Abstract
Knee forces are highly significant in osteoarthritis and in the survival and function of knee arthroplasty. A large number of studies have attempted to estimate forces around the knee during various activities. Several approaches have been used to relate knee kinematics and external forces to internal joint contact forces, the most popular being inverse dynamics, forward dynamics, and static body analyses. Knee forces have also been measured in vivo after knee arthroplasty, which serves as valuable validation of computational predictions. This review summarizes the results of published studies that measured knee forces for various activities. The efficacy of various methods to alter knee force distribution, such as gait modification, orthotics, walking aids, and custom treadmills are analyzed. Current gaps in our knowledge are identified and directions for future research in this area are outlined.
Keywords: Knee forces, modeling, in vivo, arthritis, arthroplasty
1 INTRODUCTION
The knee is an important load-bearing joint, which is distinct from the other major load-bearing joints in that soft tissues rather than articular shape are the major stabilizing factors [1]. Other important differences are the division of the joint into three compartments (two tibiofemoral and one patellofemoral) and the presence of menisci, which contribute significantly in the transfer of contact stresses from one articular surface to another [2]. While the patellofemoral joint is an important component of the knee, tibiofemoral forces are the primary focus of this review.
1.1. Knee forces and joint disease
Forces transmitted by the knee joint are of great clinical significance. Obesity, which increases the overall magnitude of loads across the knee, is associated with an increased incidence of osteoarthritis as well as accelerated progression of the disease [3–8]. Forces transmitted across the knee joint during normal walking range between 2 and 3 times body weight. This is in part due to the kinetics of acceleration, the high moments generated at the knee, and simultaneous contraction of multiple muscles. Therefore the net effect of each additional kilogram in body weight is multiplied 2 or 3 times at the knee. Malalignment of the lower extremity, which overloads one compartment at the expense of another, is also associated with progression of osteoarthritis [9–11]. Motion analysis studies, which calculate the external moments of the knee, have correlated an increased peak adduction moment at the knee with pain, radiographic progression, and biomarkers of disease severity [3, 12–15]. While these changes in adduction moment are subtle, as little as 3 to 5° of increased tibial varus alignment can induce a 50% increase in the force transmitted across the medial tibiofemoral compartment [16].
1.2. Knee arthroplasty
The only effective treatment for end-stage arthritis is knee arthroplasty. Knee forces are even more important after arthroplasty because unlike biological tissues, the materials used in knee replacement do not regenerate or remodel. Knee forces are therefore directly implicated in articular wear and damage (especially to the polyethylene component). Contact stresses on the bearing surfaces are a function of the magnitude of contact force, local material properties, and articular conformity [17]. Contact stresses are directly linked to the wear and damage of polyethylene, which is the most common bearing of the tibial articulation [17–20]. Tibiofemoral contact forces are transmitted to the underlying bone. High stresses in the bone, as a result of high tibiofemoral forces or malaligned forces, increase the risk for bone fatigue damage [16, 21]. As little as 10–20% change in the mediolateral distribution of axial tibiofemoral load can increase the volume of bone subjected to cyclic strain of greater than 0.4%, which is the threshold for fatigue damage [16, 22].
1.3. Calculation and measurement of forces
The computation of knee forces has received much attention. Modeling approaches have varied from two dimensional to three dimensional, with and without the simulation of contact, with and without soft tissues, with and without accounting for muscle cocontraction, and antagonistic effects. The inverse dynamics approach, uses experimentally measured motion analysis and external reaction forces to calculate the forces and moments about the joint [23]. Muscle forces are then derived to balance joint moments and their contribution to total joint forces computed. The forward dynamics approach uses muscle activations and forces to directly predict kinematics, which are then compared with measured kinematics for validation.
The major obstacles to accurate modeling of the knee are (1) the complexity of the geometry of the articulating surface, (2) the multiaxial forces and kinematics, (3) the importance of passive soft tissues in maintaining stability, (4) the fact that more than one muscle performs the same action, (5) the fact that several of the major muscles that act on the knee joint also act on the hip and the ankle, and (6) the complexity of determining the location of the resultant contact force. Compounding these hurdles is the complexity of analyzing motion, even for a common activity such as walking.
An alternative to computational prediction of knee forces is the direct measurement of knee forces. Advances in smart implant technology and telemetry systems have made measurement possible in vivo in patients receiving total knee arthroplasty. This article is a concise review of studies that have measured knee forces, the specific goals being to summarize the results, to establish the clinical significance of knee forces, and to suggest future research directions.
2 COMPUTATIONAL PREDICTION OF KNEE FORCES
A large number of studies have attempted to estimate forces around the knee during various activities. Several approaches have been used to relate knee kinematics and external forces to internal joint contact forces, the most popular being inverse dynamics, forward dynamics, and static body analyses [24–34]. A major challenge for most musculoskeletal joints in general and the knee in particular is the problem of redundant muscles that makes it difficult to find unique solutions for knee forces. EMG-driven and optimization methods have commonly been used to resolve this issue [26, 34–36].
The diversity of approaches, solution algorithms, and modeling assumptions has led to wide differences in predictions even for the same activities. Among the open kinetic chain activities, isokinetic knee extension has been studied for its relative simplicity for modeling. A two-dimensional static analysis of maximum voluntary isokinetic knee extension with a single quadriceps muscle estimated peak tibiofemoral compressive forces up to 9 times body weight (×BW) [24]. At the other end of the spectrum, a two-dimensional inverse dynamics model using a linear optimization algorithm to solve for the distribution of synergistic muscle forces estimated peak compressive forces of only 4 ×BW during maximal voluntary effort [25].
Examples of divergent predictions can be found for several activities. When comparing open kinetic chain to closed kinetic chain knee extension, a static free-body analysis in the sagittal plane predicted maximum compressive forces of 5 ×BW during an open kinetic chain extension exercise and 4.5 ×BW during a closed kinetic chain extension exercise [37]. On the other hand, a three-dimensional inverse dynamics model utilizing motion analysis, force plates, and EMG (quadriceps, hamstrings and gastrocnemius) estimated higher knee forces during the closed kinetic chain task (peaking at an average of 6.7 and 6.3 ×BW for the squat and leg press, respectively) compared to 5 ×BW for open chain knee extension [26]. Peak forces generated during squatting without resistance were estimated at 4.2 ×BW [27], while forces calculated at maximum flexion were 2.8 and 3.8 ×BW for squatting with heels down and heels up, respectively [28].
Although walking is a common activity, it is complex to model. The earliest report of predicting forces during walking simplified the problem by grouping muscles based on similar function, which reported peak forces that averaged 3 ×BW [29, 30]. Other reports that grouped muscles with similar function have reported peak forces in the range of 1.7 and 2.4 ×BW [31, 32]. Use of an objective function that minimized total forces and moments to solve the redundancy problem resulted in peak force predictions approaching 7 ×BW [33]. Tibiofemoral contact forces were sensitive to the quantities being minimized and varied between 4 to 6 ×BW during level walking[34].
The broad range of differences in estimated peak tibiofemoral contact forces emphasizes the need for experimental validation. All of the above-mentioned studies made several assumptions that have yet to be validated. Anthropometric measurements are particularly important when defining the attachments and wrapping of muscles. Measuring specific attachment points and vectors of action are often challenging. Due to the large muscle force to moment arm ratios around the knee, small errors in estimated or measured directions of muscle line of action can lead to large differences in estimated moments. An accurate determination of tibiofemoral contact position may also be essential but is difficult to measure. In vivo measurement of tibial compressive forces therefore provides an invaluable means of validating such models.
3 EXPERIMENTAL MEASUREMENT OF KNEE FORCES
3.1. In Vitro: Intact knee
Early attempts at measuring tibiofemoral forces in vitro (in cadavers) involved inserting a steel plate between the tibial plateau and the tibial tubercle connected to a vertical intramedullary shaft that was instrumented with strain gauges to measure compressive forces [38]. Predicted knee forces using a two-dimensional static free-body analysis of the loaded knee were within 6% of experimental measurements. Later studies used nested cylinders supporting the transected tibial plateau to measure multiaxial forces and moments in cadavers. These studies reported differences in anteroposterior shear force during a closed chain knee extension with transection of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments [39].
3.2. In Vitro: Knee arthroplasty
Tibiofemoral forces have been measured in vitro after total knee arthroplasty using an instrumented tibial tray. The tibial tray was split into upper and lower halves that were connected by four posts [40]. Strain gages, below the posts in the lower half, measured compression forces. By monitoring forces in the four quadrants, the total compressive force and center of pressure could be accurately measured, which also yielded the mediolateral distribution of tibiofemoral force. This instrumented tray was coupled with a telemetry system [41], demonstrating proof of concept that knee forces could be captured wirelessly in vivo [42]. A second-generation tibial tray that could measure all six components of force was later developed [43].
3.3. In Vivo
Knee forces in intact normal human knees have yet to be measured in vivo. In canine knees “sensate” scaffolds have been implanted to measure in vivo loads. These are synthetic scaffolds designed to fill an osteochondral defect that have been instrumented with strain gauges and a telemetry system to monitor tibiofemoral contact forces in otherwise intact knees [44, 45]. In a human subject, a distal femoral tumor replacement prosthesis was instrumented to measure femoral shaft forces in vivo [46, 47]. Femoral shaft forces were used to calculate knee forces in the rotating hinged knee component. Peak knee forces reported were 2.8 ×BW for walking, 2.8 ×BW for stair ascent, 3.1 ×BW for stair descent, and 3.6 ×BW for jogging.
The first direct measurement of in vivo tibial forces after a primary total knee arthroplasty was in 2004 [48, 49]. This “first-generation” design measured axial loads at four quadrants of the tibial tray from which the total force and net center of pressure were obtained. A “second-generation” tibial component was later designed and implanted in which all six components of force acting on the tibial tray were measured [43, 50, 51]. A different six-component knee arthroplasty design was also implanted by the team led by Georg Bergmann [52, 53]. In the early postoperative period, peak axial contact forces during walking increased substantially over the first three weeks peaking at 2.8 ×BW by the one year follow up [48, 53]. Stair descent generated higher forces (3.2 to 3.5 ×BW) than stair ascent (2.9 to 3.0 ×BW). These early results were further substantiated in a cohort of five patients [54].
4 VARIATION OF KNEE FORCES BY ACTIVITY
Knee forces have been reported in vivo for a variety of activities including recreation and exercise [51]. Peak tibial forces by activity have been summarized in Table 1. Walking on the treadmill at speeds up to 3 miles per hour generated lower peak tibial forces relative to walking on the laboratory floor. Power walking on the treadmill (at 4 miles/hour) generated higher peak tibial forces. Jogging is a high-impact activity that generated peak forces of 3.6 ×BW in two subjects implanted with instrumented distal femoral tumor replacement prostheses [46]. In subjects implanted with a primary knee arthroplasty design, jogging generated higher forces probably due to more intact musculature around the knee relative to the more extensive tissue resection required for tumor replacement surgery.
Table 1.
Activities of daily living
| Activity | Peak Tibial Forces (×BW) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Walking [48–51, 54] | 2.5 – 2.8 | Laboratory floor |
| Treadmill Walking [51] | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 1 to 3 miles per hour |
| Power walking [51] | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 4 miles per hour on treadmill |
| Jogging [46] | 3.1 – 3.6 | Tumor replacement prosthesis |
| Jogging [51] | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 5 miles per hour on treadmill |
| Stationary Bicycling [51] | 1.0 – 1.5 | Level 1–5; 60–90 rpm |
| Golf (lead knee) [51] | 4.4 ± 0.1 | Left knee in a right handed golfer |
| Golf (trailing knee) [51] | 3.0 ± 0.2 | |
| Tennis serve [51] | 4.2 ± 0.1 | |
| Tennis forehand [51] | 4.3 ± 0.4 | |
| Tennis backhand [51] | 3.5 ± 0.6 | |
| StairMaster Level 1 [51] | 2.4 ± 0.1 | |
| StairMaster Level 3[51] | 3.3 ± 0.3 | |
| Elliptical Level 1[51] | 2.3 ± 0.2 | |
| Elliptical Level 11[51] | 2.2 ± 0.3 | |
| Leg Press [51] | 2.8 ± 0.1 | Foot reaction force = 1 ×BW |
| Knee Extension [51] | 1.5 ± 0.0 | Resistance = 0.2 ×BW |
| Rowing machine [51] | 0.9 ± 0.1 |
Overall, stationary bicycling generated even lower knee forces than walking [51]. Tennis, also considered a high-impact activity, generated high knee forces in the same range as treadmill jogging. The golf swing, although considered a low impact activity, generated high peak tibial forces in the leading knee approaching those of jogging. Elliptical trainers, a low-impact exercise machine, are often recommended for patients who experience knee pain during higher impact jogging. Elliptical training generated forces comparable to treadmill walking. Rowing machines, often recommended to increase knee flexion, generated low forces. Both the leg press (against a resistance force equal to body weight) and the squat generated the same peak tibial forces. The leg-press machine can therefore be recommended to build up to a squat, if a full weight-bearing squat is not possible.
Given the wide variation in knee forces predicted by computer models for the same activity, it is not surprising that many of these predictions differed from experimental measurements. Mathematical predictions of walking ranged from 1.7 to 7 ×BW [29–34] while experimental measurements were between 2 and 3 ×BW. Predictions of forces for other activities face similar challenges. For example, a closed kinetic chain activity such as a leg press is predicted to generate between 4 and 6 ×BW, while that measured in patients averaged less than 3 ×BW. These comparisons do not serve to directly validate the computer models that predicted forces more accurately, since one cannot rule out serendipitous coincidence. For more robust validation, predictions under diverse conditions specifically designed to test major modeling assumptions or simplifications are required. Also, predictions that modeled younger subjects with intact joints cannot be directly compared to older subjects with artificial knee joints. For a more direct and unbiased assessment of modeling methodology, we are hosting an annual open “Grand Challenge Competition to Predict In Vivo Knee Loads”. Entire datasets of subject anthropometrics, motion analysis, ground reactions forces, and EMG required for predicting tibiofemoral forces during specific activities are released publicly the preceding year. Experimental measurements of tibiofemoral forces and the accuracy of predictions are only revealed at the Summer Bioengineering Conference of the ASME.
5 THERAPEUTIC MODULATION OF KNEE FORCES
5.1. Gait modifications
Knee forces have a substantial impact on joint degeneration, injury, and arthritis. The strong link between knee forces and osteoarthritis has led to interest in gait modifications to reduce the medial compartmental force or “offload” the medial compartment. The peak external knee adduction moment has been linked to pain, severity, and rate of progression of arthritis [12–14, 55]. Thus, altering the pattern of gait to reduce external adduction moment may “offload” the medial compartment and delay the progression of medial compartmental disease. By monitoring the mediolateral distribution of tibial forces in vivo, a “medial thrust” gait in which the knee is deliberately medialized was shown to reduce the external adduction and effectively reduce medial loads on the tibia by 7% to 28% [56, 57].
5.2. Walking Aids
The use of walking aids such as canes, crutches, or walkers is often recommended to alleviate pain caused by osteoarthritis of the hip and knee. These aids can form an important component of non-pharmacologic and non-surgical treatment. Walking with hiking poles is sometimes recommended to stabilize moments in the frontal plane [58]. Hiking poles can reduce in vivo medial compartmental forces by 15% to 45% [56]. Even more significantly, walking poles reduced the total tibial contact force presumably due to partial transfer of ground reaction force to the walking poles [56].
A cane is a very convenient walking aid and the efficacy of a cane in reducing hip moments and forces has been documented [59]. A cane reduced peak vertical forces measured using foot pressure sensors [60]. A cane in the contralateral hand resulted in lower shoe forces than one in the ipsilateral hand [61]. Indirect evidence through inverse dynamics analysis suggests that a cane in the contralateral hand reduces external knee adduction moments during gait analysis [62]. We therefore decided to directly measure forces at the knee in vivo to assess the magnitude of any beneficial effect of cane usage.
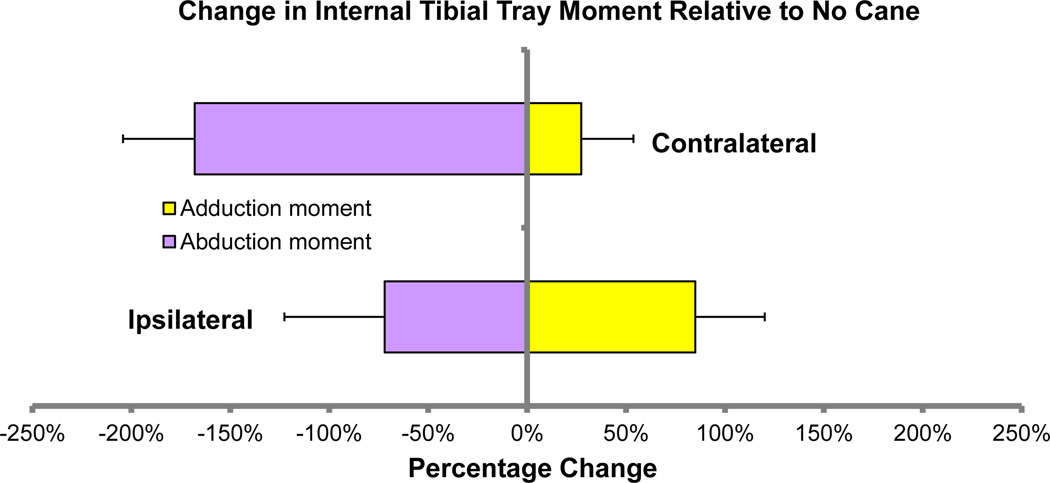
Tibial forces and moments were recorded in vivo in subjects (N = 3) previously implanted with an instrumented tibial prosthesis [51] while walking with and without a cane. The trials included walking with no cane, walking with a cane in the ipsilateral hand (same side as the implanted knee), and walking with cane in the contralateral hand (opposite side as the implanted knee). Multiple cycles (10–15 cycles) were averaged into one representative gait cycle for each condition for each subject. Peak tibial axial force and peak adduction and abduction moments on the tibial tray were recorded. The mean peak axial tibial force (Fz) was between 2 and 3 times body weight for all the gait conditions and did not appear to change consistently with or without the use of a cane. The mean peak internal abduction moments on the tibial tray were higher (range 0.19 to 1.27 percent body weight times height [%BW*HT]) when the cane was held in the hand on the same side as the implanted knee when compared to the contralateral side (range 0.02 to 0.96 %BW*HT). The mean peak internal adduction moments on the tibial tray with the cane in the contralateral hand ranged between −0.18 to −0.78 times %BW*HT compared to −0.09 to −0.38 times %BW*HT with the cane in the ipsilateral hand. Walking with a cane in the contralateral hand decreased peak adduction moment by an average of 43% relative to walking without the cane. Walking with a cane in the ipsilateral hand increased the mean peak adduction moment by an average of 9% (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Walking with a cane in the contralateral hand decreased the average peak adduction moment relative to walking without a cane. Walking with a cane in the ipsilateral hand increased the mean peak adduction moment.
A previous study found differences in external knee moments generated during cane usage in osteoarthritic patients [62]. External knee adduction moments were significantly higher with ipsilateral cane usage relative to unaided gait or contralateral usage. Measurements of adduction moments at the tray are consistent with these results. Proper use of a cane can significantly reduce the adduction moment, which provides biomechanical validation of the use of a walking aid in the conservative management of painful osteoarthritis.
5.3. Shoe orthotics
Medial compartmental osteoarthritis has been linked to varus knee alignment and to increased external adduction moment at the knee [14, 15, 63, 64]. Orthotics such as shoe wedges, insoles, and ankle-foot orthoses have been used to alter the mechanical alignment of the knee via the ankle with the objective of reducing the external knee adduction moment [65]. Biomechanically, a laterally based wedge in the sole of the shoe can generate an abduction moment or can reduce the net adduction moment at the knee [66, 67]. However, not all studies report successful changes in adduction moment [65, 68]. Further, the magnitude of any internal change in in vivo medial joint loading has not been documented. A variable stiffness shoe has been designed that simulates the effect of a dynamic lateral wedge with less subjective discomfort than a static wedge [69]. Since the lateral half of the sole is stiffer than the medial half, the medial sole compresses more on weight bearing, producing a similar effect as a lateral shoe. A variable stiffness shoe reduced the peak external adduction moment of the knee in subjects with medial compartmental osteoarthritis [70]. In a subsequent study, which measured in vivo tibial forces, medial compartment joint contact force was also reduced compared to wearing a shoe without the variable stiffness sole [71]. The change in first peak of the external knee adduction moment was also significantly correlated with the change in first peak of medial contact force. In vivo monitoring of knee forces can therefore validate some of the claims that shoe orthotics can alter the distribution of forces in the knee.
5.4. Reduction in ground reaction forces
Lower body-positive pressure chambers have been used as a novel method of reducing net ground reaction forces [72, 73]. Placing a treadmill inside a pressurized chamber reduces the effect of gravity during walking. Briefly, the patient is positioned with his or her lower body within the chamber. A neoprene seal at the waist maintains the pressure differential between the lower and upper body. A positive pressure (i.e., higher pressure within the chamber) lifts the patient and reduces the ground reaction force on the treadmill, thus countering the effect of gravity. The pressure can be controlled to generate the desired amount of reduction in ground reaction force. Lower body positive pressure was effective at reducing ground reaction forces and provided significant postoperative pain relief during ambulation after anterior cruciate reconstruction [72]. Lower body negative pressure increases the ground reaction forces and has been shown to be effective in countering weightlessness-induced bone loss [74, 75]. We monitored knee forces in vivo and compared the reduction in knee forces with the reduction in ground reaction forces [76]. Peak tibial forces correlated with peak ground reaction forces. However, even at pressure settings that reduced ground reaction force to 10%, peak tibial forces remained above 0.5 ×BW.
6 SUMMARY OF FUTURE DIRECTIONS
Experimentally and clinically measured forces provide much needed experimental validation of past and current estimates generated by computer models. Knowledge of forces in the knee provides the clinician with quantitative data to make informed decisions regarding the prevention and treatment of knee injury. Knee forces can also be used to drive computer models that predict outcomes that cannot be readily measured in vivo such as stress distributions, ligament and muscle forces, wear, damage, and remodeling. Clinical force measurements have been made in a limited number of patients with knee replacements. Extrapolation of these forces to a larger patient population or different age groups has to be validated. We are working to develop a commercially viable instrumented prosthesis. A major challenge is establishing safety across a diverse patient population using a prosthesis with sensors and electronics. Other challenges include developing of a low cost, efficient, and durable power source. Remote unsupervised monitoring and continuous data logging are highly attractive but require development of robust data acquisition systems that can be operated by patients and a strategy to manage the bandwidth of real time data as well as the storage and processing of existing data. A major unmet need is measurement of patellofemoral forces. The patellofemoral joint is an important component of the knee and biomechanical dysfunction contributes significantly to disease. Major technological advances are required to measure knee forces in normal intact joints. The current bottlenecks are primarily safety and durability of implantable sensors. Noninvasive methods of measuring forces have yet to be explored, but, if successful, will have a great impact on the field.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded by the Shiley Center for Orthopaedic Research and Education at Scripps Clinic and by the National Institutes of Health under grant numbers R01 EB009351 and R21 AR057561
REFERENCES
- 1.Gray H. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 40th ed. Elsevier: Churchill-Livingstone; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 2.McDermott ID, Amis AA. The consequences of meniscectomy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(12):1549–1556. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.88B12.18140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Amin S, Luepongsak N, McGibbon CA, LaValley MP, Krebs DE, Felson DT. Knee adduction moment and development of chronic knee pain in elders. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;51(3):371–376. doi: 10.1002/art.20396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Felson DT, Zhang Y, Hannan MT, Naimark A, Weissman B, Aliabadi P, Levy D. Risk factors for incident radiographic knee osteoarthritis in the elderly: the Framingham Study. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40(4):728–733. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Roemer FW, Zhang Y, Niu J, Lynch JA, Crema MD, Marra MD, Nevitt MC, Felson DT, Hughes LB, El-Khoury GY, Englund M, Guermazi A. Tibiofemoral joint osteoarthritis: risk factors for MR-depicted fast cartilage loss over a 30-month period in the multicenter osteoarthritis study. Radiology. 2009;252(3):772–780. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2523082197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Naimark A, Walker AM, Meenan RF. Obesity and knee osteoarthritis. The Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med. 1988;109(1):18–24. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-1-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Blagojevic M, Jinks C, Jeffery A, Jordan KP. Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(1):24–33. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2009.08.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Niu J, Zhang YQ, Torner J, Nevitt M, Lewis CE, Aliabadi P, Sack B, Clancy M, Sharma L, Felson DT. Is obesity a risk factor for progressive radiographic knee osteoarthritis? Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61(3):329–335. doi: 10.1002/art.24337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sharma L, Lou C, Felson DT, Dunlop DD, Kirwan-Mellis G, Hayes KW, Weinrach D, Buchanan TS. Laxity in healthy and osteoarthritic knees. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42(5):861–870. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199905)42:5<861::AID-ANR4>3.0.CO;2-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sharma L, Song J, Felson DT, Cahue S, Shamiyeh E, Dunlop DD. The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. JAMA. 2001;286(2):188–195. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tanamas S, Hanna FS, Cicuttini FM, Wluka AE, Berry P, Urquhart DM. Does knee malalignment increase the risk of development and progression of knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61(4):459–467. doi: 10.1002/art.24336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Thorp LE, Sumner DR, Wimmer MA, Block JA. Relationship between pain and medial knee joint loading in mild radiographic knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57(7):1254–1260. doi: 10.1002/art.22991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Prodromos CC, Andriacchi TP, Galante JO. A relationship between gait and clinical changes following high tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67(8):1188–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sharma L, Hurwitz DE, Thonar EJ, Sum JA, Lenz ME, Dunlop DD, Schnitzer TJ, Kirwan-Mellis G, Andriacchi TP. Knee adduction moment, serum hyaluronan level, and disease severity in medial tibiofemoral osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(7):1233–1240. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199807)41:7<1233::AID-ART14>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Baliunas AJ, Hurwitz DE, Ryals AB, Karrar A, Case JP, Block JA, Andriacchi TP. Increased knee joint loads during walking are present in subjects with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10(7):573–579. doi: 10.1053/joca.2002.0797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wong J, Steklov N, Patil S, Flores-Hernandez C, Kester M, Colwell CW, Jr, D'Lima DD. Predicting the effect of tray malalignment on risk for bone damage and implant subsidence after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2010;29(3):347–353. doi: 10.1002/jor.21221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.D'Lima DD, Chen PC, Colwell CW., Jr Polyethylene contact stresses, articular congruity, and knee alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;392:232–238. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200111000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fregly BJ, Sawyer WG, Harman MK, Banks SA. Computational wear prediction of a total knee replacement from in vivo kinematics. J Biomech. 2005;38(2):305–314. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2004.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McEwen HM, Barnett PI, Bell CJ, Farrar R, Auger DD, Stone MH, Fisher J. The influence of design, materials and kinematics on the in vitro wear of total knee replacements. J Biomech. 2005;38(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2004.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Knight LA, Pal S, Coleman JC, Bronson F, Haider H, Levine DL, Taylor M, Rullkoetter PJ. Comparison of long-term numerical and experimental total knee replacement wear during simulated gait loading. J Biomech. 2007;40(7):1550–1558. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2006.07.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cristofolini L, Affatato S, Erani P, Leardini W, Tigani D, Viceconti M. Long-term implant-bone fixation of the femoral component in total knee replacement. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(3):319–331. doi: 10.1243/09544119JEIM328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pattin CA, Caler WE, Carter DR. Cyclic mechanical property degradation during fatigue loading of cortical bone. J Biomech. 1996;29(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(94)00156-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Otten E. Inverse and forward dynamics: models of multi-body systems. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2003;358(1437):1493–1500. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2003.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nisell R, Ericson MO, Nemeth G, Ekholm J. Tibiofemoral joint forces during isokinetic knee extension. Am J Sports Med. 1989;17(1):49–54. doi: 10.1177/036354658901700108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kaufman KR, An KN, Litchy WJ, Morrey BF, Chao EY. Dynamic joint forces during knee isokinetic exercise. Am J Sports Med. 1991;19(3):305–316. doi: 10.1177/036354659101900317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wilk KE, Escamilla RF, Fleisig GS, Barrentine SW, Andrews JR, Boyd ML. A comparison of tibiofemoral joint forces and electromyographic activity during open and closed kinetic chain exercises. Am J Sports Med. 1996;24(4):518–527. doi: 10.1177/036354659602400418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shelburne KB, Pandy MG. A dynamic model of the knee and lower limb for simulating rising movements. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2002;5(2):149–159. doi: 10.1080/10255840290010265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Smith SM, Cockburn RA, Hemmerich A, Li RM, Wyss UP. Tibiofemoral joint contact forces and knee kinematics during squatting. Gait & posture. 2008;27(3):376–386. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2007.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Morrison JB. Bioengineering analysis of force actions transmitted by the knee joint. Biomed Eng. 1968;3(4):164–170. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Morrison JB. The mechanics of the knee joint in relation to normal walking. J Biomech. 1970;3(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(70)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Komistek RD, Kane TR, Mahfouz M, Ochoa JA, Dennis DA. Knee mechanics: a review of past and present techniques to determine in vivo loads. J Biomech. 2005;38(2):215–228. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2004.02.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Komistek RD, Stiehl JB, Dennis DA, Paxson RD, Soutas-Little RW. Mathematical model of the lower extremity joint reaction forces using Kane's method of dynamics. J Biomech. 1998;31(2):185–189. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9290(97)00128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Seireg A, Arvikar The prediction of muscular lad sharing and joint forces in the lower extremities during walking. J Biomech. 1975;8(2):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(75)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Collins JJ. The redundant nature of locomotor optimization laws. J Biomech. 1995;28(3):251–267. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(94)00072-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lloyd DG, Besier TF. An EMG-driven musculoskeletal model to estimate muscle forces and knee joint moments in vivo. J Biomech. 2003;36(6):765–776. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9290(03)00010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Winby CR, Lloyd DG, Besier TF, Kirk TB. Muscle and external load contribution to knee joint contact loads during normal gait. J Biomech. 2009;42(14):2294–2300. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lutz GE, Palmitier RA, An KN, Chao EY. Comparison of tibiofemoral joint forces during open-kinetic-chain and closed-kinetic-chain exercises. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(5):732–739. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199305000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Perry J, Antonelli D, Ford W. Analysis of knee-joint forces during flexed-knee stance. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57(7):961–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Singerman R, Berilla J, Archdeacon M, Peyser A. In vitro forces in the normal and cruciate-deficient knee during simulated squatting motion. J Biomech Eng. 1999;121(2):234–242. doi: 10.1115/1.2835109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kaufman KR, Kovacevic N, Irby SE, Colwell CW., Jr Instrumented implant for measuring tibiofemoral forces. J Biomech. 1996;29(5):667–671. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(95)00124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.D'Lima DD, Townsend CP, Arms SW, Morris BA, Colwell CW., Jr An implantable telemetry device to measure intra-articular tibial forces. J Biomech. 2005;38(2):299–304. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2004.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Morris BA, D'Lima DD, Slamin J, Kovacevic N, Arms SW, Townsend CP, Colwell CW., Jr e-Knee: evolution of the electronic knee prosthesis. Telemetry technology development. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A(Pt 1) Suppl 2:62–66. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200100021-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kirking B, Krevolin J, Townsend C, Colwell CW, Jr, D'Lima DD. A multiaxial force-sensing implantable tibial prosthesis. J Biomech. 2006;39(9):1744–1751. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2005.05.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Geffre CP, Bliss CL, Szivek JA, Deyoung DW, Ruth JT, Margolis DS. Sensate scaffolds coupled to telemetry can monitor in vivo loading from within a joint over extended periods of time. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;84(1):263–270. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.30869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Szivek JA, Bliss CL, Geffre CP, Margolis DS, DeYoung DW, Ruth JT, Schnepp AB, Tellis BC, Vaidyanathan RK. An instrumented scaffold can monitor loading in the knee joint. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2006;79(2):218–228. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.30532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Taylor SJ, Walker PS. Forces and moments telemetered from two distal femoral replacements during various activities. J Biomech. 2001;34(7):839–848. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9290(01)00042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Taylor SJ, Walker PS, Perry JS, Cannon SR, Woledge R. The forces in the distal femur and the knee during walking and other activities measured by telemetry. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(4):428–437. doi: 10.1016/s0883-5403(98)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.D'Lima DD, Patil S, Steklov N, Slamin JE, Colwell CW., Jr The Chitranjan Ranawat Award: in vivo knee forces after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;440:45–49. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000186559.62942.8c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.D'Lima DD, Patil S, Steklov N, Slamin JE, Colwell CW., Jr Tibial forces measured in vivo after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(2):255–262. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2005.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.D'Lima DD, Patil S, Steklov N, Chien S, Colwell CW. In vivo knee moments and shear after total knee arthroplasty. J Biomech. 2007;40:S11–S17. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2007.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.D'Lima DD, Steklov N, Patil S, Colwell CW., Jr The Mark Coventry Award: in vivo knee forces during recreation and exercise after knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11):2605–2611. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0345-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Heinlein B, Graichen F, Bender A, Rohlmann A, Bergmann G. Design, calibration and pre-clinical testing of an instrumented tibial tray. J Biomech. 2007;40 Suppl 1:S4–S10. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2007.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Heinlein B, Kutzner I, Graichen F, Bender A, Rohlmann A, Halder AM, Beier A, Bergmann G. ESB Clinical Biomechanics Award 2008: Complete data of total knee replacement loading for level walking and stair climbing measured in vivo with a follow-up of 6–10 months. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2009;24(4):315–326. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2009.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kutzner I, Heinlein B, Graichen F, Bender A, Rohlmann A, Halder A, Beier A, Bergmann G. Loading of the knee joint during activities of daily living measured in vivo in five subjects. J Biomech. 2010;43(11):2164–2173. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.03.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Miyazaki T, Wada M, Kawahara H, Sato M, Baba H, Shimada S. Dynamic load at baseline can predict radiographic disease progression in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61(7):617–622. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.7.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Fregly BJ, D'Lima DD, Colwell CW., Jr Effective gait patterns for offloading the medial compartment of the knee. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(8):1016–1021. doi: 10.1002/jor.20843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fregly BJ, Reinbolt JA, Rooney KL, Mitchell KH, Chmielewski TL. Design of patient-specific gait modifications for knee osteoarthritis rehabilitation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2007;54(9):1687–1695. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2007.891934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Willson J, Torry MR, Decker MJ, Kernozek T, Steadman JR. Effects of walking poles on lower extremity gait mechanics. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001;33(1):142–147. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200101000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ajemian S, Thon D, Clare P, Kaul L, Zernicke RF, Loitz-Ramage B. Cane-assisted gait biomechanics and electromyography after total hip arthroplasty. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(12):1966–1971. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2004.04.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Aragaki DR, Nasmyth MC, Schultz SC, Nguyen GM, Yentes JM, Kao K, Perell K, Fang MA. Immediate effects of contralateral and ipsilateral cane use on normal adult gait. PM R. 2009;1(3):208–213. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2008.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Edwards BG. Contralateral and ipsilateral cane usage by patients with total knee or hip replacement. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1986;67(10):734–740. doi: 10.1016/0003-9993(86)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Chan GN, Smith AW, Kirtley C, Tsang WW. Changes in knee moments with contralateral versus ipsilateral cane usage in females with knee osteoarthritis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2005;20(4):396–404. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2004.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Andriacchi TP. Dynamics of knee malalignment. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994;25(3):395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mundermann A, Dyrby CO, Hurwitz DE, Sharma L, Andriacchi TP. Potential strategies to reduce medial compartment loading in patients with knee osteoarthritis of varying severity: reduced walking speed. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(4):1172–1178. doi: 10.1002/art.20132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Schmalz T, Blumentritt S, Drewitz H, Freslier M. The influence of sole wedges on frontal plane knee kinetics, in isolation and in combination with representative rigid and semi-rigid ankle-foot-orthoses. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2006;21(6):631–639. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2006.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kerrigan DC, Lelas JL, Goggins J, Merriman GJ, Kaplan RJ, Felson DT. Effectiveness of a lateral-wedge insole on knee varus torque in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002;83(7):889–893. doi: 10.1053/apmr.2002.33225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Crenshaw SJ, Pollo FE, Calton EF. Effects of lateral-wedged insoles on kinetics at the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(375):185–192. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200006000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Nester CJ, van der Linden ML, Bowker P. Effect of foot orthoses on the kinematics and kinetics of normal walking gait. Gait & posture. 2003;17(2):180–187. doi: 10.1016/s0966-6362(02)00065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Fisher DS, Dyrby CO, Mundermann A, Morag E, Andriacchi TP. In healthy subjects without knee osteoarthritis, the peak knee adduction moment influences the acute effect of shoe interventions designed to reduce medial compartment knee load. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(4):540–546. doi: 10.1002/jor.20157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Erhart JC, Mundermann A, Elspas B, Giori NJ, Andriacchi TP. A variable-stiffness shoe lowers the knee adduction moment in subjects with symptoms of medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. J Biomech. 2008;41(12):2720–2525. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2008.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Erhart JC, Dyrby CO, D'Lima DD, Colwell CW, Andriacchi TP. Changes in in vivo knee loading with a variable-stiffness intervention shoe correlate with changes in the knee adduction moment. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(12):1548–1553. doi: 10.1002/jor.21183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Eastlack RK, Hargens AR, Groppo ER, Steinbach GC, White KK, Pedowitz RA. Lower body positive-pressure exercise after knee surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(431):213–219. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000150459.92012.f7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Cutuk A, Groppo ER, Quigley EJ, White KW, Pedowitz RA, Hargens AR. Ambulation in simulated fractional gravity using lower body positive pressure: cardiovascular safety and gait analyses. J Appl Physiol. 2006;101(3):771–7. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00644.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Smith SM, Davis-Street JE, Fesperman JV, Calkins DS, Bawa M, Macias BR, Meyer RS, Hargens AR. Evaluation of treadmill exercise in a lower body negative pressure chamber as a countermeasure for weightlessness-induced bone loss: a bed rest study with identical twins. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(12):2223–2230. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.12.2223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Zwart SR, Hargens AR, Lee SM, Macias BR, Watenpaugh DE, Tse K, Smith SM. Lower body negative pressure treadmill exercise as a countermeasure for bed rest-induced bone loss in female identical twins. Bone. 2007;40(2):529–537. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.09.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Macias BR, D'Lima DD, Patil SP, Steklov N, Colwell CW, Neuschwander TB, Meuche S, Cutuk A, Hargens AR. In Vivo Knee Forces During Lower Body Positive Pressure Treadmill Exercise at Various Body Weight Levels. ORS Trans. 2007;32:1849. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01434.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]