Abstract
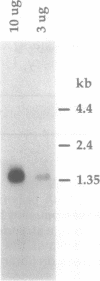
DmSII is a Drosophila RNA polymerase II elongation factor which suppresses pausing by RNA polymerase II at specific sites on double stranded templates. Using antibodies produced against the purified protein, a Drosophila cDNA expression library was screened and a cDNA was isolated which encoded a portion of DmSII. When this cDNA was used to probe Kc cell mRNA the predominant species was found to be 1.4 kb in length. The original cDNA was used to screen a Drosophila Kc cell cDNA library resulting in the isolation of a 1.4 kb cDNA which was then sequenced. The deduced protein sequence for DmSII exhibited high similarity to mouse SII protein sequence. In addition, significant sequence similarity was found with the protein encoded by the yeast gene PPR2, which is involved in regulation of URA4 gene expression. The comparison of amino acid sequences suggests that DmSII is comprised of two domains homologous to mouse SII separated by a flexible, serine rich region of low homology. The shorter yeast protein has sequence similarity only to the carboxy terminal domain.
Full text
PDF


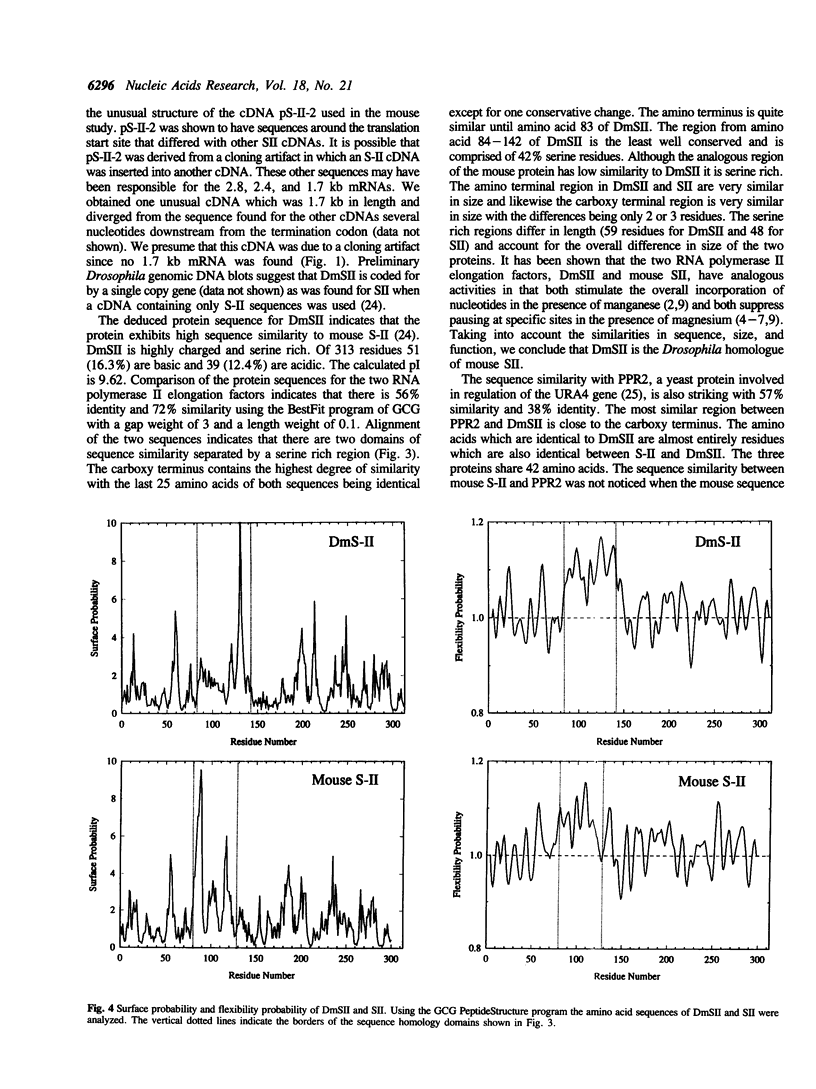


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burton Z. F., Killeen M., Sopta M., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. RAP30/74: a general initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1602–1613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. A multisubunit transcription factor essential for accurate initiation by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2357–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corton J. C., Johnston S. A. Altering DNA-binding specificity of GAL4 requires sequences adjacent to the zinc finger. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):724–727. doi: 10.1038/340724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. J., Trgovcich J., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Homologue of TFIIS in yeast. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):298–298. doi: 10.1038/345298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Factors IIE and IIF independently interact with RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8913–8921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima S., Hirai H., Nakanishi Y., Natori S. Molecular cloning and characterization of cDNA for eukaryotic transcription factor S-II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Sekimizu K., Hirashima S., Mitsuhashi Y., Natori S. Structural relationships of the three stimulatory factors of RNA polymerase II from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5739–5744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Sekimizu K., Natori S. Analysis of the stimulatory factor of RNA polymerase II in the initiation and elongation complex. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):608–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi N., Sekimizu K., Natori S. Site-directed mutagenesis of arginine 246, glutamic acid 247, and histidine 248 in the eukaryotic transcription factor S-II. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11854–11857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert J. C., Guyonvarch A., Kammerer B., Exinger F., Liljelund P., Lacroute F. Complete sequence of a eukaryotic regulatory gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2071–2073. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson B. A., Wolf H. The antigenic index: a novel algorithm for predicting antigenic determinants. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):181–186. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. L., Greenleaf A. L., Lehman I. R. Isolation of the nuclear gene encoding a subunit of the yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10348–10351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. M., Lee M. P., Wyckoff E., Hsieh T. S. Isolation and characterization of the gene encoding Drosophila DNA topoisomerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Dynamic interaction between a Drosophila transcription factor and RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L. Fractionation of transcription factors for RNA polymerase II from Drosophila Kc cell nuclear extracts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3244–3255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport J., Cho K., Saltzman A., Prenger J., Golomb M., Weinmann R. Transcription elongation factor SII interacts with a domain of the large subunit of human RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3136–3142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport J., Reinberg D., Zandomeni R., Weinmann R. Purification and functional characterization of transcription factor SII from calf thymus. Role in RNA polymerase II elongation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5227–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Transcription factor IIS stimulates elongation of RNA chains. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3331–3337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Transcription elongation factor SII (TFIIS) enables RNA polymerase II to elongate through a block to transcription in a human gene in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10799–10809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Interaction of a new polypeptide with yeast RNA polymerase B. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimizu K., Kubo Y., Segawa K., Natori S. Difference in phosphorylation of two factors stimulating RNA polymerase II of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2286–2292. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimizu K., Nakanishi Y., Mizuno D., Natori S. Purification and preparation of antibody to RNA polymerase II stimulatory factors from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1582–1588. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SivaRaman L., Reines D., Kane C. M. Purified elongation factor SII is sufficient to promote read-through by purified RNA polymerase II at specific termination sites in the human histone H3.3 gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14554–14560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluder A. E., Greenleaf A. L., Price D. H. Properties of a Drosophila RNA polymerase II elongation factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8963–8969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopta M., Carthew R. W., Greenblatt J. Isolation of three proteins that bind to mammalian RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10353–10360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]