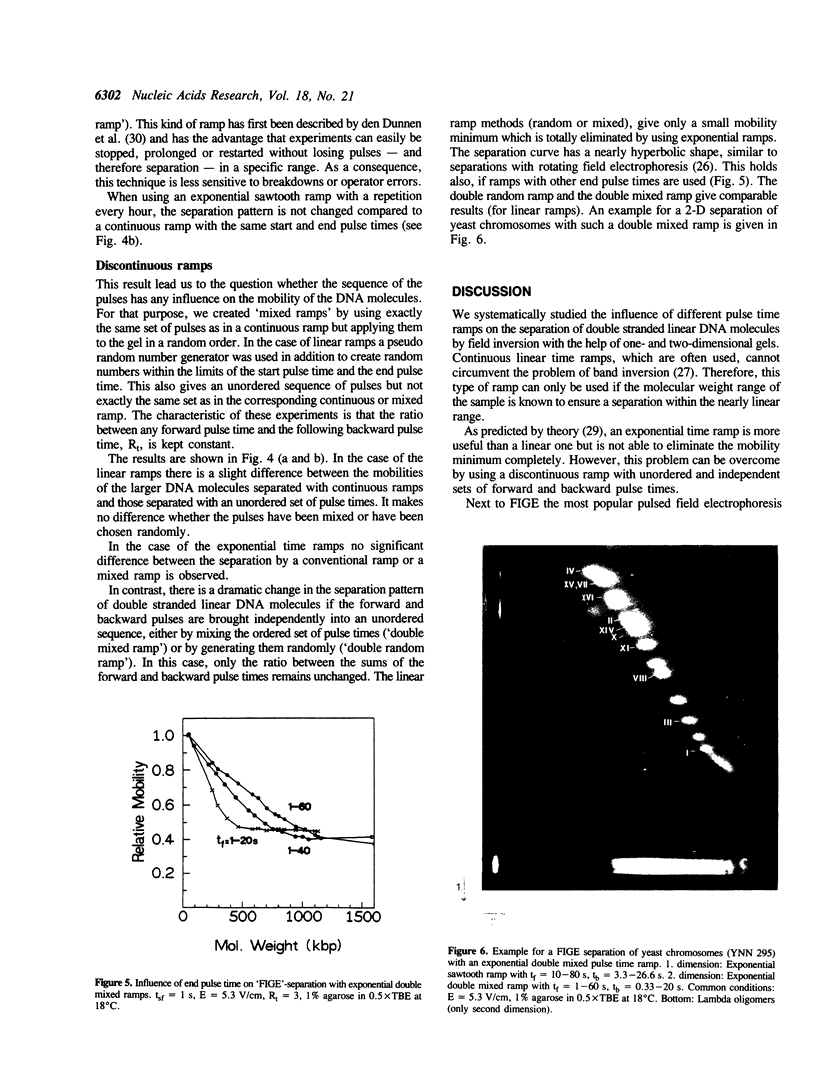
Abstract
The influence of different pulse time ramps on the separation of yeast chromosomes with field inversion gel electrophoresis (FIGE) was investigated by the means of two dimensional gel electrophoresis. The problem of band inversion, which makes it difficult to distinguish DNA molecules of different size, has been solved by using double randomized pulse times. A major disadvantage of the field inversion technique is thereby overcome, making this system comparable to other pulsed field techniques.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancroft I., Wolk C. P. Pulsed homogeneous orthogonal field gel electrophoresis (PHOGE). Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7405–7418. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birren B. W., Lai E., Clark S. M., Hood L., Simon M. I. Optimized conditions for pulsed field gel electrophoretic separations of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7563–7582. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birren B. W., Lai E., Hood L., Simon M. I. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis techniques for separating 1- to 50-kilobase DNA fragments. Anal Biochem. 1989 Mar;177(2):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birren B. W., Simon M. I., Lai E. The basis of high resolution separation of small DNAs by asymmetric-voltage field inversion electrophoresis and its application to DNA sequencing gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1481–1487. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock C. J. Parameters of field inversion gel electrophoresis for the analysis of pox virus genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4239–4252. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Gaal A., Smith C. L. High-resolution separation and accurate size determination in pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA. 3. Effect of electrical field shape. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9216–9221. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. M., Lai E., Birren B. W., Hood L. A novel instrument for separating large DNA molecules with pulsed homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1203–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.3045968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D. L., Olson C. H., Brumley R., Blattner F. R. Field inversion gel electrophoresis applied to the rapid, multi-enzyme restriction mapping of phage lambda clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1312–1312. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denko N., Giaccia A., Peters B., Stamato T. D. An asymmetric field inversion gel electrophoresis method for the separation of large DNA molecules. Anal Biochem. 1989 Apr;178(1):172–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis T. H., Cleary W. G., Burcham K. W., Bowen B. A. Ramped field inversion gel electrophoresis: a cautionary note. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5489–5489. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Laas W., Patterson D. Fractionation of large mammalian DNA restriction fragments using vertical pulsed-field gradient gel electrophoresis. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):185–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01560665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Patterson D. Transverse alternating field electrophoresis and applications to mammalian genome mapping. Electrophoresis. 1989 May-Jun;10(5-6):296–302. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham M. Y., Otani T., Boime I., Olson M. V., Carle G. F., Chaplin D. D. Cosmid mapping of the human chorionic gonadotropin beta subunit genes by field-inversion gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4437–4448. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller C., Pohl F. M. A systematic study of field inversion gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):5989–6003. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.5989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennekes H., Kühn S. Control of pulsed field gel electrophoresis at short switching intervals by a microcomputer. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):80–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Davi N. A., Hood L. E. Effect of electric field switching on the electrophoretic mobility of single-stranded DNA molecules in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis. 1989 Jan;10(1):65–67. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew M. K., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. High-resolution separation and accurate size determination in pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA. 1. DNA size standards and the effect of agarose and temperature. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9204–9210. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew M. K., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. High-resolution separation and accurate size determination in pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA. 2. Effect of pulse time and electric field strength and implications for models of the separation process. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9210–9216. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olschwang S., Thomas G. Temperature gradient increases FIGE resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2363–2363. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt KJ, Holzwarth G. Velocity of DNA in gels during field inversion. Phys Rev A Gen Phys. 1989 Dec 15;40(12):7292–7300. doi: 10.1103/physreva.40.7292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter C. D., Porter A. G., Archard L. C. BBC microcomputer controlled field inversion gel electrophoresis. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Apr;4(2):271–273. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy G., Wallenburg J. C., Chartrand P. Inexpensive and simple set-up for field inversion gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):768–768. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Saffran W., Welsh J., Haas R., Goldenberg M., Cantor C. R. New techniques for purifying large DNAs and studying their properties and packaging. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):189–195. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sor F. A computer program allows the separation of a wide range of chromosome sizes by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):4853–4863. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Anand R., Brown W. R., Fletcher D. S. A model for the separation of large DNA molecules by crossed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5925–5943. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turmel C., Brassard E., Slater G. W., Noolandi J. Molecular detrapping and band narrowing with high frequency modulation of pulsed field electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):569–575. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky L., Drouin G., Gilbert W. DNA trapping electrophoresis. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):190–192. doi: 10.1038/343190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7865–7876. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Dunnen J. T., Bakker E., Breteler E. G., Pearson P. L., van Ommen G. J. Direct detection of more than 50% of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations by field inversion gels. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):640–642. doi: 10.1038/329640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]