng M., Moras D., Thuong M. T., Westhof E. Solvation of the left-handed hexamer d(5BrC-G-5BrC-G-5 BrC-G) in crystals grown at two temperatures. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):707–719. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. L., Kolpak F. J., Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. The tetramer d(CpGpCpG) crystallizes as a left-handed double helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4016–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R., Conner B. N., Wing R. M., Fratini A. V., Kopka M. L. The anatomy of A-, B-, and Z-DNA. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):475–485. doi: 10.1126/science.7071593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Conformation and dynamics in a Z-DNA tetramer. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 15;152(4):723–736. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H., Takano T., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. High-salt d(CpGpCpG), a left-handed Z' DNA double helix. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):567–573. doi: 10.1038/286567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison M. J., Feigon J., Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Wang A. H., Habener J. F., Rich A. An assessment of the Z-DNA forming potential of alternating dA-dT stretches in supercoiled plasmids. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3648–3655. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fersht A. R., Shi J. P., Knill-Jones J., Lowe D. M., Wilkinson A. J., Blow D. M., Brick P., Carter P., Waye M. M., Winter G. Hydrogen bonding and biological specificity analysed by protein engineering. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):235–238. doi: 10.1038/314235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Daune M. Physical studies on deoxyribonucleic acid after covalent binding of a carcinogen. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2659–2666. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Wang A. H., van der Marel G., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of (m5 dC-dG)3: the role of the methyl group on 5-methyl cytosine in stabilizing Z-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7879–7892. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney B. L., Marky L. A., Jones R. A. The influence of the purine 2-amino group on DNA conformation and stability. Synthesis and conformational analysis of d[T(2-aminoA)]3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4351–4361. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta G., Bansal M., Sasisekharan V. Conformational flexibility of DNA: polymorphism and handedness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6486–6490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta G., Bansal M., Sasisekharan V. Reversal of handedness in DNA: a stable link between RU and LZ helices. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 31;97(4):1258–1267. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann B., Ramstein J., Leng M. Slow exchanging protons in the Z-form of G-C and A-C alternating polymers by using a rapid dialysis method. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. C. DNA structural dynamics: longitudinal breathing as a possible mechanism for the B in equilibrium Z transition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4867–4878. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingerty B., Broyde S. Conformation of the deoxydinucleoside monophosphate dCpdG modified at carbon 8 of guanine with 2-(acetylamino)fluorene. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3243–3252. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. C. Alternative description of the transition between B-DNA and Z-DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):129–131. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. C. Deoxyribonucleic acid structure: a new model. Science. 1981 Jan 16;211(4479):289–291. doi: 10.1126/science.7444467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. C. Transitions between B-DNA and Z-DNA: a dilemma. J Theor Biol. 1983 Apr 7;101(3):327–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(83)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaworski A., Hsieh W. T., Blaho J. A., Larson J. E., Wells R. D. Left-handed DNA in vivo. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):773–777. doi: 10.1126/science.3313728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., McIntosh L. P., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Zarling D. A., Robert-Nicoud M., van de Sande J. H., Jorgenson K. F., Eckstein F. Left-handed DNA: from synthetic polymers to chromosomes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):21–57. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., van de Sande J. H., Zarling D. A., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Eckstein F., Füldner H. H., Greider C., Grieger I., Hamori E., Kalisch B. Generation of left-handed Z-DNA in solution and visualization in polytene chromosomes by immunofluorescence. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):143–154. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUZMANN W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang D. S., Harvey S. C., Wells R. D. Diepoxybutane forms a monoadduct with B-form (dG-dC)n.(dG-dC)n and a crosslinked diadduct with the left-handed Z-form. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5645–5656. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Angelides K. J., Holloman W. K. Left-handed DNA and the synaptic pairing reaction promoted by Ustilago rec1 protein. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Holloman W. K. Synapsis promoted by Ustilago rec1 protein. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):593–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriek E., Miller J. A., Juhl U., Miller E. C. 8-(N-2-fluorenylacetamido)guanosine, an arylamidation reaction product of guanosine and the carcinogen N-acetoxy-N-2-fluorenylacetamide in neutral solution. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):177–182. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kłysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Wells R. D. Left-handed DNA. Cloning, characterization, and instability of inserts containing different lengths of (dC-dG) in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10152–10158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean M. J., Lee J. W., Wells R. D. Characteristics of Z-DNA helices formed by imperfect (purine-pyrimidine) sequences in plasmids. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7378–7385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirau P. A., Kearns D. R. Unusual proton exchange properties of Z-form poly[d(G-C)]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1594–1598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. W., Forbes D. J. The nucleus: structure, function, and dynamics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:535–565. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Peck L. J., Lafer E. M., Stollar B. D., Wang J. C., Rich A. Supercoiling and left-handed Z-DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):93–100. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. The sequence (dC-dA)n X (dG-dT)n forms left-handed Z-DNA in negatively supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1821–1825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson W. K., Srinivasan A. R., Marky N. L., Balaji V. N. Theoretical probes of DNA conformation examining the B leads to Z conformational transition. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):229–241. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Nordheim A., Rich A., Wang J. C. Flipping of cloned d(pCpG)n.d(pCpG)n DNA sequences from right- to left-handed helical structure by salt, Co(III), or negative supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4560–4564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C., Nordheim A., Rich A. Rate of B to Z structural transition of supercoiled DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 5;190(1):125–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poverenny A. M., Kiseleva V. I., Tyaglov B. V., Permogorov V. I. B-Z transition in poly(dG-dC).poly(dG-dC) in the presence of formaldehyde amino derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80707-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaswamy N., Bansal M., Gupta G., Sasisekharan V. Left-handed helices for DNA: studies on poly[d(I-C)]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6109–6113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramstein J., Leng M. Salt-dependent dynamic structure of poly(dG-dC) x poly(dG-dC). Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):413–414. doi: 10.1038/288413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage E., Leng M. Conformational changes of poly(dG-dC) . poly(dG-dC) modified by the carcinogen N-acetoxy-N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1241–1250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santella R. M., Grunberger D., Nordheim A., Rich A. N-2-Acetylaminofluorene modification of poly(dG-m5dC) . poly(dG-m5dC) induces the Z-DNA conformation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1226–1232. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santella R. M., Grunberger D., Weinstein I. B., Rich A. Induction of the Z conformation in poly(dG-dC).poly(dG-dC) by binding of N-2-acetylaminofluorene to guanine residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1451–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma M. H., Gupta G., Dhingra M. M., Sarma R. H. During B-Z transition there is no large scale breakage of Watson-Crick base pairs. A direct demonstration using 500 MHz 1H NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):59–81. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Klysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA is induced by supercoiling in physiological ionic conditions. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):312–316. doi: 10.1038/299312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. DNA supercoiling: another level for regulating gene expression. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaralingam M., Sekharudu Y. C. Water-inserted alpha-helical segments implicate reverse turns as folding intermediates. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1333–1337. doi: 10.1126/science.2734612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran-Dinh S., Taboury J., Neumann J. M., Huynh-Dinh T., Genissel B., Langlois d'Estaintot B., Igolen J. 1H NMR and circular dichroism studies of the B and Z conformations of the self-complementary deoxyhexanucleotide d(m5C-G-C-G-m5-C-G): mechanism of the Z-B-coil transitions. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 27;23(7):1362–1371. doi: 10.1021/bi00302a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Hakoshima T., van der Marel G., van Boom J. H., Rich A. AT base pairs are less stable than GC base pairs in Z-DNA: the crystal structure of d(m5CGTAm5CG). Cell. 1984 May;37(1):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90328-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. J., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., van der Marel G., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Left-handed double helical DNA: variations in the backbone conformation. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):171–176. doi: 10.1126/science.7444458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Brennan R., Chapman K. A., Goodman T. C., Hart P. A., Hillen W., Kellogg D. R., Kilpatrick M. W., Klein R. D., Klysik J. Left-handed DNA helices, supercoiling, and the B-Z junction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D. Unusual DNA structures. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1095–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig B., Dorbic T., Rich A. The level of Z-DNA in metabolically active, permeabilized mammalian cell nuclei is regulated by torsional strain. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):755–764. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



