Abstract
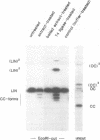
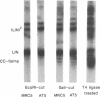
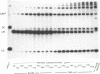
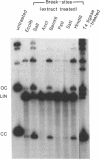
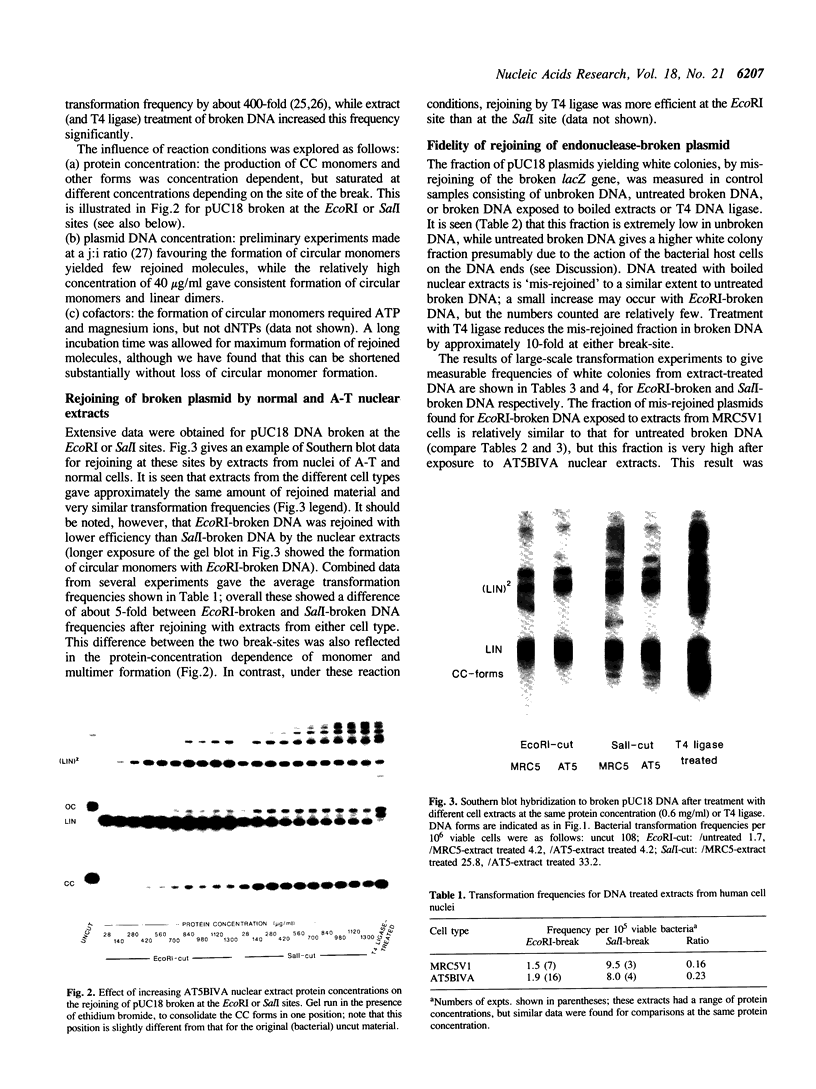
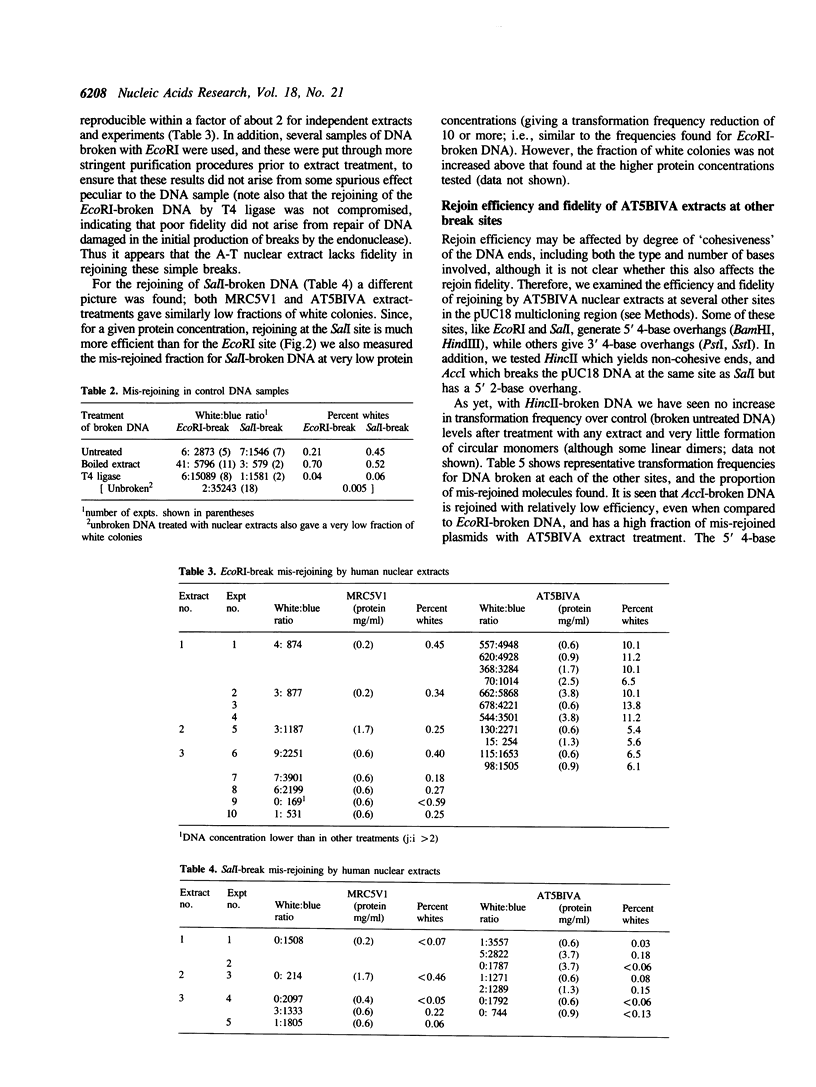
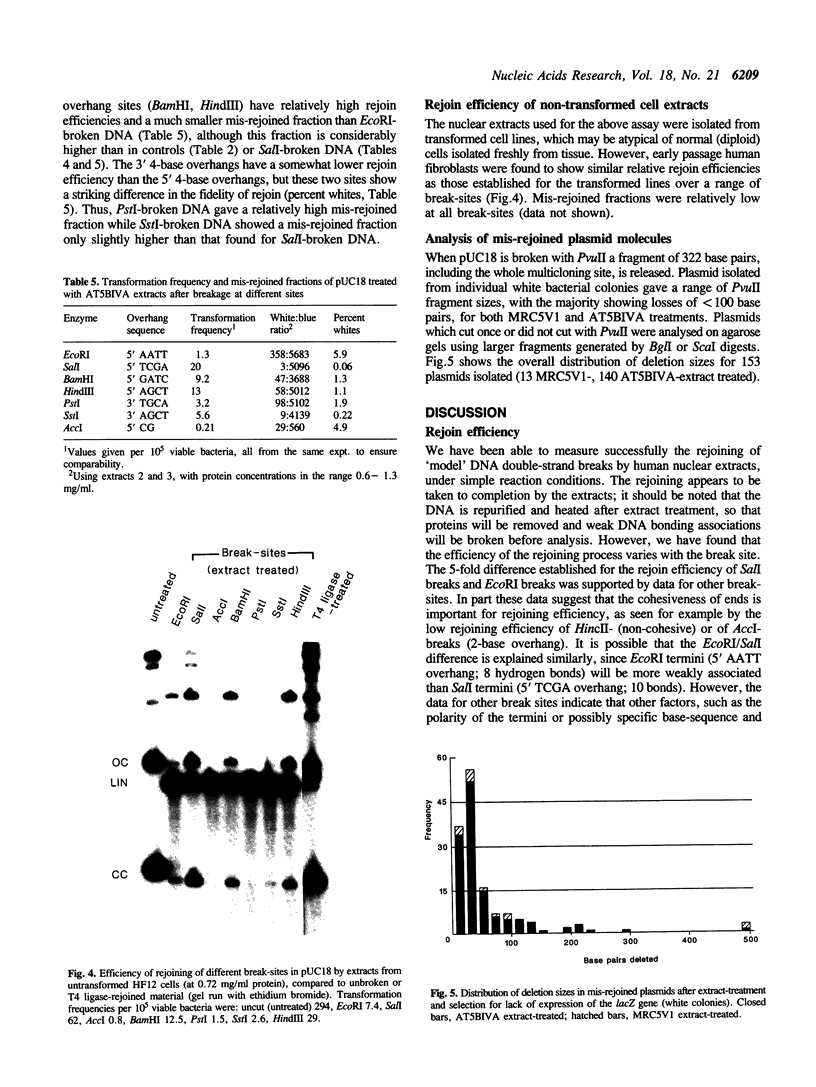
A double-strand DNA break was introduced at a specific site within the lacZ gene of plasmid pUC18 using one of several restriction enzymes, and the plasmid exposed to nuclear extracts from human cell lines. Physical rejoining of DNA was monitored by Southern analysis after gel separation, and the fidelity of rejoining by expression of the lacZ gene after bacterial transformation with the treated plasmid. Breaks at the SalI and EcoRI sites were rejoined by extracts to form circular monomers, but the efficiency of rejoining was much higher at the SalI site. Measurement of rejoining at several adjacent sites having different types of termini, consistently showed a range of efficiencies with 5' 4-base greater than 3' 4-base overhangs and 4-base greater than 2-base greater than no overhang. Similar efficiencies were found for nuclear extracts from transformed cell lines, both from a 'normal' individual and an ataxia-telangiectasia (A-T) patient, and from a non-transformed normal cell culture. In contrast at some sites, especially those with a low rejoin efficiency, the fidelity of rejoining was very much lower for the A-T extracts than for normal cell extracts. Mis-rejoining was, however, unrelated to rejoin efficiency at other sites, suggesting that factors such as the exact sequence at the break site on the molecule may also influence the fidelity of rejoining.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akroyd J., Symonds N. Localization of the gam gene of bacteriophage mu and characterisation of the gene product. Gene. 1986;49(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. C., Jiricny J. A specific mismatch repair event protects mammalian cells from loss of 5-methylcytosine. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):945–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90521-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant P. E. Enzymatic restriction of mammalian cell DNA: evidence for double-strand breaks as potentially lethal lesions. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1985 Jul;48(1):55–60. doi: 10.1080/09553008514551061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley E. C., Saunders J. R. Recombination-dependent recircularization of linearized pBR322 plasmid DNA following transformation of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(1-2):211–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00383519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley E. C., Saunders V. A., Jackson V., Saunders J. R. Mechanism of intramolecular recyclization and deletion formation following transformation of Escherichia coli with linearized plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8919–8932. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R., Masson W. K. Letter: Changes in radiosensitivity during the in vitro growth of diploid human fibroblasts. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1974 Aug;26(2):193–196. doi: 10.1080/09553007414551141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R., Masson W. K. Radiosensitivity in cultured human fibroblasts. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1980 Nov;38(5):575–576. doi: 10.1080/09553008014551391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. S., 3rd, Ziolkowski C. H., Scudiero D. A., Meyer S. A., Lubiniecki A. S., Girardi A. J., Galloway S. M., Bynum G. D. Defective repair of alkylated DNA by human tumour and SV40-transformed human cell strains. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):724–727. doi: 10.1038/288724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M. E., Oplinger M., Pegg A. E. Use of a dodecadeoxynucleotide to study repair of the O4-methylthymine lesion. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;193(2):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Boyer H. W., Goodman H. M. Ligation of EcoRI endonuclease-generated DNA fragments into linear and circular structures. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison K. S., Dogliotti E., Essigmann J. M. Construction of a shuttle vector containing a single O6-methylguanine: a probe for mutagenesis in mammalian cells. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar-May;220(2-3):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(89)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenberg D., Frankenberg-Schwager M., Blöcher D., Harbich R. Evidence for DNA double-strand breaks as the critical lesions in yeast cells irradiated with sparsely or densely ionizing radiation under oxic or anoxic conditions. Radiat Res. 1981 Dec;88(3):524–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huschtscha L. I., Holliday R. Limited and unlimited growth of SV40-transformed cells from human diploid MRC-5 fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1983 Sep;63:77–99. doi: 10.1242/jcs.63.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp L. M., Sedgwick S. G., Jeggo P. A. X-ray sensitive mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells defective in double-strand break rejoining. Mutat Res. 1984 Nov-Dec;132(5-6):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez B., Rousset S., Coppey J. Homologous recombination intermediates between two duplex DNA catalysed by human cell extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5643–5655. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malynn B. A., Blackwell T. K., Fulop G. M., Rathbun G. A., Furley A. J., Ferrier P., Heinke L. B., Phillips R. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. The scid defect affects the final step of the immunoglobulin VDJ recombinase mechanism. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinnon P. J. Ataxia-telangiectasia: an inherited disorder of ionizing-radiation sensitivity in man. Progress in the elucidation of the underlying biochemical defect. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):197–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00281059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriya M., Takeshita M., Johnson F., Peden K., Will S., Grollman A. P. Targeted mutations induced by a single acetylaminofluorene DNA adduct in mammalian cells and bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1586–1589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. Joining of nonhomologous DNA double strand breaks in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):907–924. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargentini N. J., Smith K. C. Quantitation of the involvement of the recA, recB, recC, recF, recJ, recN, lexA, radA, radB, uvrD, and umuC genes in the repair of X-ray-induced DNA double-strand breaks in Escherichia coli. Radiat Res. 1986 Jul;107(1):58–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamato T. D., Dipatri A., Giaccia A. Cell-cycle-dependent repair of potentially lethal damage in the XR-1 gamma-ray-sensitive Chinese hamster ovary cell. Radiat Res. 1988 Aug;115(2):325–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. M., Harnden D. G., Arlett C. F., Harcourt S. A., Lehmann A. R., Stevens S., Bridges B. A. Ataxia telangiectasia: a human mutation with abnormal radiation sensitivity. Nature. 1975 Dec 4;258(5534):427–429. doi: 10.1038/258427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker J. Inherited sensitivity to X-rays in man. Bioessays. 1989 Aug-Sep;11(2-3):58–62. doi: 10.1002/bies.950110205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker J. The use of integrating DNA vectors to analyse the molecular defects in ionising radiation-sensitive mutants of mammalian cells including ataxia telangiectasia. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar-May;220(2-3):187–204. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(89)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R., Achtman M. The control region of the F sex factor DNA transfer cistrons: physical mapping by deletion analysis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 16;169(1):49–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00267544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. E., Lindahl T. DNA ligase I deficiency in Bloom's syndrome. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):355–357. doi: 10.1038/325355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodek D., Hittelman W. N. The repair of double-strand DNA breaks correlates with radiosensitivity of L5178Y-S and L5178Y-R cells. Radiat Res. 1987 Oct;112(1):146–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries E., van Driel W., Bergsma W. G., Arnberg A. C., van der Vliet P. C. HeLa nuclear protein recognizing DNA termini and translocating on DNA forming a regular DNA-multimeric protein complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 5;208(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]